Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Igarashi, Takahiro
Corrosion Science, 251, p.112897_1 - 112897_15, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Experimental and modeling studies of the oxygen ingression at the crevices of stainless steels were conducted in high-temperature water (288 C). The limiting distance of oxygen ingression,
C). The limiting distance of oxygen ingression, 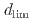 , was defined as the point beyond which the primary surface oxide changed (hematite
, was defined as the point beyond which the primary surface oxide changed (hematite  magnetite), regardless of crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and time. In situ measurements revealed increased electrical conductivity around the
magnetite), regardless of crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and time. In situ measurements revealed increased electrical conductivity around the 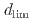 position indicating ion enrichment due to a differential oxygen concentration cell.
position indicating ion enrichment due to a differential oxygen concentration cell. 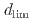 increased with increasing crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and immersion time. Modeling study suggested that oxide layer growth reduced anodic dissolution and slowed oxygen consumption, allowing oxygen ingression with time.
increased with increasing crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and immersion time. Modeling study suggested that oxide layer growth reduced anodic dissolution and slowed oxygen consumption, allowing oxygen ingression with time.
Igarashi, Takahiro
AI, Shimyureshon O Mochiita Rekka, Hakai Hyoka To Juyo Yosoku, p.323 - 329, 2025/05
Metal materials are used in various fields of daily life, especially in infrastructure like bridges, buried pipes, and concrete reinforcing bars. These materials are prone to corrosion, which can cause thinning, hydrogen generation, and embrittlement, leading to a loss of structural integrity and potentially serious accidents. Many studies have been conducted to address this issue. Recently, advances in computer performance have led to the development of corrosion diagnosis methods. One promising approach uses models that predict rust thickness and corrosion product composition by analyzing image data from surfaces, offering both ease of measurement and accuracy. This book introduces these methods, including color analysis, hyperspectral analysis, AI analysis, and feature point extraction.
Aoyama, Takahito; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Otani, Kyohei; Igarashi, Takahiro
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111229_1 - 111229_6, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Igarashi, Takahiro
Dai-71-Kai Zairyo To Kankyo Toronkai Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.253 - 256, 2024/11
In our previous study, we reported that Cl ions penetrating stainless steel crevices do not dissipate by diffusion, even in high-purity water (i.e., conductivity remains stable), likely due to electrochemical reactions inside and outside the crevice. This study further analyzes ion behavior by experimentally and computationally investigating ion concentration drivers in high-purity water. Results show that, at 50 C, the crevice conductivity of SUS316L stainless steel reached 100
C, the crevice conductivity of SUS316L stainless steel reached 100  S/cm (100-1000 times bulk water). Modeling suggests this is due to metal cations and hydroxide ions from dissolved oxygen reduction. The dissolution rate was estimated at 10nA/cm
S/cm (100-1000 times bulk water). Modeling suggests this is due to metal cations and hydroxide ions from dissolved oxygen reduction. The dissolution rate was estimated at 10nA/cm .
.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Sugawara, Yu*; Otani, Kyohei; Aoyama, Takahito
Tetsu To Hagane, 110(15), p.1244 - 1250, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Using two types of image processing techniques without machine learning, edge extraction processing and keypoint extraction processing, progressively corroded regions under rust layer from images of corroded steel surfaces was extracted. We found that there is a relatively good correlation between the keypoint strength obtained from the keypoint extraction processing for HSL transformed and histogram flattened corroded surface photographs and the corrosion depth after removing rust removal.
Sugawara, Yu*; Igarashi, Takahiro
Tetsu To Hagane, 110(15), p.1179 - 1186, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Degradation due to atmospheric corrosion is an important problem for steel structures such as bridges. In order to maintain steel structures safely over a long period of time, there is a need for a low-cost and easy-to-use method to evaluate corrosion degradation. In this study, corrosion morphology under atmospheric corrosion environment was focused on. The relation between the surface appearance and the distribution of corrosion depth of the carbon steel specimen after atmospheric exposure was analyzed, and the prediction of corrosion morphology under rust layers by surface observation of steel specimens was examined. It was found that deeply-corroded areas were possible to be located within the dark brown regions in the rusted specimen after the atmospheric exposure. As the exposure period increased, the correspondence between the dark brown regions in the rusted specimen and deeply-corroded areas became clearer.
Sato, Tomonori; Hata, Kuniki; Kato, Chiaki; Igarashi, Takahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 73(4), p.102 - 109, 2024/04
To evaluate the effects of dissolved oxygen concentration to water quality within SCC crack and the distribution of water quality in the depth direction under irradiation, immersion tests of stainless steel specimens given a gap and water radiolysis calculations for the water quality in the crevice gap were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that Fe O
O was formed in the entire area within the crevice regardless of the dissolved oxygen concentration. It was also estimated that under irradiation, the oxidant species produced directly by radiolysis in the crack are consumed by the oxide growth, and anion enrichment occurs in the crack even in the irradiation conditions.
was formed in the entire area within the crevice regardless of the dissolved oxygen concentration. It was also estimated that under irradiation, the oxidant species produced directly by radiolysis in the crack are consumed by the oxide growth, and anion enrichment occurs in the crack even in the irradiation conditions.
Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Igarashi, Takahiro
Corrosion Modelling with Cellular Automata; European Federation of Corrosion Publications, Number 71, p.131 - 153, 2024/03
In order to elucidate corrosion phenomena in spent fuel reprocessing plant, experimental corrosion tests and computer simulations were carried out. From experimental results, variation of intergranular corrosion rate were caused by following; (i) surface corrosion, (ii) increase of corrosion rate due to a part of grains dropping out, (iii) high corrosion rate due to continuous of dropping out of grains. Intergranular corrosion rates obtained from the simulation using the developed intergranular corrosion model were relatively good agreement with those from the experimental data.
Otani, Kyohei; Kato, Chiaki; Igarashi, Takahiro
Corrosion, 79(11), p.1277 - 1286, 2023/11
 Sr and
Sr and  Cs in HCl solutions on the corrosion potential of Type 316L stainless steel
Cs in HCl solutions on the corrosion potential of Type 316L stainless steelAoyama, Takahito; Sato, Tomonori; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Igarashi, Takahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 72(11), p.284 - 288, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
Soma, Yasutaka; Igarashi, Takahiro
Dai-70-Kai Zairyo To Kankyo Toronkai Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.199 - 202, 2023/10
Since an acidic corrosive environment (crevice environment) is formed inside the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel in high temperature water, it is important to understand the corrosion behavior in the crevice environment for the better understanding of crack growth behavior. In the previous study, the authors measured the electrical conductivity inside the crevice and obtained values of 380  S/cm and 1600
S/cm and 1600  S/cm for the crevice with and without intergranular corrosion, respectively. In this study, we defined the crevice environment I (pH
S/cm for the crevice with and without intergranular corrosion, respectively. In this study, we defined the crevice environment I (pH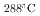 =4.41) and II (pH
=4.41) and II (pH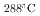 =3.13) corresponding the above conductivity values, and the corrosion behavior of Fe-xCr-20Ni (x=16.9, 19.8, 22.9, 24.3, 25.9) in each crevice environment was investigated. In the simulated crevice environment-I, the all alloys showed passive behavior, while in the environment-II, severe corrosion with intergranular cracking was observed for x = 16.9 and 19.8, and a thick oxide film was formed. On the other hand, above x=22.9, oxide film growth was suppressed and a clear passive region appeared on the polarization curve.
=3.13) corresponding the above conductivity values, and the corrosion behavior of Fe-xCr-20Ni (x=16.9, 19.8, 22.9, 24.3, 25.9) in each crevice environment was investigated. In the simulated crevice environment-I, the all alloys showed passive behavior, while in the environment-II, severe corrosion with intergranular cracking was observed for x = 16.9 and 19.8, and a thick oxide film was formed. On the other hand, above x=22.9, oxide film growth was suppressed and a clear passive region appeared on the polarization curve.
Nagata, Sho*; Miyake, Shugo*; Igarashi, Takahiro; Ota, Hiromichi*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*
Jikken Rikigaku, 22(2), p.105 - 111, 2022/06
Thermal easy axis and thermal diffusivity of uniaxial carbon fiber-reinforced plastic sheets were determined by a offset periodic laser heating method, and investigated relationship between the thermal easy axis and fiber orientation with different thickness of CFRP sheet specimen, experimentally. It was clarified that the orientation of the thermal easy axis spreads in the in-plane direction with the sheet thickness deceases. Then, thermal diffusivity of CFRP specimens in the out-of-plane and in-plane direction were measured by two method: a variable-frequency method and a variable-displacement method, respectively. In the results of the out-of-plane directions, thermal diffusivity almost consistent with the carbon fiber direction were obtained. In contrast, the in-plane directions of those were exhibited unexpected value. Moreover, thermal diffusivity determination by offset periodic heating method was carried out. Finally, it is found that the thermal diffusivity considering the thermal easy axis with fiber angle was different characteristics from the in-plane direction measurement.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Otani, Kyohei; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*
Bosei Kanri, 66(4), p.141 - 145, 2022/04
Metal corrosion is a material deterioration phenomenon based on electrochemical reactions on an atomic scale. In this paper, various methods for acquiring physical properties on metal surfaces using first-principles calculations were described. As examples of applying first-principles calculation to metal corrosion, the effect of hydrogen adsorption on the metal surface on the potential change and the effect of cation atoms in the aqueous solution on the corrosion resistance of the metal were reported.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*
Tetsu To Hagane, 107(12), p.998 - 1003, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.80(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)In order to clarify the effect of environmental factors on the amount of atmospheric corrosion of steel, novel model for predicting the reduction of atmospheric corrosion considering relative humidity and rain falls was developed. We conducted a one-year calculation simulation of atmospheric corrosion in Miyakojima City, Choshi City, and Tsukuba City using the developed model. Corrosion weight loss by the simulation could reproduce the measured value well. Corrosion weight loss at each point was greatly affected by the amount of flying sea salt, relative humidity, and rain falls.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*
Bosei Kanri, 65(10), p.365 - 370, 2021/10
We have developed a new atmospheric simulation model considering important environmental factors such as airborne sea salt, temperature, relative humidity, and rainfall. The developed model was verified by comparing predicted values by the simulation and measured data for the weight loss by atmospheric corrosion. In addition, atmospheric corrosion simulations under open and sheltered exposure condition were conducted, and it was confirmed that the air corrosion weight loss was strongly suppressed by the surface cleaning effect due to rainfall.
Nagata, Sho*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Igarashi, Takahiro; Miyake, Shugo*
Proceedings of 34th International Microprocesses and Nanotechnology Conference (MNC 2021) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2021/10
Due to the increasing heat generation density of electronic devices, unidirectional Carbon-fiber-reinforced Plastic (CFRP) has gained interest as a heat-dissipating material owing to its high thermal conductivity, high anisotropy, and high strength. If CFRPs can be used to conduct heat in the desired direction of dissipation, more efficient thermal designs are possible. To control heat propagation, it is necessary to understand the heat propagation behavior within CFRPs at each fiber angle by determining the direction of heat propagation, referred to as thermal orientation. We previously demonstrated an approach for determining the thermal orientation of CFRPs using a periodic heating method, wherein the heat propagation in CFRPs was classified into two directions: the direction of the carbon fiber direction and the direction of the fiber-matrix interface. It has been suggested that the fiber-matrix interface has a significant effect on the heat propagation of CFRPs, which increases with the increase in CFRP thickness. However, the effect of CFRP thickness on thermal orientation is yet unknown. In the current study, we investigated the effect of the fiber-matrix interface on thermal orientation using the periodic heating method for CFRPs with varying thicknesses.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Corrosion Science and Technology, 20(3), p.105 - 111, 2021/06
We constructed three dimensional computational model using cellular automata method to simulate the intergranular corrosion propagation of stainless steel. In the model, the computational system was constructed by three types of cells: grain (bulk), grain boundary (GB), and solution cell. Our simulations revealed that the surface roughness calculated by the model adopted distributed dissolution rates of GBs was greater than that adopted constant dissolution rates of GBs. The cross-sectional images obtained by our simulation were comparable with that obtained by corrosion tests. These results indicate that the surface roughness during corrosion relates the distribution of corrosion rate.
Kano, Koichi*; Hagiwara, Satoshi*; Igarashi, Takahiro; Otani, Minoru*
Electrochimica Acta, 377, p.138121_1 - 138121_10, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:64.59(Electrochemistry)We investigated the free corrosion potential at an interface between an Al electrode and an aqueous NaCl solution under acidic conditions via density functional theory combined with the effective screening medium and reference interaction site model (ESM-RISM). The electrode potentials for the anodic and cathodic corrosion reactions were obtained from the grand potential profile as a function of the electron chemical potential at the interface. Thereafter, we determined the free corrosion potential using the Tafel extrapolation method. The results of the free corrosion potential were consistent with previous experimental data. By controlling the pH, we determined the pH dependence of the free corrosion potential, and the results agreed well with the experimental results. Our results indicated that the ESM-RISM method duly described the environmental effect of an acidic solution and precisely determined the free corrosion potential.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Otani, Kyohei; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Togashi, Yusuke*; Baba, Kazuhiko*; Takagi, Shusaku*
ISIJ International, 61(4), p.1085 - 1090, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.12(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)In order to clarify the effect of metal cations (Zn , Mg
, Mg , Na
, Na ) in aqueous solution on hydrogen permeation into iron, the amount of hydrogen permeation from iron surface was measured by electrochemical tests with a laser ablation. Moreover, in order to obtain the basic mechanism of hydrogen permeation with metal cation, first-principles calculations were used to acquire the adsorption potential of the metal cation and the electronic state around iron surface. By Zn
) in aqueous solution on hydrogen permeation into iron, the amount of hydrogen permeation from iron surface was measured by electrochemical tests with a laser ablation. Moreover, in order to obtain the basic mechanism of hydrogen permeation with metal cation, first-principles calculations were used to acquire the adsorption potential of the metal cation and the electronic state around iron surface. By Zn in solution, anodic reaction on ablated surface by laser irradiation was suppressed. Also, by quantum analysis Zn atoms were chemically bonded stronger than Na and Mg atoms to iron surface. It was suggested that the dissolution reaction of iron was suppressed by the formation of the Zn layer, and that lead suppression of hydrogen permeation into iron.
in solution, anodic reaction on ablated surface by laser irradiation was suppressed. Also, by quantum analysis Zn atoms were chemically bonded stronger than Na and Mg atoms to iron surface. It was suggested that the dissolution reaction of iron was suppressed by the formation of the Zn layer, and that lead suppression of hydrogen permeation into iron.
Yamamoto, Masahiro; Irisawa, Eriko; Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Proceedings of Annual Congress of the European Federation of Corrosion (EUROCORR 2019) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2019/09
Intergranular corrosion phenomena were analysed using modified reprocessing solution. The data indicated that corrosion rates increased with time at the initial stage, and these stayed at constant value. Intergranular corrosion propagated at grain boundary in the initial stage and then attacked whole grain boundary causing drop out of grains. Corrosion rates of steady state were sum of intergranular corrosion amounts and weight losses of dropped grains. Surface appearances and cross sections of corroded samples were analyzed. The results indicated that the initial stage of intergranular corrosion was characterized by the ratio of corrosion rates between grain boundary and matrix. These ratios differed from individual grain boundaries. Total corrosion rates were affected by the distribution of these ratios. These data were based on the numerical modelling of intergranular corrosion using cellular automata. And also, calculated results were compared with these analytical data.