Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morita, Hisashi; Daigo, Fumihisa; Sayato, Natsuki; Watahiki, Shunsuke; Kojima, Kazuki; Nakayama, Kazuhiko; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2021-030, 166 Pages, 2022/05
When the roof of the JMTR Hot Laboratory (HL) building was repaired for rain leaks in January, 2015, thinning was found at one of the anchor bolts on base of the HL exhaust stack. Moreover, the thinning of some anchor bolts and gaps between the anchor bolt nuts and flange plate was found in the later investigation for the exhaust stack. Since the possibility of the exhaust stack collapsing cannot be denied, it was removed. Therefore, it became necessary to rebuild a new exhaust stack as soon as possible. The design of the new exhaust stack was based on the measures to prevent rainwater intrusion into the base, which was the cause of the thinning of the anchor bolts found in the investigation, and on the new regulatory standards established after the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Furthermore, since the new exhaust stack corresponds to buildings and structures that must undergo building confirmation, the soundness of the new exhaust stack against seismic force and wind load was evaluated based on the Building Standards Law and the Stack Structure Design Guideline. This report described the basic design of the new exhaust stack.
Urano, Hajime; Fujita, Takaaki*; Ide, Shunsuke; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Matsunaga, Go; Matsukawa, Makoto
Fusion Engineering and Design, 100, p.345 - 356, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:79.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)The operation scenarios for plasma breakdown and current ramp-up phases in JT-60SA tokamak have been developed. The induced current in the in-vessel conducting elements such as vacuum vessel and stabilizing plate increases to the comparable level of plasma current of  600 kA during the breakdown phase and thus enhances the strength of error field. The optimized scenarios for half and full pre-magnetization cases satisfied the conditions required for the plasma initiation. At the initial plasma, the vertical magnetic field required to sustain the plasma position was controlled by the outer equilibrium field (EF) coil currents which compensate for a vertical field due to a large eddy current. The condition for the formation of divertor configurations given by the combination of the magnetic flux for plasma and the plasma current enables us to develop the operational scenarios with a smooth transition from a limiter to a divertor configuration.
600 kA during the breakdown phase and thus enhances the strength of error field. The optimized scenarios for half and full pre-magnetization cases satisfied the conditions required for the plasma initiation. At the initial plasma, the vertical magnetic field required to sustain the plasma position was controlled by the outer equilibrium field (EF) coil currents which compensate for a vertical field due to a large eddy current. The condition for the formation of divertor configurations given by the combination of the magnetic flux for plasma and the plasma current enables us to develop the operational scenarios with a smooth transition from a limiter to a divertor configuration.
Matsunaga, Go; Takechi, Manabu; Sakurai, Shinji; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.1113 - 1117, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)Toma, Mitsunori; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Ide, Shunsuke
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 57(9), p.095007_1 - 095007_9, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.56(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Integrated tokamak modelling that enables the simulation of an entire discharge periodis indispensable for designing advanced tokamak plasmas. For this purpose, we extend the integrated code TOPICS to make it more suitable for transient analyses in the fast-ion part. The fast-ion Fokker-Planck solver is integrated into TOPICS at the same level as the bulk transport solver so that the time evolutions of the fast ion and the bulk plasma are consistent with each other as well as with the equilibrium magnetic field. The integrated code is applied to ramp-up simulations for JT-60SA and ITER to confirm its capability and effectiveness in transient analyses. In the integrated simulations, the coupled evolution of the fast ions, plasma profiles, and equilibrium magnetic fields are presented.
Yoshida, Maiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Narita, Emi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urano, Hajime; Nakata, Motoki; Miyato, Naoaki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ide, Shunsuke; Kamada, Yutaka
Nuclear Fusion, 55(7), p.073014_1 - 073014_9, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:57.79(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Conditions without the increases in the thermal and particle transport with ECH have been experimentally investigated in positive magnetic shear (PS), weak magnetic shear (WS) and reversed magnetic shear (RS) plasmas with internal transport barriers (ITBs) on JT-60U. The ion heat diffusivity around an internal transport barrier in the ion temperature (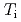 -ITB) remains constant with ECH when a large negative toroidal rotation shear is formed before the ECH. The condition does not depend on the electron to ion temperature ratio (
-ITB) remains constant with ECH when a large negative toroidal rotation shear is formed before the ECH. The condition does not depend on the electron to ion temperature ratio ( /
/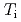 ) and ECH power. The electron heat diffusivity around a
) and ECH power. The electron heat diffusivity around a  -ITB stays constant with ECH when the magnetic shear is negative around the Te-ITB region. Effective particle transport remains constant or reduces during ECH under the condition of negative magnetic shear.
-ITB stays constant with ECH when the magnetic shear is negative around the Te-ITB region. Effective particle transport remains constant or reduces during ECH under the condition of negative magnetic shear.
Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Yoshida, Maiko; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kamiya, Kensaku; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Shinohara, Koji; Matsunaga, Go; Nakata, Motoki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(7), p.073033_1 - 073033_11, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:28.43(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Miyata, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Takechi, Manabu; Urano, Hajime; Ide, Shunsuke
Review of Scientific Instruments, 86(7), p.073511_1 - 073511_13, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.1(Instruments & Instrumentation)It is essential for a stable plasma equilibrium control to reconstruct an accurate plasma boundary in tokamak devices. Cauchy Condition Surface (CCS) method is a numerical approach to calculate the spatial distribution of the magnetic flux outside a hypothetical plasma surface and reconstruct the plasma boundary from the magnetic measurements located outside the plasma. It is found that the optimum number of unknown parameters and shape of the CCS for minimizing errors in the reconstructed plasma shape increase in proportion to the plasma size. It is shown that the accuracy of the plasma shape reconstruction greatly improves by using the optimum number of unknown parameters. The assessment of accuracy of plasma shape reconstruction by CCS method in JT-60SA is reported.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Shiraishi, Junya; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Wakatsuki, Takuma; Hoshino, Kazuo; Toma, Mitsunori; Suzuki, Takahiro; Urano, Hajime; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; et al.
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 39E, p.P5.145_1 - P5.145_4, 2015/06
Wakatsuki, Takuma; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Shiraishi, Junya; Ide, Shunsuke; Takase, Yuichi*
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 39E, p.P5.144_1 - P5.144_4, 2015/06
Wakatsuki, Takuma; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Shiraishi, Junya; Ide, Shunsuke; Takase, Yuichi*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 57(6), p.065005_1 - 065005_12, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:41.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hada, Kazuyoshi*; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Masuda, Kai*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Ide, Shunsuke; Isayama, Akihiko; Kajiwara, Ken
Fusion Science and Technology, 67(4), p.693 - 704, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Narita, Emi*; Honda, Mitsuru; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urano, Hajime; Ide, Shunsuke; Fukuda, Takeshi*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 10, p.1403019_1 - 1403019_11, 2015/03
Isayama, Akihiko; Urano, Hajime; Miyato, Naoaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 90(12), p.830 - 833, 2014/12
no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Matsunaga, Go; Shinohara, Koji; Yoshida, Maiko; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime
Nuclear Fusion, 54(11), p.114005_1 - 114005_14, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:59.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Yoshida, Maiko; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kamiya, Kensaku; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Shinohara, Koji; Matsunaga, Go; Nakata, Motoki; et al.
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/10
Shiraishi, Junya; Miyato, Naoaki; Matsunaga, Go; Honda, Mitsuru; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Ide, Shunsuke
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/10
Extension of the kinetic-magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) model is presented to include toroidal rotation shear effect for the first time. The sheared rotation is introduced through generalization of the guiding center Lagrangian, yielding two additional terms in a quadratic form of mode-particle resonance. Additionally, another new term is introduced by using the equilibrium distribution function with rotation effect. These three terms are overlooked in conventional models. The new model is applied to stability analysis of resistive wall modes (RWMs) successfully. Numerical results show that the rotation shear reduces RWM growth rates further, which is consistent with experimental results.
Garcia, J.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Baiocchi, B.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Honda, Mitsuru; Ide, Shunsuke; Maget, P.*; Narita, Emi*; Schneider, M.*; Urano, Hajime; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(9), p.093010_1 - 093010_13, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:86.74(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hoshino, Kazuo; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Nakano, Tomohide; Ide, Shunsuke
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 54(4-6), p.404 - 408, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:61.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Garcia, J.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Giruzzi, G.*; Schneider, M.*; Joffrin, E.*; Ide, Shunsuke; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Urano, Hajime; JT-60 Team; et al.
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 38F, p.P1.029_1 - P1.029_4, 2014/06
Miyata, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 9(Sp.2), p.3403045_1 - 3403045_5, 2014/05
The precise control of the plasma position is essential in safe and stable plasma operation. An MHD equilibrium control simulator has been developed in order to study the techniques of plasma equilibrium control for JT-60SA. In this study, the modules of plasma shape reconstruction, power supply, PF and FPPC coils are incorporated in order to simulate the real plasma equilibrium control. The plasma equilibrium control is simulated during Ip ramp-up within the power supply capability using MECS.