Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
He, X.*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Okajima, Hajime*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Goto, Hirotada*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Structure, 1310, p.138271_1 - 138271_8, 2024/08
High-pressure responses of the O-D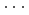 F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)
F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)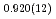 F
F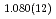 and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm
and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm . The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm
. The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Kurihara, Yuichi*; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Higaki, Shogo*; Kobayashi, Toru; Tanida, Hajime; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 661, p.317 - 332, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0no abstracts in English
Kato, Masato; Oki, Takumi; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Ozawa, Takayuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 107(5), p.2998 - 3011, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Ceramics)Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Chazono, Yoshiki*
Computer Physics Communications, 297, p.109058_1 - 109058_16, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0PIKOE is a Fortran 90 program that calculates triple- and quadruple-differential cross sections, vector analyzing powers, and momentum distributions of reaction residues, for proton-induced nucleon knockout reactions in normal and inverse kinematics. The distorted-wave impulse approximation is adopted, and the distorted waves are calculated quantum mechanically. Kinematics of the reaction particles are treated in a relativistic manner, which gives the proper asymptotics of the three-body scattering wave in the plane-wave limit.

Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Honda, Fuminori*; Aoki, Dai*; Haga, Yoshinori; Kida, Takanori*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; Karube, Kosuke*; Harima, Hisatomo*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044708_1 - 044708_10, 2024/04
 -Ga
-Ga O
O (001)
(001)Tsai, Y. H.*; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tanida, Hajime; Kobayashi, Toru; Yamashita, Yoshiyuki*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(11), p.112105_1 - 112105_5, 2024/03
Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Machida, Masahiko
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2024/03
In order to safely carry out the decommission of reactor buildings, it is extremely important to identify the radiation source distribution. It has been reported that when the structural model of the building is constructed by uniform cells, the source distribution can be estimated from the measured air dose rates by minimizing an evaluation function using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO). Moreover, if cells are non-uniform, we can estimate the distribution using the fused LASSO which minimizes the evaluation function that takes account of the connectivity between the adjacent cells. However, when a group of some cells is considered disconnected from the surrounding ones due to the precision of the measured structural data, the concentration of the group can be singularly high. Therefore, in order to avoid the problem, we propose a new evaluation function that can prevent the singularity. We estimated the distribution for the test model using the proposed evaluation function and confirmed the validity of the function. Moreover, we succeeded in estimating the source distribution in the pool canal circulation system room in JMTR in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the fused LASSO for the new function more accurately than previous analysis.
Kamiya, Tomohiro; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of the Symposium on Shock Waves in Japan (Internet), 7 Pages, 2024/03
We developed a ghost fluid method satisfying conservation laws to simulate steam explosions that can occur at the accident of a nuclear power plant. In the developed method, a first-order approximation is applied to interface effect regions, and a high-order approximation is applied to bulk regions. In other words, the algorithm of the developed method is not consistent. Therefore, we modify the way of getting ghost fluids and propose a comprehensive algorithm that applies a high-order approximation to interface effect regions. In the presentation, we will report the outlines and results of the numerical tests of it.
Kang, Z.; Okuda, Yukihiko; Nishida, Akemi; Tsubota, Haruji; Li, Y.
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/03
Most studies conducted till now on local damage of reinforced concrete (RC) slab structures subjected to projectile impact are about normal impact, while few research related to oblique impact can be found. The objective of this study is to carry out impact tests under different impact conditions including oblique impacts, to confirm the different impact behaviors of the RC slab structure, to develop an analysis method by investigating the test results and analytical conditions, and to validate the analysis method through comparison with the test results. This study focuses on the scabbing damage which is one of the local damage modes of RC slab. Based on oblique impact test results due to soft projectile with hemispherical nose shape, we investigate the relationship between the criterion related to the concrete fracture and the occurrence of scabbing damage.
Okuda, Yukihiko; Kang, Z.; Nishida, Akemi; Tsubota, Haruji; Li, Y.
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/03
The outer walls of nuclear facility buildings consist of reinforced concrete (RC) panels. When a projectile collides with a nuclear facility building, local damages such as penetration, scabbing, and perforation can occur in the RC panels. Numerical simulation using finite element analysis (FEA) is generally employed to assess these damage conditions. However, the impact analysis by FEA modelled with continuum elements is difficult to address phenomena such as scattering fragments of concrete because the elements deletion method for large deformation is used to prevent interruption of numerical calculations. Recently, a numerical method known as Smooth Particles Hydrodynamics (SPH), one of the particle methods, has been employed to address discontinuous phenomena. In this paper, we focus on the scabbing damages to RC panels and report on the findings obtained through the validation of the numerical analysis using the SPH method.
Higuchi, Yuki*; Yoshimune, Wataru*; Kato, Satoru*; Hibi, Shogo*; Setoyama, Daigo*; Isegawa, Kazuhisa*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Harada, Masashi*; et al.
Communications Engineering (Internet), 3, p.33_1 - 33_7, 2024/02
Ishida, Takekazu*; Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 214(3-4), p.152 - 157, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Applied)Tsuru, Tomohito; Han, S.*; Matsuura, Shutaro*; Chen, Z.*; Kishida, Kyosuke; Lobzenko, I.; Rao, S.*; Woodward, C.*; George, E.*; Inui, Haruyuki*
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1706_1 - 1706_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0Refractory high-entropy alloys (RHEAs) have attracted attention because of their potential for use in ultrahigh-temperature applications. Unfortunately, their body-centered-cubic (BCC) crystal structures make them more brittle than the ductile and fracture-resistant face-centered-cubic (FCC) HEAs. RHEAs also display significantly lower creep strengths than a leading Ni-base superalloy and its FCC matrix. To overcome these drawbacks and develop RHEAs into viable structural materials, improved fundamental understanding is needed of factors that control strength and ductility. Here we investigate two model RHEAs, TiZrHfNbTa and VNbMoTaW, and show that the former is plastically compressible down to 77 K, whereas the latter is not below 298 K. We find that hexagonal close-packed (HCP) elements in TiZrHfNbTa lower its dislocation core energy, increase its lattice distortion, and lower its shear modulus relative to VNbMoTaW whose elements are all BCC, leading to the formers higher ductility and modulus-normalized yield strength. Consistent with our yield strength models, primarily screw dislocations are present in TiZrHfNbTa after deformation, but equal numbers of edge and screw segments in VNbTaMoW. Dislocation cores are compact in VNbTaMoW and extended in TiZrHfNbTa, and different macroscopic slip planes are activated in the two RHEAs, which we attribute to the concentration of HCP elements. Our findings demonstrate how electronic structure changes related to the ratio of HCP to BCC elements can be used to control strength, ductility, and slip behavior to develop the next generation of high-temperature materials for more efficient power plants and transportation.
 CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
Okuda, Yukihiko; Takito, Kiyotaka; Nishida, Akemi; Li, Y.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/00
After the Great East Japan earthquake and the accident at the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Stations in March 2011, the regulation for nuclear power plants (NPPs) has been enhanced to take countermeasures against beyond-design-basis events. To improve the seismic safety of nuclear facilities against earthquakes that exceed the design input ground motion, the importance of seismic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) has drawn much attention. It is essential to evaluate the realistic seismic response of the equipment and piping in NPPs for fragility assessment in seismic PRA. In particular, since piping systems have plant-specific complex route geometries, it is known that the arrangement and stiffness of piping support structures have a significant impact on seismic response characteristics of the entire piping system. To construct a realistic seismic response analysis method for excessive input ground motion exceeding the elastic response, it is desired to develop an elastic-plastic response analysis method that can estimate the realistic response of piping systems including pipe support structures. In this study, the applicability of the method is confirmed by the simulation analysis of the elasto-plastic response for the piping support structure loading test previously reported. Moreover, based on the good correlation between the ductility factor and the damage status obtained from the test results and simulation analysis results, it is shown that the ductility factor is effective as a damage evaluation index for piping support structures.
Kamiya, Tomohiro; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Dai-37-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/12
We developed a sharp-interface method satisfying a conservation law for a compressible two-phase flow. In this presentation, the outline and numerical test results of the developed method in multi-dimension were reported. The ghost fluid method does not cause numerical diffusion at a gas-liquid interface because difference between gas and liquid phases is avoided. It cannot satisfy the conservation law because cells in which liquid and gas coexist are not prepared although in fact an interface crosses a cell. Hence, we developed the ghost fluid method satisfying a conservation law by preparing cells in which liquid and gas coexist by VOF method. Multi-dimensional basic equations are solved by a split method which is one of the geometric VOF methods. We solved an underwater explosion problem and confirmed that gas bubble expansion and compressible wave propagation which are observed in the steam explosion can be represented and developed method satisfies the conservation law.
 unheated rod bundle
unheated rod bundleNagatake, Taku; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1417 - 1430, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In recent years, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) codes have been used to evaluate two-phase flow behavior inside a fuel bundle for nuclear core design and accident management. A space-time distribution of void fraction and interfacial velocity in bundle systems at high temperatures and pressures, are important for validation of two-phase flow CFD codes. However, it is difficult to obtain a space-time distribution of void fraction and interfacial velocity in a bundle system at high temperature and pressure conditions. We have so far developed an experimental apparatus with a 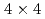 unheated rod bundle by adapting a through-rod WMS to measure distributions of a void fraction and an interfacial velocity in high pressure conditions. We newly measured distributions of the void fraction and interfacial velocity in the water-vapor system under high pressure up to 2.6 MPa by the developed apparatus. It has been confirmed that reasonable results were obtained by the experimental apparatus.
unheated rod bundle by adapting a through-rod WMS to measure distributions of a void fraction and an interfacial velocity in high pressure conditions. We newly measured distributions of the void fraction and interfacial velocity in the water-vapor system under high pressure up to 2.6 MPa by the developed apparatus. It has been confirmed that reasonable results were obtained by the experimental apparatus.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionKobayashi, Hiroki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Ito, Hayate*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(47), p.10664 - 10669, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)Ice IV is a metastable high-pressure phase of ice in which the water molecules exhibit orientational disorder. Although orientational ordering is commonly observed for other ice phases, it has not been reported for ice IV. We conducted  powder neutron diffraction experiments for DCl-doped D
powder neutron diffraction experiments for DCl-doped D O ice IV to investigate hydrogen ordering in ice IV. We found abrupt changes in the temperature derivative of unit cell volume, dV/dT, at about 120 K, and revealed their slightly ordered structure at low temperatures based on the Rietveld method. The occupancy of the D1 site deviates from 0.5; it increased when samples were cooled at higher pressures and reached 0.282(5) at 2.38 GPa, 58 K. Our results evidence the presence of a low-symmetry hydrogen-ordered state corresponding to ice IV. It seems, however, difficult to experimentally access the completely ordered phase corresponding to ice IV by slow cooling at high pressure.
O ice IV to investigate hydrogen ordering in ice IV. We found abrupt changes in the temperature derivative of unit cell volume, dV/dT, at about 120 K, and revealed their slightly ordered structure at low temperatures based on the Rietveld method. The occupancy of the D1 site deviates from 0.5; it increased when samples were cooled at higher pressures and reached 0.282(5) at 2.38 GPa, 58 K. Our results evidence the presence of a low-symmetry hydrogen-ordered state corresponding to ice IV. It seems, however, difficult to experimentally access the completely ordered phase corresponding to ice IV by slow cooling at high pressure.
 Sr (
Sr (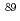 Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areas
Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areasMachida, Masahiko; Iwata, Ayako; Yamada, Susumu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Funasaka, Hideyuki*; Morita, Takami*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(4), p.119 - 139, 2023/11
We estimate monthly discharged inventory of  Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of
Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of  Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kaneko, Akiko*; Abe, Yutaka*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Kanto Shibu Dai-29-Ki Sokai, Koenkai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/10
To elucidate the behavior of molten fuels as a liquid jet in a shallow pool, which is assumed in a core meltdown accident of an LWR, and develop the evaluation method, we investigated the behavior of the vortical liquid film of the simulated wall-impinging liquid jet using 3-dimensional interface shape data obtained by the experiment in a liquid-liquid system.