Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kato, Atsushi; Kubo, Shigenobu; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Miyagawa, Takayuki*; Uchita, Masato*; Suzuno, Tetsuji*; Endo, Junji*; Kubo, Koji*; Murakami, Hisatomo*; Uzawa, Masayuki*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2022/04
The authors are carrying out conceptual design studies for a pool-type sodium-cooled fast reactor. There are main challenges such as measures against severe earthquake in Japan, thermal hydraulic in a reactor vessel (RV), a decay heat removal system design. When the JP-pool SFR of 650 MWe is installed in Japan, it shall be designed against the severe seismic conditions. Additionally, a newly three-dimensional seismic isolation system is under development.
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Ichikawa, Masahiro; Takahashi, Yasuyuki*; Kubo, Takashi*; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Kasugai, Atsushi; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Gobin, R.*; Girardot, P.*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1009 - 1012, 2014/10
The prototype accelerator is being developed as an engineering validation for the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) equipped with an accelerator-driven-type neutron source for developing fusion reactor materials. This prototype accelerator is a deuteron linear accelerator consisting of an injector, an RFQ, a superconducting linac and their auxiliaries. It aims to produce a CW D beam with the energy and current of 9 MeV/125 mA. The injector test was completed at CEA/Saclay in 2012 for producing a CW H
beam with the energy and current of 9 MeV/125 mA. The injector test was completed at CEA/Saclay in 2012 for producing a CW H beam and a CW D
beam and a CW D beam with the energy and current of 100 keV/140 mA. After the beam test at CEA/Saclay, the injector was transported to the International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) located in Rokkasho, Aomori, Japan. In the end of 2013, installation of the injector was started at IFERC for the injector beam test beginning from summer 2014 in order to obtain better beam qualities to be satisfied with the injection and acceleration of the following accelerators. In this paper, some results of the injector beam test performed at CEA/Saclay and the status quo of the installation of the injector at IFERC are presented.
beam with the energy and current of 100 keV/140 mA. After the beam test at CEA/Saclay, the injector was transported to the International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) located in Rokkasho, Aomori, Japan. In the end of 2013, installation of the injector was started at IFERC for the injector beam test beginning from summer 2014 in order to obtain better beam qualities to be satisfied with the injection and acceleration of the following accelerators. In this paper, some results of the injector beam test performed at CEA/Saclay and the status quo of the installation of the injector at IFERC are presented.

Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 108(20), p.205501_1 - 205501_5, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:70.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen atoms absorbed in a metal occupy the interstitial sites of the metal lattice. In an fcc metal lattice, each metal atom has two tetrahedral (T) and one octahedral (O) sites that can accommodate hydrogen. Rare-earth metal La forms T-site occupied LaH and fully occupied LaH
and fully occupied LaH . O-site occupied or NaCl-type monohydride has yet to be reported for rare-earth metals. Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH
. O-site occupied or NaCl-type monohydride has yet to be reported for rare-earth metals. Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH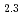 into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. The present neutron diffraction measurements on LaD
into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. The present neutron diffraction measurements on LaD confirm the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a counterpart of the D-rich LaD
confirm the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a counterpart of the D-rich LaD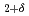 by disproportionation. First-principle calculations demonstrate that the NaCl-type LaH is stabilized at high pressures. Finding the NaCl-type LaH will pave the way for investigations on the site-dependent nature of hydrogen-metal interactions.
by disproportionation. First-principle calculations demonstrate that the NaCl-type LaH is stabilized at high pressures. Finding the NaCl-type LaH will pave the way for investigations on the site-dependent nature of hydrogen-metal interactions.
 Hs and
Hs and  Hs
HsSato, Nozomi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kudo, Yuki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(9), p.094201_1 - 094201_7, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:65.60(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Decay properties of  Hs and
Hs and  Hs produced in the
Hs produced in the 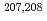 Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, 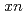 ) [
) [ =1, 2] reactions were studied using a gas-filled recoil ion separator at the linear accelerator facility of RIKEN. A total of 6 decay chains were assigned to
=1, 2] reactions were studied using a gas-filled recoil ion separator at the linear accelerator facility of RIKEN. A total of 6 decay chains were assigned to  Hs. Cross sections for the
Hs. Cross sections for the  Hs production in the
Hs production in the  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe,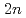 ) and
) and  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, ) reactions were measured to be
) reactions were measured to be 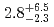 pb and
pb and 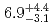 pb, respectively. The isotope
pb, respectively. The isotope  Hs decayed with a half-life of
Hs decayed with a half-life of 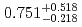 ms by
ms by  -particle emission and spontaneous fission. The
-particle emission and spontaneous fission. The  -particle energy of
-particle energy of  Hs was observed at 10.61
Hs was observed at 10.61 0.04 and 10.80
0.04 and 10.80 0.08 MeV. The spontaneous fission branch of
0.08 MeV. The spontaneous fission branch of  Hs was found to be
Hs was found to be 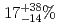 .
.
Kamakura, Nozomu; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Tsubota, Masami*; Paik, B.*; Ichikawa, Takayuki*; Kojima, Yoshitsugu*; Muro, Takayuki*; Kato, Yukako*; et al.
Physical Review B, 83(3), p.033103_1 - 033103_4, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The electronic structure of lithium amide, which is lightweight complex hydride expected as a high-capacity hydrogen storage material, is investigated by N 1 soft X-ray emission spectroscopy (XES) and absorption spectroscopy (XAS). The overall feature of the electronic structure of lithium amide by the XES and XAS is consistent with the band calculation, while the strongly hybridized state with H 1
soft X-ray emission spectroscopy (XES) and absorption spectroscopy (XAS). The overall feature of the electronic structure of lithium amide by the XES and XAS is consistent with the band calculation, while the strongly hybridized state with H 1 is located at higher binding energy than the band calculation.
is located at higher binding energy than the band calculation.
 -FeSi
-FeSi
Maeda, Yoshihito; Ichikawa, Takayuki*; Jonishi, Takafumi*; Narumi, Kazumasa
Physics Procedia, 11, p.83 - 86, 2011/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Optics) -edges
-edgesIshimatsu, Naoki*; Sasada, Ryohei*; Maruyama, Hiroshi*; Ichikawa, Takayuki*; Miyaoka, Hiroki*; Kimura, Toru*; Tsubota, Masami*; Kojima, Yoshitsugu*; Tsumuraya, Takao*; Oguchi, Tamio*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 190, p.012070_1 - 012070_4, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:78.54(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have investigated the effect of hydrogenation on La 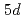 and
and 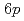 electronic states in metallic LaH
electronic states in metallic LaH by X-ray absorption near edge structure at the La
by X-ray absorption near edge structure at the La  -edges. As the hydrogen content
-edges. As the hydrogen content  increases from 0 to 2.6, white-line intensity at the La
increases from 0 to 2.6, white-line intensity at the La 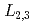 -edges shows a remarkable increase in the range of
-edges shows a remarkable increase in the range of 
 2.0. This is interpreted as the increase in La
2.0. This is interpreted as the increase in La 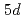 hole induced by interstitial H atoms on the octahedral sites. On the other hand, the shoulder structure at the La
hole induced by interstitial H atoms on the octahedral sites. On the other hand, the shoulder structure at the La 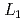 -edge disappears in the process of
-edge disappears in the process of  = 0.0
= 0.0  2.0, indicating that the
2.0, indicating that the  -
-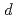 hybridization is weakened by H atoms on the tetrahedral sites. This study demonstrates that H atoms on the two interstitial H sites provide different contribution to the modification of the electronic states.
hybridization is weakened by H atoms on the tetrahedral sites. This study demonstrates that H atoms on the two interstitial H sites provide different contribution to the modification of the electronic states.
 Bh and
Bh and  Db produced in the
Db produced in the  Cm +
Cm +  Na reaction
Na reactionMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(6), p.064201_1 - 064201_6, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:77.45(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Decay properties of an isotope  Bh and its daughter nucleus
Bh and its daughter nucleus  Db produced by the
Db produced by the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 ) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.
) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.  Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,
Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,  Db. The obtained decay properties of
Db. The obtained decay properties of  Bh and
Bh and  Db are consistent with those observed in the
Db are consistent with those observed in the  113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of
113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of  113.
113.
 Hs
HsKaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Sato, Nozomi*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Yuki*; Ozawa, Akira*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(3), p.035003_1 - 035003_2, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.57(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A new neutron deficient hassium ( =108) isotope of
=108) isotope of  Hs was identified via two different reactions of
Hs was identified via two different reactions of  Pb(
Pb( Fe,n) and
Fe,n) and  Pb(
Pb( Fe,n) by using a gas-filled recoil separator GARIS at June 2008. During the 25-h irradiation of
Fe,n) by using a gas-filled recoil separator GARIS at June 2008. During the 25-h irradiation of  Pb with the
Pb with the  Fe beam and 46-h irradiation of
Fe beam and 46-h irradiation of  Pb with the
Pb with the  Fe beam, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, have been observed. The half-life of
Fe beam, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, have been observed. The half-life of  Hs is 0.60
Hs is 0.60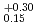 ms. In this experiment, the total beam doses of the Fe and
ms. In this experiment, the total beam doses of the Fe and  Fe was 4.1
Fe was 4.1 10
10 ions and 6.2
ions and 6.2 10
10 ions, respectively. The production cross sections corresponding to the 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain have been deduced to be 21
ions, respectively. The production cross sections corresponding to the 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain have been deduced to be 21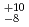 pb and 1.6
pb and 1.6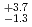 pb by assuming the transmission of the system to be 80%.
pb by assuming the transmission of the system to be 80%.
 Hs
HsKaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Sato, Nozomi*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Yuki*; Ozawa, Akira*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(3), p.035003_1 - 035003_2, 2009/03
A new hassium isotopes  Hs is directly produced for the first time. The experiment was performed at the linear accelerator (RILAC) facility in RIKEN (the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research) from Jun. 19 to 25. In the 25-h irradiation of
Hs is directly produced for the first time. The experiment was performed at the linear accelerator (RILAC) facility in RIKEN (the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research) from Jun. 19 to 25. In the 25-h irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb and 46-h irradiation of
Pb and 46-h irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, were observed. All decay chains were assigned to subsequent decays from
Pb, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, were observed. All decay chains were assigned to subsequent decays from  Hs. The half-life of
Hs. The half-life of  Hs is 0.60
Hs is 0.60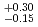 ms. In this experiment, the total beam dose was
ms. In this experiment, the total beam dose was 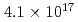 ions for
ions for  Fe and
Fe and 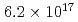 ions for
ions for  Fe. The production cross section corresponding to 8 decay events and 1 decay chain was deduced to be 21
Fe. The production cross section corresponding to 8 decay events and 1 decay chain was deduced to be 21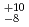 pb and 1.6
pb and 1.6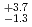 pb by assuming that the transmission of the system is 80%.
pb by assuming that the transmission of the system is 80%.
 Hs,
Hs, 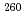 Sg, and
Sg, and  Rf
RfSato, Nozomi*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Yuki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Ozawa, Akira*; et al.
RIKEN Accelerator Progress Report, Vol.42, P. 16, 2009/00
New Decay Properties of  Hs and its
Hs and its  -decay daughter nuclei were studied by using reactions of
-decay daughter nuclei were studied by using reactions of  Pb(
Pb( Fe,2n) and
Fe,2n) and  Pb(
Pb( Fe,n) by using a gas-filled recoil ion separator, GARIS at RIKEN. We observed three correlated events in irradiation of
Fe,n) by using a gas-filled recoil ion separator, GARIS at RIKEN. We observed three correlated events in irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb, and eight events in irradiation of
Pb, and eight events in irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb. A half-life was deduced to be 0.90
Pb. A half-life was deduced to be 0.90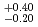 . We assigned these eleven events to be the decays of
. We assigned these eleven events to be the decays of  Hs. We found different decay-chain events of
Hs. We found different decay-chain events of  Hs from a previous report. One is a long-lived
Hs from a previous report. One is a long-lived  -decay of
-decay of 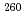 Sg with 180
Sg with 180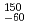 ms of half-life. Another is a long-lived
ms of half-life. Another is a long-lived  -decay of
-decay of  Rf with 10.4
Rf with 10.4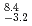 s of half-life. For
s of half-life. For 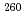 Sg and
Sg and  Rf, the decay of such a long-lived state have not been reported. These are the first observations of isomerism in
Rf, the decay of such a long-lived state have not been reported. These are the first observations of isomerism in 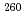 Sg and
Sg and  Rf.
Rf.
Maki, Takashi*; Ichikawa, Hajime*; Asao, Takayuki*; Horiuchi, Nobutake*
JNC TJ9400 2002-004, 228 Pages, 2001/02
We developed two computer codes to evaluate fuel cycle requirements of FR systems, which were selected in "the feasibility studies on commercialized FBR cycle systems". One code (CODE for material balance analysis) is to calculate the material balance data to evaluate the characteristics of each candidate. The other is to calculate the time-series data of material balance of fuel cycle as a whole, to evaluate an optimum scenario of FR systems introduction. The main characteristics of these codes are as follows: (1) Common function of both codes (a) They execute burn up calculation using characteristics values of reactor calculated with ORIGEN2 code. And they adjust Pu content using a concept of physical accounting method for adjusted fissile enrichment. (b) They simulate 18 type of FR systems, 10 reactor types and 6 reprocessing types. (2) Function of CODE for material balance analysis (a) It calculates nuclide inventory and thermal power, radioactivity, radio-toxicity in the waste and environmental release. (b) It evaluates safety of geological disposal of HLW and TRU waste (iodine waste) with simplified safety estimation method. (3) Function of CODE for time-series analysis (a) In addition to FR systems, it simulates 4 type of LWR systems and 5 type of Pu-Thermal LWR systems. (b)It calculates the Pu demand-and-supply situation. The precision of these codes was checked and verified by using other code result. Then we investigation characteristics of each FR system by evaluating material balance of fuel cycle. In addition we clarified differences between scenarios of introduction of FR systems.
 Hs
HsKaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Sato, Nozomi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Yuki*; Ozawa, Akira*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
A new neutron deficient hassium (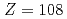 ) isotope of
) isotope of  Hs was identified via two different reactions of
Hs was identified via two different reactions of  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, ) and
) and  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, ) by using the gas-filled recoil separator GARIS. During irradiation of
) by using the gas-filled recoil separator GARIS. During irradiation of  Pb with the
Pb with the  Fe beam and irradiation of
Fe beam and irradiation of  Pb with the
Pb with the  Fe beam, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, were observed. The properties of decay events obtained by irradiation of
Fe beam, 8 decay chains and 1 decay chain, respectively, were observed. The properties of decay events obtained by irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb match well with those by irradiation of
Pb match well with those by irradiation of  Fe on
Fe on  Pb. The mean
Pb. The mean  -decay energies for the 3 groups are 10.82, 10.55, and 10.37 MeV, respectively. The half-life of
-decay energies for the 3 groups are 10.82, 10.55, and 10.37 MeV, respectively. The half-life of  Hs is determined to be 0.60 ms.
Hs is determined to be 0.60 ms.
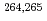 Hs
HsSato, Nozomi; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Yuki*; Ozawa, Akira*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
In this work, the production and decay properties of 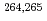 Hs produced in the
Hs produced in the  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, 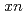 ) [
) [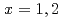 ] and
] and  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe,  ) reactions were investigated. The experiment was performed at the RILAC facility in RIKEN. The evaporation residues (ERs) were separated from the primary beam with the gas-filled recoil ion separator, GARIS. In the focal plane of GARIS the products were implanted into a position-sensitive Si detector for measuring the arrival of ERs and subsequent
) reactions were investigated. The experiment was performed at the RILAC facility in RIKEN. The evaporation residues (ERs) were separated from the primary beam with the gas-filled recoil ion separator, GARIS. In the focal plane of GARIS the products were implanted into a position-sensitive Si detector for measuring the arrival of ERs and subsequent  -decays or spontaneous fission from ERs. We have measured production cross-sections of
-decays or spontaneous fission from ERs. We have measured production cross-sections of 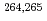 Hs in the
Hs in the  Fe +
Fe +  Pb reaction at several bombarding energies. For the
Pb reaction at several bombarding energies. For the  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe,  )
) Hs reaction, the cross-section maximum of (
Hs reaction, the cross-section maximum of (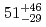 ) pb was obtained at the bombarding energy of 220.5 MeV at the middle of the target. For even-even nucleus
) pb was obtained at the bombarding energy of 220.5 MeV at the middle of the target. For even-even nucleus  Hs, we have also observed accurate decay data with good statistics.
Hs, we have also observed accurate decay data with good statistics.

Aoki, Katsutoshi; Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi; Otomo, Toshiya*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction measurements have revealed that LaD undergoes phase separation at high pressure with the relocation of deuterium atoms in the interstitial sites of La metal lattice. Deuterium atoms, which occupy the tetrahedral sites of the fcc metal lattice in LaD
undergoes phase separation at high pressure with the relocation of deuterium atoms in the interstitial sites of La metal lattice. Deuterium atoms, which occupy the tetrahedral sites of the fcc metal lattice in LaD , move into the empty octahedral sites at 11 GPa to form LaD and LaD
, move into the empty octahedral sites at 11 GPa to form LaD and LaD both having fcc metal lattices. Mono-hydride with an NaCl structure, which is common for mono-hydrides of transition metals, is formed in rare-earth metals for the first time. The first-principle calculations showed that LaH
both having fcc metal lattices. Mono-hydride with an NaCl structure, which is common for mono-hydrides of transition metals, is formed in rare-earth metals for the first time. The first-principle calculations showed that LaH is stable at low pressure and it undergoes a phase separation into LaH and LaH
is stable at low pressure and it undergoes a phase separation into LaH and LaH at 10 GPa, which is excellent agreement with the experimental results. Enthalpy comparison shows that unusual volume contraction in LaH
at 10 GPa, which is excellent agreement with the experimental results. Enthalpy comparison shows that unusual volume contraction in LaH than LaH
than LaH explains the phase separation phenomena. Lattice dynamics calculations on these lanthanum hydrides shed light on the detailed mechanism.
explains the phase separation phenomena. Lattice dynamics calculations on these lanthanum hydrides shed light on the detailed mechanism.

Aoki, Katsutoshi; Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi; Otomo, Toshiya*; et al.
no journal, ,
Synchrotron X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements have revealed that LaD undergoes phase separation at high pressure with the relocation of deuterium atoms in the interstitial sites of La metal lattice. Synchrotron X-ray and neutron experiments were made at BL22XU, SPring-8 and a total scattering device, NOVA, J-PARC. Deuterium atoms, which occupy the tetrahedral sites of the fcc metal lattice in LaD
undergoes phase separation at high pressure with the relocation of deuterium atoms in the interstitial sites of La metal lattice. Synchrotron X-ray and neutron experiments were made at BL22XU, SPring-8 and a total scattering device, NOVA, J-PARC. Deuterium atoms, which occupy the tetrahedral sites of the fcc metal lattice in LaD , move into the empty octahedral sites at 11 GPa to form LaD and LaD
, move into the empty octahedral sites at 11 GPa to form LaD and LaD both having fcc metal lattices. Mono-hydride with an NaCl structure, which is common for mono-hydrides of transition metals, is formed in rare-earth metals for the first time. The first-principle calculations showed that LaH
both having fcc metal lattices. Mono-hydride with an NaCl structure, which is common for mono-hydrides of transition metals, is formed in rare-earth metals for the first time. The first-principle calculations showed that LaH is stable at low pressure and it undergoes a phase separation into LaH and LaH
is stable at low pressure and it undergoes a phase separation into LaH and LaH at 10 GPa, which is excellent agreement with the experimental results.
at 10 GPa, which is excellent agreement with the experimental results.
Kamakura, Nozomu; Takeda, Yukiharu; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Miyaoka, Hiroki*; Tsubota, Masami*; Ichikawa, Takayuki*; Kojima, Yoshitsugu*; Muro, Takayuki*; Kinoshita, Toyohiko*
no journal, ,
Metal amide has been attracted much attention as a lightweight hydride being considered for high capacity hydrogen storage materials. In this research, the electronic states of the insulator alkali metal amide (KNH , NaNH
, NaNH ) and alkaline earth metal amide (Ca(NH
) and alkaline earth metal amide (Ca(NH )
) , Mg(NH
, Mg(NH )
) ) are investigated by the soft X-ray emission spectroscopy (XES) and absorption spectroscopy (XAS) in the total fluorescence yield mode. The localized character of the valence electrons is shown by the sharp three peak structure commonly observed in the XES spectrum of alkali metal amide. The localized character of the valence electrons is shown by the sharp peak structure commonly observed in the XES spectrum of alkali metal amide. The broadening of the N 2p states by the hybridization is observed in the XES spectrum of the alkaline earth metal amide. Decomposition temperature of the metal amide is found to relate to the character of the chemical bond observed in the XAS.
) are investigated by the soft X-ray emission spectroscopy (XES) and absorption spectroscopy (XAS) in the total fluorescence yield mode. The localized character of the valence electrons is shown by the sharp three peak structure commonly observed in the XES spectrum of alkali metal amide. The localized character of the valence electrons is shown by the sharp peak structure commonly observed in the XES spectrum of alkali metal amide. The broadening of the N 2p states by the hybridization is observed in the XES spectrum of the alkaline earth metal amide. Decomposition temperature of the metal amide is found to relate to the character of the chemical bond observed in the XAS.
Sato, Tetsuya; Sato, Nozomi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kojima, Takayuki*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
no journal, ,
The first ionization potential (IP) of the heaviest actinide lawrencium (Lr) is predicted to be lower than those of other actinides. To determine the IP of Lr based on the surface ionization technique, we have developed a surface ionization ion source coupled to a gas-jet transport system for the Isotope Separator On-Line at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. We measured ionization efficiencies of short-lived lanthanides isotopes as a function of ion-source temperature as a model experiment of Lr.
 by using a soft X-ray emission spectroscopy
by using a soft X-ray emission spectroscopyMizumaki, Masaichiro*; Agui, Akane; Uozumi, Takayuki*; Ichikawa, Noriya*; Shimakawa, Yuichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Hs
HsKaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Sato, Nozomi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Yuki*; Ozawa, Akira*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English