Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Re in the keV energy region
Re in the keV energy regionKatabuchi, Tatsuya*; Sato, Yaoki*; Takebe, Karin*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Umezawa, Seigo*; Fujioka, Ryo*; Saito, Tatsuhiro*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(2), p.224 - 229, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) -ray spectrum of
-ray spectrum of  Sr in the stellar nucleosynthesis energy region
Sr in the stellar nucleosynthesis energy regionKatabuchi, Tatsuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Kamada, So*; Tajika, Michihide*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kawano, Toshihiko*
Physical Review C, 108(3), p.034610_1 - 034610_12, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)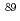 Y
YKatabuchi, Tatsuya*; Toh, Yosuke; Mizumoto, Motoharu*; Saito, Tatsuhiro*; Terada, Kazushi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Huang, M.*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Igashira, Masayuki*
European Physical Journal A, 57(1), p.4_1 - 4_4, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.33(Physics, Nuclear) -wave direct capture and interference effect observed in the
-wave direct capture and interference effect observed in the  O
O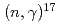 O reaction
O reactionNagai, Yasuki*; Kinoshita, Mitsutaka*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Nobuhara, Yuriko*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mishima, Kenji*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Mengoni, A.*
Physical Review C, 102(4), p.044616_1 - 044616_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.67(Physics, Nuclear) Am neutron capture and total cross sections with ANNRI at J-PARC
Am neutron capture and total cross sections with ANNRI at J-PARCKimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Terada, Kazushi*; Nakao, Taro*; Mizuyama, Kazuhito*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.479 - 492, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:79.66(Nuclear Science & Technology) Am with ANNRI at J-PARC
Am with ANNRI at J-PARCTerada, Kazushi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakao, Taro*; Nakamura, Shoji; Mizuyama, Kazuhito*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(10), p.1198 - 1211, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:83.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)Wu, P.*; Zhang, B.*; Peng, K. L.*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Kofu, Maiko; Lee, S. H.*; Kumigashira, Hiroshi*; Hu, C. S.*; Qi, Z. M.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(9), p.094305_1 - 094305_7, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and inelastic neutron scattering, we have studied how electronic structures and lattice dynamics evolve with temperature in Na-doped SnSe.
Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kimura, Atsushi; Terada, Kazushi; Nakao, Taro; Nakamura, Shoji; Mizuyama, Kazuhito; Igashira, Masayuki*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.11001_1 - 11001_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)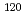 Sn,
Sn, 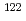 Sn and
Sn and 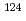 Sn with the array of Ge spectrometer at the J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI
Sn with the array of Ge spectrometer at the J-PARC/MLF/ANNRIKimura, Atsushi; Harada, Hideo; Nakamura, Shoji; Toh, Yosuke; Igashira, Masayuki*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Mizumoto, Motoharu*; Hori, Junichi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.11031_1 - 11031_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:58.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakao, Taro; Terada, Kazushi; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Hori, Junichi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.03021_1 - 03021_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:95.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new data acquisition system (DAQ system) in J-PARC Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) ANNRI was developed. Increasing beam power of MLF in recent years allows beam line users to obtain high quantity experimental data yields. Compared to 2008, more than 20 times beam current is achieved in 2015. For the purpose to correspond strong beam power of MLF, a new DAQ system for the array of the Ge detectors in ANNRI is developed. The DAQ system is also going to be used for processing signals from a Li glass detector, which is under development at ANNRI for measurement of total neutron cross sections. Commissioning experiment of a new DAQ system at ANNRI was performed by using 0.1mmt Au sample with 500kW J-PARC proton beam power. An applicability of time-of-flight method for both neutron capture and total cross-sections measurements was checked. ADC and TDC nonlinearity, energy resolution, multi-channel coincidence and dead time performance for the array of the Ge detectors were also evaluated. The dead time value for Ge detectors was successfully decreased to 1/4 from the previous DAQ system with minor deterioration on energy resolution. The author would like to thank the accelerator and technical staff at J-PARC for operation of the accelerator and the neutron production target and for the other experimental supports. Present study includes the result of "Research and Development for accuracy improvement of neutron nuclear data on minor actinides" entrusted to the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT).
 -ray emission probabilities
-ray emission probabilitiesTerada, Kazushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakao, Taro; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Hori, Junichi*
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.21 - 25, 2016/09
To obtain accurate cross section data, precise determination of the sample mass used in TOF measurements is essential, because uncertainties due to the sample mass are directly propagated to those of measured cross sections over the entire neutron energy region. Therefore,  -ray emission probabilities of
-ray emission probabilities of 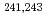 Am,
Am, 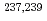 Np and
Np and  Pa have been precisely measured with gamma- and alpha-ray spectroscopic methods. The activities of the samples were determined by measuring alpha particles using a Si semiconductor detector.
Pa have been precisely measured with gamma- and alpha-ray spectroscopic methods. The activities of the samples were determined by measuring alpha particles using a Si semiconductor detector.  -rays emitted from the samples were measured with a planar type High-Purity Germanium (HPGe) detector. An efficiency curve of the Ge detector was derived by combining measured efficiencies and Monte Carlo simulation. The
-rays emitted from the samples were measured with a planar type High-Purity Germanium (HPGe) detector. An efficiency curve of the Ge detector was derived by combining measured efficiencies and Monte Carlo simulation. The  -ray emission probabilities for the major
-ray emission probabilities for the major  -rays of these nuclides were determined with uncertainties less than 2%.
-rays of these nuclides were determined with uncertainties less than 2%.
 Se(
Se( , n) cross section and uncertainty evaluation of the
, n) cross section and uncertainty evaluation of the  Se(n,
Se(n,  ) cross section
) cross sectionKitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Goko, Shinji*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Kawakatsu*; Igashira, Masayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(4), p.475 - 485, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)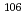 Pd
PdNakamura, Shoji; Kimura, Atsushi; Toh, Yosuke; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Mizumoto, Motoharu*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Hori, Junichi*; Kino, Koichi*
JAEA-Conf 2015-003, p.113 - 118, 2016/03
Experiments were carried out with the Ge detector of ANNRI to confirm whether or not the weak resonances were surely due to 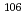 Pd. The prompt
Pd. The prompt  rays due to capture reaction of
rays due to capture reaction of 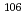 Pd were clearly observed at the
Pd were clearly observed at the  -ray energy at 115 kev and around 300 keV. When a TOF spectrum was extracted by gating at the prompt
-ray energy at 115 kev and around 300 keV. When a TOF spectrum was extracted by gating at the prompt  ray around 300 keV, the small resonance peaks were revealed at the neutron energy of 146 and 156 eV.
ray around 300 keV, the small resonance peaks were revealed at the neutron energy of 146 and 156 eV.
Nakao, Taro; Nakamura, Shoji; Terada, Kazushi; Kimura, Atsushi; Harada, Hideo; Igashira, Masayuki*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Hori, Junichi*
JAEA-Conf 2015-003, p.303 - 306, 2016/03
In spite of that the precise information of the total amount of the measurement sample is required for the neutron capture cross-section determination, it is not always performed in sufficient accuracy. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the absolute amount of samples accurately with non-destructively. This presentation will report on the future plan about the heat deposit measurement from minor actinides samples in order to determine the absolute amount of samples non-destructively, especially about the radiation shielding which is a unique problem of RI sample case. Also report about the result of the benchmark test measurement using  Am
Am  -ray standard source. Present study includes the result of "Research and Development for accuracy improvement of neutron nuclear data on minor actinides" entrusted to the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT).
-ray standard source. Present study includes the result of "Research and Development for accuracy improvement of neutron nuclear data on minor actinides" entrusted to the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT).
Kimura, Atsushi; Harada, Hideo; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Toh, Yosuke; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Igashira, Masayuki*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 51(12), p.180_1 - 180_8, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.63(Physics, Nuclear) ) cross-sections using multi-nucleon transfer reactions
) cross-sections using multi-nucleon transfer reactionsMakii, Hiroyuki; Ota, Shuya*; Ishii, Tetsuro; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Chiba, Satoshi; Igashira, Masayuki*; Czeszumska, A.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 797, p.83 - 93, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.26(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have installed new experimental apparatus to measure  rays from highly excited states populated by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions with heavy-ion projectiles to determine the (
rays from highly excited states populated by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions with heavy-ion projectiles to determine the ( ) cross sections by means of the surrogate reaction method. Apparatus consists of two anti-Compton LaBr
) cross sections by means of the surrogate reaction method. Apparatus consists of two anti-Compton LaBr (Ce) spectrometers to measure the
(Ce) spectrometers to measure the  rays and a Si
rays and a Si 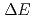 -
- detector system to detect outgoing projectile-like particles. Reactions of 153-MeV
detector system to detect outgoing projectile-like particles. Reactions of 153-MeV  O beams with
O beams with  Gd and
Gd and  Gd targets were used to study the performance of apparatus. By using the LaBr
Gd targets were used to study the performance of apparatus. By using the LaBr (Ce) scintillators with relatively large volume (101.6 mm in diameter and 127 mm in length), we have successfully measured
(Ce) scintillators with relatively large volume (101.6 mm in diameter and 127 mm in length), we have successfully measured  rays from the compound nuclei, which have excitation energy above neutron separation energy, populated by
rays from the compound nuclei, which have excitation energy above neutron separation energy, populated by  Gd(
Gd( O,
O,  O)
O) Gd and
Gd and  Gd(
Gd( O,
O,  O)
O)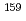 Gd two-neutron transfer reactions. The present study has demonstrated high capability of apparatus to measure the de-excitation
Gd two-neutron transfer reactions. The present study has demonstrated high capability of apparatus to measure the de-excitation  rays in the compound nuclei produced by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions for determination of the (
rays in the compound nuclei produced by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions for determination of the ( ) cross sections by using the surrogate reaction method.
) cross sections by using the surrogate reaction method.
 -ray spectra of
-ray spectra of 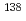 Ba in the keV-neutron energy region
Ba in the keV-neutron energy regionKatabuchi, Tatsuya*; Yanagida, Shotaro*; Terada, Kazushi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Igashira, Masayuki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 93, p.02008_1 - 02008_2, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)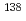 Ba has the smallest neutron capture cross section among the stable Ba isotopes. The neutron capture reaction of
Ba has the smallest neutron capture cross section among the stable Ba isotopes. The neutron capture reaction of 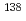 Ba is dominated by resolved resonances in the astrophysically relevant energy region. Thus, reliable experimental data of the capture cross section are necessary. In the present work, we measured the neutron capture cross section of
Ba is dominated by resolved resonances in the astrophysically relevant energy region. Thus, reliable experimental data of the capture cross section are necessary. In the present work, we measured the neutron capture cross section of 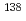 Ba in the energy region from 15 to 100 keV by the time-of-flight method at the Tokyo Institute of Technology. The capture cross sections were obtained from the pulse height spectra by the pulse-height weighting technique. A comparison of the present results with previous experimental data and evaluated data was made. We also derived
Ba in the energy region from 15 to 100 keV by the time-of-flight method at the Tokyo Institute of Technology. The capture cross sections were obtained from the pulse height spectra by the pulse-height weighting technique. A comparison of the present results with previous experimental data and evaluated data was made. We also derived  -ray spectra by unfolding the pulse height spectra. It was revealed that the shape of
-ray spectra by unfolding the pulse height spectra. It was revealed that the shape of  -ray spectra strongly depends on neutron energy.
-ray spectra strongly depends on neutron energy.
Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kimura, Atsushi; Terada, Kazushi; Nakao, Taro; Nakamura, Shoji; Mizuyama, Kazuhito; Igashira, Masayuki*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 93, p.06001_1 - 06001_5, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:83.57(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Improvement of accuracy of neutron nuclear data for minor actinides (MAs) and long-lived fission products (LLFPs) is required for developing innovative nuclear system transmuting these nuclei. In order to meet the requirement, the project entitled as "Research and development for Accuracy Improvement of neutron nuclear data on Minor ACtinides (AIMAC)" has been started as one of the "Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program" at October 2013. The AIMAC project team is composed of researchers in four different fields: differential nuclear data measurement, integral nuclear data measurement, nuclear chemistry, and nuclear data evaluation. By integrating all of the forefront knowledge and techniques in these fields, the team aims at improving the accuracy of the data. The background, overall plan, and recent progress of the AIMAC project will be reviewed.
 Nd and stellar neutron capture cross sections
Nd and stellar neutron capture cross sectionsKatabuchi, Tatsuya*; Matsuhashi, Taihei*; Terada, Kazushi; Igashira, Masayuki*; Mizumoto, Motoharu*; Hirose, Kentaro; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Hara, Kaoru*; Harada, Hideo; et al.
Physical Review C, 91(3), p.037603_1 - 037603_5, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:48.00(Physics, Nuclear) ) reactions with the ANNRI-Cluster Ge detectors at J-PARC
) reactions with the ANNRI-Cluster Ge detectors at J-PARCHara, Kaoru; Goko, Shinji*; Harada, Hideo; Hirose, Kentaro; Kimura, Atsushi; Kin, Tadahiro*; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Nakamura, Shoji; Toh, Yosuke; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2014-002, p.88 - 92, 2015/02