Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ichikawa, Nozomi*; Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
NUMO-TR-22-02, p.55 - 57, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Takubo, Yusaku*; Takayama, Yusuke; Ichikawa, Nozomi*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi*
NUMO-TR-22-02, p.68 - 71, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.05001_1 - 05001_6, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We measured ionization efficiencies of fermium, einsteinium, mendelevium, and lawrencium by using a newly developed gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of the elements have not been determined so far due to their low production rates and/or their short half-lives. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potentials of these actinide elements have been successfully determined.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
Nature, 520(7546), p.209 - 211, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:112 Percentile:97.11(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We successfully measured ionization efficiencies of lawrencium (Lr,  =103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
=103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
 gas-jet system coupled to a surface-ionization type ion-source in JAEA-ISOL; Towards determination of the first ionization potential of Lr (Z = 103)
gas-jet system coupled to a surface-ionization type ion-source in JAEA-ISOL; Towards determination of the first ionization potential of Lr (Z = 103)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Miyashita, Sunao*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Osa, Akihiko; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1253 - 1257, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:56.63(Chemistry, Analytical)We have developed a surface-ionization ion-source coupled to the He/CdI gas-jet transport system for the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator for experimental determination of the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr,
gas-jet transport system for the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator for experimental determination of the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr, 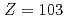 ). We performed to ionize a short-lived Lr isotope and various lanthanide isotopes. We successfully observed mass-separated ions of
). We performed to ionize a short-lived Lr isotope and various lanthanide isotopes. We successfully observed mass-separated ions of  Lr by using our present system at the first time. The first ionization potential of Lr was evaluated based on a correlation between of effective ionization potential and ionization efficiency of short-lived lanthanide isotopes in our system.
Lr by using our present system at the first time. The first ionization potential of Lr was evaluated based on a correlation between of effective ionization potential and ionization efficiency of short-lived lanthanide isotopes in our system.
 Lr in the
Lr in the 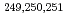 Cf +
Cf +  B,
B,  Am +
Am +  O, and
O, and  Cm +
Cm +  N reactions
N reactionsSato, Nozomi; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Li, Z.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
del, M.; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 102(3), p.211 - 219, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:57.73(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Production cross-sections of the isotope  Lr in the
Lr in the 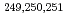 Cf +
Cf +  B,
B,  Am +
Am +  O, and
O, and  Cm +
Cm +  N reactions were measured using a He/KCl gas-jet transport system and a rotating wheel
N reactions were measured using a He/KCl gas-jet transport system and a rotating wheel  -particle detection apparatus. The
-particle detection apparatus. The  -particle energy of
-particle energy of  Lr was distributed from 8.3 to 8.7 MeV and its half-life,
Lr was distributed from 8.3 to 8.7 MeV and its half-life, 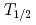 , was measured to be
, was measured to be 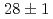 s. The maximum cross sections in the
s. The maximum cross sections in the  Cf(
Cf( B, 4
B, 4 )
) Lr and
Lr and  Am(
Am( O, 5
O, 5 )
) Lr reactions were determined to be
Lr reactions were determined to be 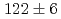 nb at the beam energy of 63 MeV and
nb at the beam energy of 63 MeV and 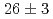 nb at 96 MeV, respectively. In the
nb at 96 MeV, respectively. In the  Cm(
Cm( N, 6
N, 6 )
) Lr reaction, the cross section was measured to be
Lr reaction, the cross section was measured to be 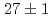 nb at 91 MeV.
nb at 91 MeV.
Sato, Tetsuya; Sato, Nozomi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyashita, Sunao; Sch del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 84(2), p.023304_1 - 023304_5, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:58.35(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed the surface ion-source coupled to the He/CdI gas-jet transport system to measure the ionization potential of Lr atatom-at-a-time conditions. We successfully ionized and mass-separated for the first time
gas-jet transport system to measure the ionization potential of Lr atatom-at-a-time conditions. We successfully ionized and mass-separated for the first time  Lr ions by applying the present ion-source and the ISOL technique. The ionization efficiencies of Lr were estimated to be approximately 42% and 24% at 2600 K on Re and Ta surfaces, respectively. These values were higher than those of Lu in all of ionization condition. The results indicate that the ionization potential of Lr would be lower than that of Lu, 5.4 eV. Therefore, it is concluded that the surface ion-source is a promising apparatus tomeasure the first ionization potential of Lr. Using the present system, determination of the ionization potential of Lr is being performed.
Lr ions by applying the present ion-source and the ISOL technique. The ionization efficiencies of Lr were estimated to be approximately 42% and 24% at 2600 K on Re and Ta surfaces, respectively. These values were higher than those of Lu in all of ionization condition. The results indicate that the ionization potential of Lr would be lower than that of Lu, 5.4 eV. Therefore, it is concluded that the surface ion-source is a promising apparatus tomeasure the first ionization potential of Lr. Using the present system, determination of the ionization potential of Lr is being performed.
 Lr in the
Lr in the  Cm +
Cm +  N reaction
N reactionSato, Nozomi; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Li, Z.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
del, M.; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
RIKEN Accelerator Progress Report, Vol.46, P. 237, 2013/00
Due to the strong relativistic effects, the weakly-bound outermost electron results in a significantly low first ionization potential (IP) of Lr as compared with its neighboring heavy actinides. The isotope  Lr, with a relatively long half-life of 27 s, is the suitable candidates for the IP measurement of Lr through the surface ionization method. In the present study, we measured the cross section of the
Lr, with a relatively long half-life of 27 s, is the suitable candidates for the IP measurement of Lr through the surface ionization method. In the present study, we measured the cross section of the  Cm(
Cm( N, 6
N, 6 )
) Lr reaction to evaluate the production rate of
Lr reaction to evaluate the production rate of  Lr. A
Lr. A  Cm target with 960
Cm target with 960  60
60  g/cm
g/cm thickness was bombarded with a
thickness was bombarded with a  N
N beam from the RIKEN AVF Cyclotron. The beam energy was 91 MeV in the middle of the target. The average beam intensity was 1.2 particle-
beam from the RIKEN AVF Cyclotron. The beam energy was 91 MeV in the middle of the target. The average beam intensity was 1.2 particle- A. Reaction products were transported to the rotating wheel
A. Reaction products were transported to the rotating wheel  -particle detection system with a He/KCl gas-jet system. The
-particle detection system with a He/KCl gas-jet system. The  Lr cross section of 27
Lr cross section of 27 1 nb was calculated based on the
1 nb was calculated based on the  -particle events between 8.3 and 8.7 MeV.
-particle events between 8.3 and 8.7 MeV.
 Hs and
Hs and  Hs
HsSato, Nozomi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kudo, Yuki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(9), p.094201_1 - 094201_7, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:65.66(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Decay properties of  Hs and
Hs and  Hs produced in the
Hs produced in the 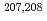 Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, 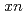 ) [
) [ =1, 2] reactions were studied using a gas-filled recoil ion separator at the linear accelerator facility of RIKEN. A total of 6 decay chains were assigned to
=1, 2] reactions were studied using a gas-filled recoil ion separator at the linear accelerator facility of RIKEN. A total of 6 decay chains were assigned to  Hs. Cross sections for the
Hs. Cross sections for the  Hs production in the
Hs production in the  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe,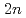 ) and
) and  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, ) reactions were measured to be
) reactions were measured to be 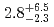 pb and
pb and 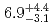 pb, respectively. The isotope
pb, respectively. The isotope  Hs decayed with a half-life of
Hs decayed with a half-life of 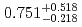 ms by
ms by  -particle emission and spontaneous fission. The
-particle emission and spontaneous fission. The  -particle energy of
-particle energy of  Hs was observed at 10.61
Hs was observed at 10.61 0.04 and 10.80
0.04 and 10.80 0.08 MeV. The spontaneous fission branch of
0.08 MeV. The spontaneous fission branch of  Hs was found to be
Hs was found to be 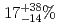 .
.
 Bh and
Bh and  Db produced in the
Db produced in the  Cm +
Cm +  Na reaction
Na reactionMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(6), p.064201_1 - 064201_6, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:77.51(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Decay properties of an isotope  Bh and its daughter nucleus
Bh and its daughter nucleus  Db produced by the
Db produced by the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 ) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.
) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.  Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,
Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,  Db. The obtained decay properties of
Db. The obtained decay properties of  Bh and
Bh and  Db are consistent with those observed in the
Db are consistent with those observed in the  113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of
113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of  113.
113.
 Hs
HsKaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Sato, Nozomi*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Yuki*; Ozawa, Akira*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(3), p.035003_1 - 035003_2, 2009/03
A new hassium isotopes  Hs is directly produced for the first time. The experiment was performed at the linear accelerator (RILAC) facility in RIKEN (the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research) from Jun. 19 to 25. In the 25-h irradiation of
Hs is directly produced for the first time. The experiment was performed at the linear accelerator (RILAC) facility in RIKEN (the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research) from Jun. 19 to 25. In the 25-h irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb and 46-h irradiation of
Pb and 46-h irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, were observed. All decay chains were assigned to subsequent decays from
Pb, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, were observed. All decay chains were assigned to subsequent decays from  Hs. The half-life of
Hs. The half-life of  Hs is 0.60
Hs is 0.60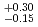 ms. In this experiment, the total beam dose was
ms. In this experiment, the total beam dose was 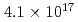 ions for
ions for  Fe and
Fe and 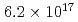 ions for
ions for  Fe. The production cross section corresponding to 8 decay events and 1 decay chain was deduced to be 21
Fe. The production cross section corresponding to 8 decay events and 1 decay chain was deduced to be 21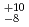 pb and 1.6
pb and 1.6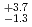 pb by assuming that the transmission of the system is 80%.
pb by assuming that the transmission of the system is 80%.
 Hs
HsKaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Sato, Nozomi*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Yuki*; Ozawa, Akira*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(3), p.035003_1 - 035003_2, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A new neutron deficient hassium ( =108) isotope of
=108) isotope of  Hs was identified via two different reactions of
Hs was identified via two different reactions of  Pb(
Pb( Fe,n) and
Fe,n) and  Pb(
Pb( Fe,n) by using a gas-filled recoil separator GARIS at June 2008. During the 25-h irradiation of
Fe,n) by using a gas-filled recoil separator GARIS at June 2008. During the 25-h irradiation of  Pb with the
Pb with the  Fe beam and 46-h irradiation of
Fe beam and 46-h irradiation of  Pb with the
Pb with the  Fe beam, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, have been observed. The half-life of
Fe beam, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, have been observed. The half-life of  Hs is 0.60
Hs is 0.60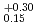 ms. In this experiment, the total beam doses of the Fe and
ms. In this experiment, the total beam doses of the Fe and  Fe was 4.1
Fe was 4.1 10
10 ions and 6.2
ions and 6.2 10
10 ions, respectively. The production cross sections corresponding to the 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain have been deduced to be 21
ions, respectively. The production cross sections corresponding to the 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain have been deduced to be 21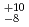 pb and 1.6
pb and 1.6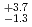 pb by assuming the transmission of the system to be 80%.
pb by assuming the transmission of the system to be 80%.
 Hs,
Hs, 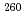 Sg, and
Sg, and  Rf
RfSato, Nozomi*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Yuki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Ozawa, Akira*; et al.
RIKEN Accelerator Progress Report, Vol.42, P. 16, 2009/00
New Decay Properties of  Hs and its
Hs and its  -decay daughter nuclei were studied by using reactions of
-decay daughter nuclei were studied by using reactions of  Pb(
Pb( Fe,2n) and
Fe,2n) and  Pb(
Pb( Fe,n) by using a gas-filled recoil ion separator, GARIS at RIKEN. We observed three correlated events in irradiation of
Fe,n) by using a gas-filled recoil ion separator, GARIS at RIKEN. We observed three correlated events in irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb, and eight events in irradiation of
Pb, and eight events in irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb. A half-life was deduced to be 0.90
Pb. A half-life was deduced to be 0.90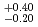 . We assigned these eleven events to be the decays of
. We assigned these eleven events to be the decays of  Hs. We found different decay-chain events of
Hs. We found different decay-chain events of  Hs from a previous report. One is a long-lived
Hs from a previous report. One is a long-lived  -decay of
-decay of 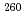 Sg with 180
Sg with 180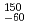 ms of half-life. Another is a long-lived
ms of half-life. Another is a long-lived  -decay of
-decay of  Rf with 10.4
Rf with 10.4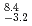 s of half-life. For
s of half-life. For 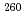 Sg and
Sg and  Rf, the decay of such a long-lived state have not been reported. These are the first observations of isomerism in
Rf, the decay of such a long-lived state have not been reported. These are the first observations of isomerism in 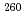 Sg and
Sg and  Rf.
Rf.
Sato, Tetsuya; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sonoda, Nozomi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyashita, Sunao; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to determine the first ionization potential (IP) of lawrencium (Lr, Z=103), we have developed a surface ionization type ion-source coupled to a He/CdI gas-jet transport system for the JAEA-ISOL. We measured ionization efficiencies of
gas-jet transport system for the JAEA-ISOL. We measured ionization efficiencies of  Lr and various short-lived lanthanide isotopes by applying the ion-source. We successfully ionized and mass-separated for the first time
Lr and various short-lived lanthanide isotopes by applying the ion-source. We successfully ionized and mass-separated for the first time  Lr ions. From a correlation between the IPs and ionization efficiencies of the short-lived lanthanide isotopes, we estimated the IP of Lr in this work.
Lr ions. From a correlation between the IPs and ionization efficiencies of the short-lived lanthanide isotopes, we estimated the IP of Lr in this work.
 Hs
HsKaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Sato, Nozomi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Yuki*; Ozawa, Akira*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
A new neutron deficient hassium (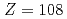 ) isotope of
) isotope of  Hs was identified via two different reactions of
Hs was identified via two different reactions of  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, ) and
) and  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, ) by using the gas-filled recoil separator GARIS. During irradiation of
) by using the gas-filled recoil separator GARIS. During irradiation of  Pb with the
Pb with the  Fe beam and irradiation of
Fe beam and irradiation of  Pb with the
Pb with the  Fe beam, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, were observed. The properties of decay events obtained by irradiation of
Fe beam, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, were observed. The properties of decay events obtained by irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb match well with those by irradiation of
Pb match well with those by irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb. The mean
Pb. The mean  -decay energies for the 3 groups are 10.82, 10.55, and 10.37 MeV, respectively. The half-life of
-decay energies for the 3 groups are 10.82, 10.55, and 10.37 MeV, respectively. The half-life of  Hs is determined to be 0.60 ms.
Hs is determined to be 0.60 ms.
Asai, Masato; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Nozomi; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Sato, Tetsuya; Toyoshima, Atsushi; et al.
no journal, ,
Alpha-decay spectroscopy of odd-mass Rf and Lr isotopes was performed to establish proton and neutron single-particle orbitals.  rays following the
rays following the  decay of
decay of  Rf were observed for the first time through the
Rf were observed for the first time through the  -
- coincidence measurement, and the neutron configuration of the ground state of
coincidence measurement, and the neutron configuration of the ground state of  Rf was assigned. It was found that the ground-state configuration of
Rf was assigned. It was found that the ground-state configuration of  Rf is different from those of the lighter N = 155 isotones
Rf is different from those of the lighter N = 155 isotones  Fm and
Fm and 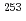 Cf. For the Lr isotopes, the proton configurations of the ground and isomeric states in
Cf. For the Lr isotopes, the proton configurations of the ground and isomeric states in  Lr and the ground states of
Lr and the ground states of  Lr and
Lr and  Lr were definitely identified through the high-resolution
Lr were definitely identified through the high-resolution  fine structure spectroscopy. Theoretical calculations based on the macroscopic-microscopic model revealed that the change of the ground-state configuration in the N = 155 isotones is strongly associated with the rapidly decreasing hexadecapole deformation with increasing atomic number.
fine structure spectroscopy. Theoretical calculations based on the macroscopic-microscopic model revealed that the change of the ground-state configuration in the N = 155 isotones is strongly associated with the rapidly decreasing hexadecapole deformation with increasing atomic number.
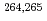 Hs
HsSato, Nozomi; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Yuki*; Ozawa, Akira*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
In this work, the production and decay properties of 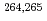 Hs produced in the
Hs produced in the  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, 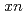 ) [
) [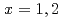 ] and
] and  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe,  ) reactions were investigated. The experiment was performed at the RILAC facility in RIKEN. The evaporation residues (ERs) were separated from the primary beam with the gas-filled recoil ion separator, GARIS. In the focal plane of GARIS the products were implanted into a position-sensitive Si detector for measuring the arrival of ERs and subsequent
) reactions were investigated. The experiment was performed at the RILAC facility in RIKEN. The evaporation residues (ERs) were separated from the primary beam with the gas-filled recoil ion separator, GARIS. In the focal plane of GARIS the products were implanted into a position-sensitive Si detector for measuring the arrival of ERs and subsequent  -decays or spontaneous fission from ERs. We have measured production cross-sections of
-decays or spontaneous fission from ERs. We have measured production cross-sections of 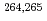 Hs in the
Hs in the  Fe +
Fe +  Pb reaction at several bombarding energies. For the
Pb reaction at several bombarding energies. For the  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe,  )
) Hs reaction, the cross-section maximum of (
Hs reaction, the cross-section maximum of (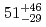 ) pb was obtained at the bombarding energy of 220.5 MeV at the middle of the target. For even-even nucleus
) pb was obtained at the bombarding energy of 220.5 MeV at the middle of the target. For even-even nucleus  Hs, we have also observed accurate decay data with good statistics.
Hs, we have also observed accurate decay data with good statistics.
Sato, Tetsuya; Sonoda, Nozomi; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyashita, Sunao; Osa, Akihiko; Ichikawa, Shinichi; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to determine the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr, Z=103), we have developed an appropriate surface-ionization type ion source as a part of the JAEA-ISOL setup, which is coupled to a He/CdI gas-jet transport system. The new ion source is an improved version based on our previously used ion source, which already had a good ionization efficiencies for lanthanide. To achieve higher ionization efficiencies of low volatility elements like Lr, an additional filament was newly installed. We report, here, on the development and performance of our new gas-jet coupled surface-ionization ion source, and on the first successful ionization and mass separation of 27-s
gas-jet transport system. The new ion source is an improved version based on our previously used ion source, which already had a good ionization efficiencies for lanthanide. To achieve higher ionization efficiencies of low volatility elements like Lr, an additional filament was newly installed. We report, here, on the development and performance of our new gas-jet coupled surface-ionization ion source, and on the first successful ionization and mass separation of 27-s  Lr produced in the
Lr produced in the  Cf +
Cf +  B reaction.
B reaction.
 113 produced by the
113 produced by the  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113 reaction
113 reactionMorimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We performed the experiment to synthesize an isotope of the element 113 produced by a  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113 reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN. Two decay chains were observed, and assigned to those originating from an isotope
113 reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN. Two decay chains were observed, and assigned to those originating from an isotope  113. Both chains were connected into the previously known decays of
113. Both chains were connected into the previously known decays of  Bh and
Bh and  Db via previously unknown decays of
Db via previously unknown decays of  113,
113, 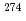 Rg, and
Rg, and 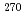 Mt. Although the
Mt. Although the  Bh was known nuclide, a number of atoms reported so far was limited. In order to study more precise decay property of the
Bh was known nuclide, a number of atoms reported so far was limited. In order to study more precise decay property of the  Bh, we performed the direct production of
Bh, we performed the direct production of  Bh by the
Bh by the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5n)
Na,5n) Bh reaction. In this experiment, the
Bh reaction. In this experiment, the  Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the nuclide,
Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the nuclide,  Db. The obtained decay properties of
Db. The obtained decay properties of  Bh and
Bh and  Db are consistent with those observed in the
Db are consistent with those observed in the  113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of
113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of  113.
113.
Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Tetsuya; Sonoda, Nozomi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyashita, Sunao; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to determine the first ionization energy of lawrencium (Lr, 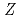 = 103), we have developed a new surface ionization ion source coupled to a gas-jet transport system in ISOL (Isotopes Separator On-Line) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. On-line experiments with short-lived lanthanide isotopes using the new ion-source were performed. It would be confirmed that the ionization energy of lanthanide which boiling point is up to 3000
= 103), we have developed a new surface ionization ion source coupled to a gas-jet transport system in ISOL (Isotopes Separator On-Line) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. On-line experiments with short-lived lanthanide isotopes using the new ion-source were performed. It would be confirmed that the ionization energy of lanthanide which boiling point is up to 3000 C can be determined.
C can be determined.