Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iimura, Hideki; Katakura, Junichi*; Oya, Susumu*
Nuclear Data Sheets, 180, p.1 - 413, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:77.17(Physics, Nuclear)In order to contribute to the international collaboration for revising Evaluated Nuclear Structure Data File (ENSDF), nuclear structure and decay data have been evaluated for 16 known A=126 nuclides (Rh, Pd, Ag, Cd, In, Sn, Sb, Te, I, Xe, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Pr, Nd). A=126 mass chain was last evaluated in 2002, which was published in Nuclear Data Sheets. The current work is an update of that evaluation. Experimental data from about 50 new publications since the previous evaluation have been incorporated. Even when no new publications appeared, some previous datasets have been modified for  -decay Q values and conversion coefficients. Adopted values for about 1300 levels and 2300 gammas have been presented from data of various decays and reactions. Inconsistencies and discrepancies have been noted.
-decay Q values and conversion coefficients. Adopted values for about 1300 levels and 2300 gammas have been presented from data of various decays and reactions. Inconsistencies and discrepancies have been noted.
Dimitriou, P.*; Basunia, S*; Bernstein, L.*; Chen, J.*; Elekes, Z.*; Huang, X.*; Hurst, A.*; Iimura, Hideki; Jain, A. K.*; Kelley, J.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.15004_1 - 15004_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Evaluated Nuclear Structure Data File (ENSDF) includes the most extensive and comprehensive set of nuclear structure and decay data evaluations performed by the international network of Nuclear Structure and Decay Data evaluators (NSDD) under the auspices of the IAEA. In this report we describe some of the recent NSDD activities and provide future perspectives.
Sonoda, Tetsu*; Katayama, Ichiro*; Wada, Michiharu*; Iimura, Hideki; Sonnenschein, V.*; Iimura, Shun*; Takamine, Aiko*; Rosenbusch, M.*; Kojima, Takao*; Ahn, D. S.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(11), p.113D02_1 - 113D02_12, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary)An in-flight separator, BigRIPS, at RIBF in RIKEN provides each experiment with specific nuclides separated from many nuclides produced by projectile fragmentation or in-flight fission. In this process, nuclides other than separated ones are discarded on the slits in BigRIPS, although they include many nuclides interested from the view point of nuclear structure. In order to extract these nuclides for parasitic experiments, we are developing a method using laser ion-source (PALIS). A test experiment with 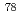 Se beam from RIBF has been performed by using a gas cell set in BigRIPS. Unstable nuclides around
Se beam from RIBF has been performed by using a gas cell set in BigRIPS. Unstable nuclides around  Se were stopped in the gas cell in accordance with a calculation using LISE code. The stopping efficiency has been estimated to be about 30%. As a next step, we will establish the technique for extracting reaction products from the gas cell.
Se were stopped in the gas cell in accordance with a calculation using LISE code. The stopping efficiency has been estimated to be about 30%. As a next step, we will establish the technique for extracting reaction products from the gas cell.
Koura, Hiroyuki; Minato, Futoshi; Iimura, Hideki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 60(1), p.35 - 40, 2018/01
, 60(1), p.35 - 40, 2018/01
no abstracts in English
Sonoda, Tetsu*; Iimura, Hideki; Reponen, M.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Katayama, Ichiro*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Takamatsu, Takahide*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kojima, Takao*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 877, p.118 - 123, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.30(Instruments & Instrumentation)In order to produce low-energy RI beams at RIKEN RIBF, a laser ion source, PALIS, is under construction. This ion source is based on resonance ionization of RI atoms captured in Ar gas. Because the ion source is located 70m away from lasers, we have developed an optical system for laser beam transport. This system can be controlled remotely when the ion source is not accessible because of high radiation level. The position of laser beam after transport is reasonably stable, and the transport efficiency is about 50%.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Jung, K.; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Khumaeni, A.*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 134, p.42 - 51, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:91.41(Spectroscopy)Spectroscopic properties of atomic species of plutonium were investigated by combining laser ablation and resonance absorption techniques for the analysis of a plutonium oxide sample. For 17 transitions of Pu atoms and ions, the absorbance, isotope shift, and hyperfine splitting were determined via Voigt profile fitting of the recorded absorption spectra. Three transitions were selected as candidates for analytical use. Using these transitions, we investigated the analytical performance that was attainable and determined a correlation coefficient R2 between the absorbance and plutonium concentration of 0.9999, a limit of detection of 30-130 ppm, and a relative standard deviation of approximately 6% for an abundance of  Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Iimura, Hideki
Isotope News, (746), p.39 - 42, 2016/08
Various nuclear data tables are available for radioisotopes users. In this article properties of these tables are compared. Also, it is explained how the recommended values in these tables are determined from f large amount of experimental data.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Khumaeni, A.*; Kato, Masaaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 110, p.101 - 117, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:81.38(Spectroscopy)The dynamic behavior of an ablation plume in ambient gas has been investigated by laser-induced fluorescence imaging spectroscopy. The second harmonic beam from an Nd:YAG laser (0.5-6J/cm ) was focused on a sintered oxide pellet or a metal chip of gadolinium. The produced plume was subsequently intersected with a sheet-shaped UV beam from a dye laser so that time-resolved fluorescence images were acquired with an intensified CCD camera at various delay times. The obtained cross-sectional images of the plume indicate that the ablated ground state atoms and ions of gadolinium accumulate in a hemispherical contact layer between the plume and the ambient gas, and a cavity containing a smaller density of ablated species is formed near the center of the plume. At earlier expansion stage, another luminous component also expands in the cavity so that it coalesces into the hemispherical layer. The splitting and coalescence for atomic plume occur later than those for ionic plume. Furthermore, the hemispherical layer of neutral atoms appears later than that of ions; however, the locations of the layers are nearly identical. This coincidence of the appearance locations of the layers strongly suggests that the neutral atoms in the hemispherical layer are produced as a consequence of three-body recombination of ions through collisions with gas atoms. The obtained knowledge regarding plume expansion dynamics and detailed plume structure is useful for optimizing the experimental conditions for ablation-based spectroscopic analysis.
) was focused on a sintered oxide pellet or a metal chip of gadolinium. The produced plume was subsequently intersected with a sheet-shaped UV beam from a dye laser so that time-resolved fluorescence images were acquired with an intensified CCD camera at various delay times. The obtained cross-sectional images of the plume indicate that the ablated ground state atoms and ions of gadolinium accumulate in a hemispherical contact layer between the plume and the ambient gas, and a cavity containing a smaller density of ablated species is formed near the center of the plume. At earlier expansion stage, another luminous component also expands in the cavity so that it coalesces into the hemispherical layer. The splitting and coalescence for atomic plume occur later than those for ionic plume. Furthermore, the hemispherical layer of neutral atoms appears later than that of ions; however, the locations of the layers are nearly identical. This coincidence of the appearance locations of the layers strongly suggests that the neutral atoms in the hemispherical layer are produced as a consequence of three-body recombination of ions through collisions with gas atoms. The obtained knowledge regarding plume expansion dynamics and detailed plume structure is useful for optimizing the experimental conditions for ablation-based spectroscopic analysis.
Iimura, Hideki; M ller, P.*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Sagawa, Hiroyuki*; Iwamoto, Akira*
ller, P.*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Sagawa, Hiroyuki*; Iwamoto, Akira*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030102_1 - 030102_4, 2015/06
no abstracts in English
Takamine, Jun; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kureta, Masatoshi; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Seya, Michio; Iimura, Hideki
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-35-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 10 Pages, 2015/01
A prototype device of neutron resonance densitometry (NRD) with a D-T neutron generator was planned for basic studies of actual NRD devices. D-T neutron generators had features of simple handling and compact compared with photo neutron sources driven by electron beam accelerators. But those of D-T neutron are higher energy and lower intensity than those of photo neutron. We designed a new type moderator to compensate for the shortcomings. In the new type moderator, the D-T neutron generator is surrounded by Lead, and Polyethylene is arranged in the beam direction on the surface of Lead. As the result of analysis using Monte Carlo code MCNP5, it was found that the new moderator achieved about four times larger production of low energy neutrons than polyethylene moderator without distorting the energy resolution below at least 100 eV. The lead part in the new moderator are changed to other heavy metals, which is Uranium, and Tungsten. Analysis like the above were performed. We report these results.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Kimura, Atsushi; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-35-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/01
We are developing neutron resonance densitometry that combines neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) and neutron resonance capture analysis. The aim is to establish a non-destructive technique that can quantify nuclear materials in particle-like debris of melted fuel resulting from severe nuclear accidents like the one at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Systematic effects due to sample thickness and mixed sample for the areal density measurement by NRTA were investigated at a neutron time-of-facility GELINA, IRMM. The experiments were conducted utilizing natural Cu metal discs with different thickness and a B C disc. Areal densities were derived with a resonance shape analysis code REFIT. It was found that they were inconsistent with those calculated by mass and area, when using recommended resonance parameters. Hence, a neutron width of resonance parameters was newly evaluated with the NRTA data and we found that derived areal density agreed within 2% with the expected ones. We also discuss the impacts of mixed sample for the areal density derived from NRTA measurement.
C disc. Areal densities were derived with a resonance shape analysis code REFIT. It was found that they were inconsistent with those calculated by mass and area, when using recommended resonance parameters. Hence, a neutron width of resonance parameters was newly evaluated with the NRTA data and we found that derived areal density agreed within 2% with the expected ones. We also discuss the impacts of mixed sample for the areal density derived from NRTA measurement.
 scintillation detector system for neutron resonance densitometry
scintillation detector system for neutron resonance densitometryKoizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Seya, Michio; Kimura, Atsushi; Iimura, Hideki; Becker, B.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-35-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/01
We have proposed neutron resonance densitometry (NRD) as a method to quantify special nuclear materials in particle-like debris of melted fuel. NRD is a combination of neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA), and neutron resonance capture analysis (NRCA) (and prompt  -ray analysis (PGA)). NRCA/PGA is used to identify contaminant elements, which is difficult to be detected by NRTA. To observe
-ray analysis (PGA)). NRCA/PGA is used to identify contaminant elements, which is difficult to be detected by NRTA. To observe  rays emitted in neutron capture reaction, a spectrometer consisting of LaBr
rays emitted in neutron capture reaction, a spectrometer consisting of LaBr scintillation detectors has been constructed. A newly installed data acquisition system enables us to measure 500 k event/s for each 8-channel inputs. In this presentation, the research and development of NRD is introduced and the status of the development of the spectrometer system is given as well.
scintillation detectors has been constructed. A newly installed data acquisition system enables us to measure 500 k event/s for each 8-channel inputs. In this presentation, the research and development of NRD is introduced and the status of the development of the spectrometer system is given as well.
Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Seya, Michio; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Nuclear Back-end and Transmutation Technology for Waste Disposal, p.13 - 20, 2015/00
Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) has been proposed for quantification of nuclear materials in melted fuel. NRD is a combined TOF technique of Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA) or Prompt Gamma ray Analysis (PGA). To establish the method, development of detectors is in progress. Experiments were carried out at a TOF facility, GELINA, under the collaboration with EC-JRC-IRMM. The progress of the project is reported.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Kimura, Atsushi; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 767, p.364 - 371, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.73(Instruments & Instrumentation)The impact of systematic effects on the areal density derived from a neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is investigated by measurements at the time-of-flight facility GELINA. The experiments were carried out at a 25 m station using metallic natural Cu discs with different thicknesses. To derive the areal density from a fit to the experimental transmission, the resonance shape analysis code REFIT was used. Large bias effects were observed using recommended resonance parameters. Therefore, neutron resonance parameters, in particular resonance energies and neutron widths, were derived from the transmission data obtained with a 0.25 mm thick Cu metallic sample. These parameters were used to study the impact of the resonance strength and sample thickness, on the accuracy of the areal density derived by NRTA.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Kimura, Atsushi; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2014/07
 scintillation detector system for neutron resonance densitometry (NRD)
scintillation detector system for neutron resonance densitometry (NRD)Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Seya, Michio; Kimura, Atsushi; Iimura, Hideki; Becker, B.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2014/07
Harada, Hideo; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Kimura, Atsushi; Seya, Michio; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2014/07
Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Iimura, Hideki; Seya, Michio; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 118, p.502 - 504, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.39(Physics, Nuclear) -ray detector for neutron resonance densitometry
-ray detector for neutron resonance densitometryTsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 729, p.338 - 345, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.09(Instruments & Instrumentation) -ray detector for neutron resonance densitometry
-ray detector for neutron resonance densitometryTsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki
JAEA-Conf 2013-002, p.119 - 124, 2013/10
We have proposed a system to quantify nuclear materials in melted fuels in the reactors of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The system utilizes non destructive techniques combining neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) and neutron resonance capture analysis (NRCA). This is because the melted fuels are though to involve not only nuclear materials but also impurities such as  Hydrogen, Boron, Zirconium, and Iron. Using the combined system, we would be able to identify those non-nuclear materials by NRCA and accurately measure nuclear materials by NRTA. A
Hydrogen, Boron, Zirconium, and Iron. Using the combined system, we would be able to identify those non-nuclear materials by NRCA and accurately measure nuclear materials by NRTA. A  -ray detector for NRCA consists of a cylindrical LaBr
-ray detector for NRCA consists of a cylindrical LaBr scintillation counter and a well-type LaBr
scintillation counter and a well-type LaBr one. The well-type counter is served as a back-catcher detector and individual signals recorded in the two counters are summed to aim at reducing the Compton edge originating from
one. The well-type counter is served as a back-catcher detector and individual signals recorded in the two counters are summed to aim at reducing the Compton edge originating from  Cs that generate intense background for the NRCA measurement. According to GEANT4 simulation, It can be seen that the Compton edge is suppressed by the well-type counter. For example, thanks to the well-type counter, a count at an energy of
Cs that generate intense background for the NRCA measurement. According to GEANT4 simulation, It can be seen that the Compton edge is suppressed by the well-type counter. For example, thanks to the well-type counter, a count at an energy of  B-derived
B-derived  -rays (478 keV) is reduced by
-rays (478 keV) is reduced by  0.15. In this presentation, we show performance of the
0.15. In this presentation, we show performance of the  -ray detector using GEANT4 simulation. In addition, comparing results based on evaluated cross sections of ENDF-VII.0 with those based on JENDL-4.0, we discuss differences in performance expected for the
-ray detector using GEANT4 simulation. In addition, comparing results based on evaluated cross sections of ENDF-VII.0 with those based on JENDL-4.0, we discuss differences in performance expected for the  -ray detector.
-ray detector.