Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
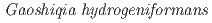 sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formation
sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formationUeno, Akio*; Sato, Kiyoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 75(6), p.006802_1 - 006802_11, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
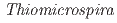 sp. strain V2501 isolated from 250 m below the ground level in Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan
sp. strain V2501 isolated from 250 m below the ground level in Horonobe, Hokkaido, JapanUeno, Akio*; Sato, Kiyoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
Microbiology Resource Announcements (Internet), 13(11), p.e00108-24_1 - e00108-24_4, 2024/11
Tamamura, Shuji*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Aramaki, Noritaka*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Kaneko, Katsuhiko*
Groundwater, 56(1), p.118 - 130, 2018/01
Groundwater saturated with gas forms bubble under atmospheric pressure, bothering most authorized methods to determine in-situ dissolved gas concentrations. To circumvent this problem, a simple theory to quantify effect of 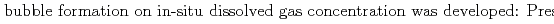 [bar]) of a gas component "
[bar]) of a gas component "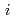 " (e.g., CH
" (e.g., CH , CO
, CO and H
and H ) in equilibrium with in-situ dissolved concentration (
) in equilibrium with in-situ dissolved concentration (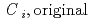 [mol L
[mol L  ]) was related to partial pressure of the
]) was related to partial pressure of the 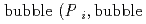 [bar]) emerged from groundwater in the form:
[bar]) emerged from groundwater in the form: 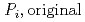 =
= 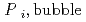 +
+ 
 (k
(k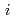 '
' 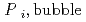 /(
/(
 k
k '
' 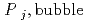 )), where
)), where 
 [bar] is groundwater pressure difference before and after the
[bar] is groundwater pressure difference before and after the 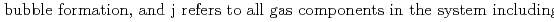 " The k
" The k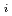 ' and k
' and k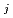 ' corresponds to the Henry's constant [bar L mol
' corresponds to the Henry's constant [bar L mol ] of
] of 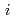 (k
(k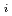 ) and
) and  (k
(k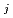 ), respectively, except for k
), respectively, except for k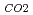 ', which is pH-dependent function. Dissolved CH
', which is pH-dependent function. Dissolved CH concentrations were successfully estimated by the model within the error of
concentrations were successfully estimated by the model within the error of  4.0% from the direct measurements by the sealed sampler method. Similar TIC concentration in the groundwater before and after the rm bubble formation was consistent with the model prediction. The wide application of the model is suggested without selecting sampling locations.
4.0% from the direct measurements by the sealed sampler method. Similar TIC concentration in the groundwater before and after the rm bubble formation was consistent with the model prediction. The wide application of the model is suggested without selecting sampling locations.
Tamamura, Shuji*; Endo, Ryo*; Shimizu, Satoru*; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Amano, Yuki; Omi, Yasushi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
Journal of MMIJ, 128(10,11), p.570 - 575, 2012/10
no abstracts in English
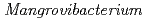 sp. strain Z1-71, isolated from the terrestrial subsurface environment and its co-cultivation within a methanogenic archaeon
sp. strain Z1-71, isolated from the terrestrial subsurface environment and its co-cultivation within a methanogenic archaeonUeno, Akio*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ueda, Takahiro*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Hokora, Hideyuki*; Sataka, Hiroyuki; Shimada, Tomohiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Ueda, Takahiro*; Hokora, Hideyuki*; Jo, Mayumi*; Kudo, Hajime
no journal, ,
Horonobe Underground Research Center, located in northern Hokkaido, Japan, has been excavating shafts and drifts of an underground research facility to establish general techniques for the assessment of deep geological environment. In this site, the groundwater seepage from the shafts and drifts as well as leachate from the excavated rock storage site contain high concentrations of total nitrogen. Ammonium-nitrogen (NH -N), the major nitrogen species in the seepage and leachate, has been removed by a nearby treatment facility. However, NH
-N), the major nitrogen species in the seepage and leachate, has been removed by a nearby treatment facility. However, NH -N is easily oxidized to nitrite-nitrogen (NO
-N is easily oxidized to nitrite-nitrogen (NO -N) and nitrate-nitrogen (NO
-N) and nitrate-nitrogen (NO -N) by nitrification in the excavated rock storage site, which makes the removal process employed on site less effective. Therefore, column experiments that simulated the infiltration of rainwater through the storage site were carried out to understand the leaching and nitrification of nitrogen species and the factors affecting the phenomena. The results showed that the nitrification was inhibited when the rock layer was almost saturated, and that this process was temperature dependent. These indicate that nitrification can be mitigated by controlling hydrological conditions like water saturation.
-N) by nitrification in the excavated rock storage site, which makes the removal process employed on site less effective. Therefore, column experiments that simulated the infiltration of rainwater through the storage site were carried out to understand the leaching and nitrification of nitrogen species and the factors affecting the phenomena. The results showed that the nitrification was inhibited when the rock layer was almost saturated, and that this process was temperature dependent. These indicate that nitrification can be mitigated by controlling hydrological conditions like water saturation.
Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Ueno, Akio*; Murakami, Takuma*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Tamamura, Shuji*; Kiyama, Tamotsu*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Kaneko, Katsuhiko*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ueda, Takahiro*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Hokora, Hideyuki*; Sataka, Hiroyuki; Shimada, Tomohiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ueda, Takahiro*; Hokora, Hideyuki*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Jo, Mayumi*; Sataka, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
Horonobe Underground Research Center, located in northern Hokkaido, Japan, has been excavating shafts of an underground research facility to establish general techniques for the assessment of deep geological environment. In this site, the groundwater seepage from the shafts and leachate from the waste rock storage site contain high concentrations of total nitrogen. Ammonium-nitrogen (NH -N), the major nitrogen species in the seepage and leachate, has been removed by a nearby treatment facility. However, NH
-N), the major nitrogen species in the seepage and leachate, has been removed by a nearby treatment facility. However, NH -N is easily oxidized to nitrite-nitrogen (NO
-N is easily oxidized to nitrite-nitrogen (NO -N) and nitrate-nitrogen (NO
-N) and nitrate-nitrogen (NO -N) by nitrification in the excavated rock storage site, which makes the removal process employed on site less effective. Therefore, column experiments that simulated the infiltration of rainwater through the storage site were carried out to understand the phenomena and the factors affecting the leaching behavior of nitrogen species and nitrification, and to propose countermeasures for preventing nitrification. The results showed that the nitrification was inhibited when the rock layer was almost saturated, and that this process was temperature dependent. These indicate that nitrification can be mitigated by controlling hydrological conditions like water saturation.
-N) by nitrification in the excavated rock storage site, which makes the removal process employed on site less effective. Therefore, column experiments that simulated the infiltration of rainwater through the storage site were carried out to understand the phenomena and the factors affecting the leaching behavior of nitrogen species and nitrification, and to propose countermeasures for preventing nitrification. The results showed that the nitrification was inhibited when the rock layer was almost saturated, and that this process was temperature dependent. These indicate that nitrification can be mitigated by controlling hydrological conditions like water saturation.
Sekiya, Yoshitomo; Kitagawa, Yoshito*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Hokora, Hideyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ueno, Akio*; Sato, Kiyoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sekiya, Yoshitomo; Kitagawa, Yoshito*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Hokora, Hideyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sekiya, Yoshitomo; Kitagawa, Yoshito*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Hokora, Hideyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tomiyama, Shingo*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Odashiro, Kana*; Yamaguchi, Kohei*; Fukushima, Shigeru; Ohara, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English