Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kato, Atsushi; Kubo, Shigenobu; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Miyagawa, Takayuki*; Uchita, Masato*; Suzuno, Tetsuji*; Endo, Junji*; Kubo, Koji*; Murakami, Hisatomo*; Uzawa, Masayuki*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2022/04
The authors are carrying out conceptual design studies for a pool-type sodium-cooled fast reactor. There are main challenges such as measures against severe earthquake in Japan, thermal hydraulic in a reactor vessel (RV), a decay heat removal system design. When the JP-pool SFR of 650 MWe is installed in Japan, it shall be designed against the severe seismic conditions. Additionally, a newly three-dimensional seismic isolation system is under development.
Ichikawa, Kenta*; Kanda, Hironori; Yoshioka, Naoki*; Ara, Kuniaki; Saito, Junichi; Nagai, Keiichi
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/07
Studies on the suppression of the reactivity of sodium itself have been performed on the basis of the concept of suspended nanoparticles in liquid sodium (sodium nanofluid). According to the experimental and theoretical results of studies for sodium nanofluid, velocity and heat of sodium nanofluid-water reaction are lower than those of the pure sodium-water reaction. The analytical model for the peak temperature of a sodium nanofluid-water reaction jet has been developed in consideration of these suppression effects by the authors. In this paper, the prediction method for mitigation effects for a damage of adjacent tubes in a steam generator tube rupture (SGTR) accidents is arranged by applying this analytical model for the peak temperature of the reaction jet. On the assumption that the sodium nanofluid is used for the secondary coolant of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), mitigation effects under the design-base accident (DBA) condition and the design-extension condition (DEC) of SGTR are estimated by using this method. As a result, there is a possibility to reduce the number of damaged tubes and to suppress the pressure generated by SGTR accidents by using sodium nanofluid in the secondary coolant.
Sako, Hiroyuki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Sakaguchi, Takao*; Chujo, Tatsuya*; Esumi, Shinichi*; Gunji, Taku*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hwang, S.; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 956, p.850 - 853, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:65.66(Physics, Nuclear)
Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 108(20), p.205501_1 - 205501_5, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:67.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen atoms absorbed in a metal occupy the interstitial sites of the metal lattice. In an fcc metal lattice, each metal atom has two tetrahedral (T) and one octahedral (O) sites that can accommodate hydrogen. Rare-earth metal La forms T-site occupied LaH and fully occupied LaH
and fully occupied LaH . O-site occupied or NaCl-type monohydride has yet to be reported for rare-earth metals. Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH
. O-site occupied or NaCl-type monohydride has yet to be reported for rare-earth metals. Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH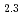 into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. The present neutron diffraction measurements on LaD
into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. The present neutron diffraction measurements on LaD confirm the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a counterpart of the D-rich LaD
confirm the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a counterpart of the D-rich LaD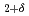 by disproportionation. First-principle calculations demonstrate that the NaCl-type LaH is stabilized at high pressures. Finding the NaCl-type LaH will pave the way for investigations on the site-dependent nature of hydrogen-metal interactions.
by disproportionation. First-principle calculations demonstrate that the NaCl-type LaH is stabilized at high pressures. Finding the NaCl-type LaH will pave the way for investigations on the site-dependent nature of hydrogen-metal interactions.
Ichikawa, Kenta*; Ara, Kuniaki; Saito, Junichi; Toda, Mikio*; Yoshioka, Naoki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Saito, Junichi; Konomura, Mamoru; Ara, Kuniaki; Toda, Mikio*; Yoshioka, Naoki*; Ichikawa, Kenta*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuya, Kentaro; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Ichikawa, Hiroshi*; Kohara, Shinji*
no journal, ,
The local atomic structure and intermediate-range order of Si-C-O fibers produced from the pyrolysis of a polycarbosilane precursor have been investigated by high-energy (61.6 keV) X-ray diffraction (HEXRD) at SPring-8 and reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique. In previous study (Okamura et. al., Key Eng. 352 (2007) 65), we suggest that the Si-C-O fibers basically have a network structure that consists of two tetrahedral units: SiC and SiO
and SiO from the pair distribution function analysis of HEXRD data. In the network model, 3-membered ring of SiC
from the pair distribution function analysis of HEXRD data. In the network model, 3-membered ring of SiC as that in SiC crystal and 6-membered ring of SiO
as that in SiC crystal and 6-membered ring of SiO as that in silica glass are assumed as intermediate-range order. Thus, we carried out RMC modelling analysis with the HEXRD data to study more detailed short- and intermediate-range ordering structure. The relationship between the intermediate-range ordering and these behaviors has also been discussed.
as that in silica glass are assumed as intermediate-range order. Thus, we carried out RMC modelling analysis with the HEXRD data to study more detailed short- and intermediate-range ordering structure. The relationship between the intermediate-range ordering and these behaviors has also been discussed.
Ichikawa, Kenta*; Sato, Mitsuru*; Watanabe, Osamu*; Kotake, Shoji*; Kamide, Hideki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Eguchi, Yuzuru*
no journal, ,
A system configuration consisting of a direct reactor auxiliary cooling system (DRACS) and two primary reactor auxiliary cooling systems (PRACSs) is under development for the decay heat removal system (DHRS) of Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR) as a candidate of innovative technology which allows the DHRS to be operated fully by natural circulation without being dependent on active devices. This innovative technology is aimed at ensuring safety and reliability and streamlining facilities and is being developed in the Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT) project. This paper reports the result of its applicability study.
Saito, Junichi; Yoshioka, Naoki*; Ichikawa, Kenta*; Oyama, Kazuhiro*; Toda, Mikio*; Ara, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuya, Kentaro; Kohara, Shinji*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Ichikawa, Hiroshi*; Suzuki, Kenji*
no journal, ,
Polymer-derived Si-C-O fibers have high tensile strength and characteristic electrical properties. The atomic scale structure of the polymer (Polycarbosilane) and the polymer-derived Si-C-O ceramics amorphous fibers has been investigated by high-energy X-ray diffraction. In addition, we applied the reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling method to the diffraction data to visualize for better understanding of the complex structure. By the RMC modelling, the basic structures of the Si-C-O fibers are the three-dimensionally connected SiC
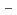
 O
O (x = 0-4) tetrahedral random-network structure which is the successive assembly of the SiC
(x = 0-4) tetrahedral random-network structure which is the successive assembly of the SiC
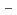
 O
O tetrahedral unit which share elements (corners and edges) and the excess carbon atoms which are interconnected and distributed widely in the network cage.
tetrahedral unit which share elements (corners and edges) and the excess carbon atoms which are interconnected and distributed widely in the network cage.
Machida, Akihiko; Hattori, Takanori; Honda, Mitsunori*; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have investigated the structural properties of rare-earth metal hydrides under high pressure. LaH has the CaF
has the CaF type structure in which the H atoms locate at the tetrahedral interstitial sites (T-sites) of the fcc metal lattice. Synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction and infrared reflection experiments revealed disproportionation reaction of LaH
type structure in which the H atoms locate at the tetrahedral interstitial sites (T-sites) of the fcc metal lattice. Synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction and infrared reflection experiments revealed disproportionation reaction of LaH into the H-poor and H-rich phases around 11 GPa. Before the disproportionation reaction, we have found that the fcc metal lattice transformed into tetragonal lattice. The ordering of the H atoms in the octahedral-sites (O-sites) causes the tetragonal distortion of LaH
into the H-poor and H-rich phases around 11 GPa. Before the disproportionation reaction, we have found that the fcc metal lattice transformed into tetragonal lattice. The ordering of the H atoms in the octahedral-sites (O-sites) causes the tetragonal distortion of LaH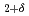 . The tetragonal transformation and successive disproportionation reaction of LaH
. The tetragonal transformation and successive disproportionation reaction of LaH would closely relate to the inter-site transfer of the H atoms between the T- and O-sites. We have performed the neutron diffraction experiments of LaD
would closely relate to the inter-site transfer of the H atoms between the T- and O-sites. We have performed the neutron diffraction experiments of LaD to investigate the change of the positions and occupancies of the hydrogen atoms under high pressure.
to investigate the change of the positions and occupancies of the hydrogen atoms under high pressure.
Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Hydrogen atoms absorbed in a metal occupy the interstitial sites of the metal lattice. In an fcc metal lattice, each metal atom has two tetrahedral (T) and one octahedral (O) sites that can accommodate hydrogen. Rare-earth metal La forms T-site occupied LaH and fully occupied LaH
and fully occupied LaH . Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH
. Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. We performed the neutron diffraction measurements on LaD
into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. We performed the neutron diffraction measurements on LaD , and found the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a phase separation products. We have first found the NaCl-type rare-earth metal monohydride.
, and found the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a phase separation products. We have first found the NaCl-type rare-earth metal monohydride.
Yoshimura, Kazuo; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ichikawa, Kenta; Mori, Takero; Yamada, Fumiaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsui, Kazuaki; Yoshimura, Kazuo; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ichikawa, Kenta; Yamada, Fumiaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kato, Atsushi; Ichikawa, Kenta*; Nakata, Shuhei*; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Ando, Masato
no journal, ,
In the conceptual study of a tank-type sodium-cooled fast reactor, a decay heat removal system concept was developed, taking into account the use of natural circulation heat removal and the diversity of heat removal methods, and a basic plant operation way after the reactor trip was established.