Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakashima, Yosuke*; Takeda, Hisahito*; Ichimura, Kazuya*; Hosoi, Katsuhiro*; Oki, Kensuke*; Sakamoto, Mizuki*; Hirata, Mafumi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Ikezoe, Ryuya*; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 463, p.537 - 540, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:84.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nakashima, Yosuke*; Sakamoto, Mizuki*; Yoshikawa, Masayuki*; Oki, Kensuke*; Takeda, Hisahito*; Ichimura, Kazuya*; Hosoi, Katsuhiro*; Hirata, Mafumi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Ikezoe, Ryuya*; et al.
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/10
 Si
Si
Tabata, Chihiro*; Inami, Toshiya; Michimura, Shinji*; Yokoyama, Makoto*; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Philosophical Magazine, 94(32-33), p.3691 - 3701, 2014/00
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:56.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Shoichi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Yamaguchi, Yusuke*; Katano, Makoto*; Imai, Yasutaka*; Murakami, Tatsuya*; Miyake, Yuichiro*; Yokoyama, Takuro*; Moriyama, Shinichi; Kobayashi, Takayuki; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 5, p.S2067_1 - S2067_4, 2010/12
Ion cyclotron emissions (ICEs) due to deuterium-deuterium fusion-product (FP) ions on JT-60U are studied. ICE due to H-ions is identified from the difference of the toroidal wave number of 2nd ICE(D). The parameter dependence for the appearance of ICE(H) is investigated from the experimental conditions and also is studied by using "Escape Particle Orbit analysis Code (EPOC)".
Ichimura, Makoto*; Higaki, Hiroyuki*; Kakimoto, Shingo*; Yamaguchi, Yusuke*; Nemoto, Tatsuki*; Katano, Makoto*; Ishikawa, Masao; Moriyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Takahiro
Nuclear Fusion, 48(3), p.035012_1 - 035012_7, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:86.54(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In this paper, experimental observations of spontaneously excited waves in the ion cyclotron range of frequency (ICRF) on JT-60U are described. The fluctuations in ICRF are driven by the presence of non-thermal ion distribution in magnetic confinement plasmas. Two types of magnetic fluctuations are detected: one is due to high energy D ions from neutral beam injections and the other is due to fusion products (FPs) of  He and T ions. These fluctuations have been reported as ion cyclotron emissions (ICEs) in the burning plasma experiments on large tokamaks. This paper describes the first measurement of the spatial structures of the excited modes in the poloidal and toroidal directions. It is confirmed by using ICRF antennas as magnetic probes that all modes excited spontaneously have magnetic components and couple to the antenna straps. The modes due to D ions have small toroidal wave number
He and T ions. These fluctuations have been reported as ion cyclotron emissions (ICEs) in the burning plasma experiments on large tokamaks. This paper describes the first measurement of the spatial structures of the excited modes in the poloidal and toroidal directions. It is confirmed by using ICRF antennas as magnetic probes that all modes excited spontaneously have magnetic components and couple to the antenna straps. The modes due to D ions have small toroidal wave number 
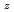 and will behave as electrostatic waves. On the while, the measurement of finite
and will behave as electrostatic waves. On the while, the measurement of finite 
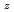 in the modes due to FP ions supports the excitation of the Alfv
in the modes due to FP ions supports the excitation of the Alfv n waves is the possible origin of FP-ICEs. It is also confirmed that the excited modes due to FP ions have different wave structures and are suggested to be in the different branch of the Alfv
n waves is the possible origin of FP-ICEs. It is also confirmed that the excited modes due to FP ions have different wave structures and are suggested to be in the different branch of the Alfv n waves, that is, the fast Alfv
n waves, that is, the fast Alfv n wave and the slow Alfv
n wave and the slow Alfv n wave. Frequency peaks due to FP ions are sometimes split into doublet shape as observed in JET experiments. The phase differences of both peaks are measured and indicate that two waves are traveling in both toroidal directions. Both beam-driven ICEs and FP-ICEs are observed and those spatial structures are obtained on JT-60U.
n wave. Frequency peaks due to FP ions are sometimes split into doublet shape as observed in JET experiments. The phase differences of both peaks are measured and indicate that two waves are traveling in both toroidal directions. Both beam-driven ICEs and FP-ICEs are observed and those spatial structures are obtained on JT-60U.
Kojima, Atsushi; Ishii, Kameo*; Miyata, Yoshiaki*; Kakiuchi, Hideto*; Kaido, Norihiro*; Yoshikawa, Masayuki*; Itakura, Akiyoshi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Chujo, T.*
Fusion Science and Technology, 51(2T), p.274 - 276, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ichimura, Makoto*; Higaki, Hiroyuki*; Kakimoto, Shingo*; Yamaguchi, Yusuke*; Nemoto, Kenju*; Katano, Makoto*; Kozawa, Isao*; Muro, Taishi*; Ishikawa, Masao; Moriyama, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 51(2T), p.150 - 153, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)In magnetically confined plasmas, fluctuations in the ion cyclotron range of frequency (ICRF) will be driven by the presence of non-thermal ion energy distribution. In strong ICRF heating experiments on the GAMMA 10 tandem mirror, plasmas with a strong temperature anisotropy have been formed. Alfven-ion-cyclotron (AIC) modes are spontaneously excited due to strong temperature anisotropy. High-energy ions are trapped in the local mirror and will form the velocity distribution with the strong anisotropy. To study the relation among the AIC modes, ICEs and beam-driven electrostatic instabilities with non-thermal energy distribution is the main purpose of this work. When the NBs are injected, the magnetic fluctuations due to injected beams and FP ions are detected by ICRF antennas used as pickup loops on JT-60U. The wave excitation near ion cyclotron and its higer harmonic frequencies are studied experimentally and theoretically in plasmas with non-thermal ion energy distribution.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Fujita, Takaaki; Takase, Yuichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kurita, Genichi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S29 - S38, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.56(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The National Centralized Tokamak (NCT) facility program is a domestic research program for advanced tokamak research to succeed JT-60U incorporating Japanese university accomplishments. The mission of NCT is to establish high beta steady-state operation for DEMO and to contribute to ITER. The machine flexibility and mobility is pursued in aspect ratio and shape controllability, feedback control of resistive wall modes, wide current and pressure profile control capability for the demonstration of the high-b steady state.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1599 - 1605, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 plasma operation
plasma operationTamai, Hiroshi; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ichimura, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1676 - 1683, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:44.52(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design studies are shown on the National Centralized Tokamak facility. The machine design is carried out to investigate the capability for the flexibility in aspect ratio and shape controllability for the demonstration of the high-beta steady state operation with nation-wide collaboration, in parallel with ITER towards DEMO. Two designs are proposed and assessed with respect to the physics requirements such as confinement, stability, current drive, divertor, and energetic particle confinement. The operation range in the aspect ratio and the plasma shape is widely enhanced in consistent with the sufficient divertor pumping. Evaluations of the plasma performance towards the determination of machine design are presented.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Kudo, Yusuke; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(1), p.2141 - 2150, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.31(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The dominant issue for the the modification program of JT-60 (JT-60SC) is to demonstrate the steady state reactor relevant plasma operation. Physics design on plasma parameters, operation scenarios, and the plasma control method are investigated for the achievement of high- . Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
. Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Chujo, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Cho, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:67.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Shobu, Takahisa; Urushisaki, Yukinori*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Amaya, Koichi*; Yada, Hiroki; Takase, Kazuyuki; Muramatsu, Toshiharu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ichimura, Makoto*; Yamaguchi, Yusuke*; Nemoto, Kenju*; Katano, Makoto*; GAMMA10 Group*; Ishikawa, Masao*; Moriyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Takahiro
no journal, ,
The measurement of fusion product (FP) ICEs will become a significant diagnostic tool for fusion reactions. The precise study of the excitation mechanism is important for future burning plasma experiments. In strong ICRF heating experiments on the GAMMA 10 tandem mirror, plasmas with a strong temperature anisotropy have been formed when the resonance layer exists near the mid-plane of the central cell. In a typical discharge, Alfven-ion-cyclotron (AIC) modes are spontaneously excited due to such a strong temperature anisotropy. On the while, the injection of low power ICRF waves into the plasma as active diagnostics has been tested in GAMMA 10. A wide band ICRF probe system was constructed. In the present experimental conditions, the inhomogeneity scale length of the plasma and the magnetic field configuration is in the same order of the wavelength. Wave excitation is strongly affected by the boundary conditions. The waves excited in the plasma are detected with a magnetic probe. In the presentation, the experimental results of the ICRF probe system in GAMMA 10 for active diagnostics and the observation of ICEs in JT-60U for passive diagnostics are reported.
Sakamoto, Mizuki*; Oki, Kensuke*; Yoshikawa, Motoki*; Terakado, Akihiro*; Nohara, Ryo*; Nojiri, Kumpei*; Nakashima, Yosuke*; Fukumoto, Masakatsu; Ichimura, Kazuya*; Hosoda, Yasunari*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakashima, Yosuke*; Ichimura, Kazuya*; Takeda, Hisahito*; Iwamoto, Miki*; Hosoda, Yasunari*; Shimizu, Keita*; Oki, Kensuke*; Sakamoto, Mizuki*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Kado, Shinichiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Makoto; Ichimura, Seiji; Suyama, Kenya; Tonoike, Kotaro; Kamohara, Keiko*; Suzuki, Norihisa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Shoichi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Yamaguchi, Yusuke*; Katano, Makoto*; Imai, Yasutaka*; Murakami, Tatsuya*; Miyake, Yuichiro*; Yokoyama, Takuro*; Moriyama, Shinichi; Kobayashi, Takayuki; et al.
no journal, ,
Ion cyclotron emissions (ICEs) due to deuterium-deuterium fusion-product (FP) ions on JT-60U are studied. ICE due to H-ions is identified from the difference of the toroidal wave number of 2nd ICE(D). The parameter dependence for the appearance of ICE(H) is investigated from the experimental conditions and also is studied by using "Escape Particle Orbit analysis Code (EPOC)".