Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 dynamics in the H
dynamics in the H conductors LaH
conductors LaH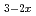 O
O
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Fukui, Keiga*; Iimura, Soshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Tada, Tomofumi*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Kuramoto, Yoshio*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Yamada, Takeshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 107(18), p.184114_1 - 184114_8, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) D
D measured with inelastic neutron spectroscopy
measured with inelastic neutron spectroscopyYamaura, Junichi*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Iimura, Soshi*; Muraba, Yoshinori*; Bang, J.*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Honda, Takashi*; Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(22), p.220505_1 - 220505_6, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.31(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Inelastic neutron scattering was performed for an iron-based superconductor, where most of D (deuterium) replaces oxygen, while a tiny amount goes into interstitial sites. By first-principle calculation, we characterize the interstitial sites for D (and for H slightly mixed) with four equivalent potential minima. Below the superconducting transition temperature Tc = 26 K, new excitations emerge in the range 5-15 meV, while they are absent in the reference system LaFeAsO F
F . The strong excitations at 14.5 meV and 11.1 meV broaden rapidly around 15 K and 20 K, respectively, where each energy becomes comparable to twice of the superconducting gap. The strong excitations are ascribed to a quantum rattling, or a band motion of hydrogen, which arises only if the number of potential minima is larger than two.
. The strong excitations at 14.5 meV and 11.1 meV broaden rapidly around 15 K and 20 K, respectively, where each energy becomes comparable to twice of the superconducting gap. The strong excitations are ascribed to a quantum rattling, or a band motion of hydrogen, which arises only if the number of potential minima is larger than two.
Takamine, Jun; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kureta, Masatoshi; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Seya, Michio; Iimura, Hideki
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-35-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 10 Pages, 2015/01
A prototype device of neutron resonance densitometry (NRD) with a D-T neutron generator was planned for basic studies of actual NRD devices. D-T neutron generators had features of simple handling and compact compared with photo neutron sources driven by electron beam accelerators. But those of D-T neutron are higher energy and lower intensity than those of photo neutron. We designed a new type moderator to compensate for the shortcomings. In the new type moderator, the D-T neutron generator is surrounded by Lead, and Polyethylene is arranged in the beam direction on the surface of Lead. As the result of analysis using Monte Carlo code MCNP5, it was found that the new moderator achieved about four times larger production of low energy neutrons than polyethylene moderator without distorting the energy resolution below at least 100 eV. The lead part in the new moderator are changed to other heavy metals, which is Uranium, and Tungsten. Analysis like the above were performed. We report these results.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Kimura, Atsushi; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-35-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/01
We are developing neutron resonance densitometry that combines neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) and neutron resonance capture analysis. The aim is to establish a non-destructive technique that can quantify nuclear materials in particle-like debris of melted fuel resulting from severe nuclear accidents like the one at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Systematic effects due to sample thickness and mixed sample for the areal density measurement by NRTA were investigated at a neutron time-of-facility GELINA, IRMM. The experiments were conducted utilizing natural Cu metal discs with different thickness and a B C disc. Areal densities were derived with a resonance shape analysis code REFIT. It was found that they were inconsistent with those calculated by mass and area, when using recommended resonance parameters. Hence, a neutron width of resonance parameters was newly evaluated with the NRTA data and we found that derived areal density agreed within 2% with the expected ones. We also discuss the impacts of mixed sample for the areal density derived from NRTA measurement.
C disc. Areal densities were derived with a resonance shape analysis code REFIT. It was found that they were inconsistent with those calculated by mass and area, when using recommended resonance parameters. Hence, a neutron width of resonance parameters was newly evaluated with the NRTA data and we found that derived areal density agreed within 2% with the expected ones. We also discuss the impacts of mixed sample for the areal density derived from NRTA measurement.
 scintillation detector system for neutron resonance densitometry
scintillation detector system for neutron resonance densitometryKoizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Seya, Michio; Kimura, Atsushi; Iimura, Hideki; Becker, B.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-35-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/01
We have proposed neutron resonance densitometry (NRD) as a method to quantify special nuclear materials in particle-like debris of melted fuel. NRD is a combination of neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA), and neutron resonance capture analysis (NRCA) (and prompt  -ray analysis (PGA)). NRCA/PGA is used to identify contaminant elements, which is difficult to be detected by NRTA. To observe
-ray analysis (PGA)). NRCA/PGA is used to identify contaminant elements, which is difficult to be detected by NRTA. To observe  rays emitted in neutron capture reaction, a spectrometer consisting of LaBr
rays emitted in neutron capture reaction, a spectrometer consisting of LaBr scintillation detectors has been constructed. A newly installed data acquisition system enables us to measure 500 k event/s for each 8-channel inputs. In this presentation, the research and development of NRD is introduced and the status of the development of the spectrometer system is given as well.
scintillation detectors has been constructed. A newly installed data acquisition system enables us to measure 500 k event/s for each 8-channel inputs. In this presentation, the research and development of NRD is introduced and the status of the development of the spectrometer system is given as well.
Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Seya, Michio; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Nuclear Back-end and Transmutation Technology for Waste Disposal, p.13 - 20, 2015/00
Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) has been proposed for quantification of nuclear materials in melted fuel. NRD is a combined TOF technique of Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA) or Prompt Gamma ray Analysis (PGA). To establish the method, development of detectors is in progress. Experiments were carried out at a TOF facility, GELINA, under the collaboration with EC-JRC-IRMM. The progress of the project is reported.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Kimura, Atsushi; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 767, p.364 - 371, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.98(Instruments & Instrumentation)The impact of systematic effects on the areal density derived from a neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is investigated by measurements at the time-of-flight facility GELINA. The experiments were carried out at a 25 m station using metallic natural Cu discs with different thicknesses. To derive the areal density from a fit to the experimental transmission, the resonance shape analysis code REFIT was used. Large bias effects were observed using recommended resonance parameters. Therefore, neutron resonance parameters, in particular resonance energies and neutron widths, were derived from the transmission data obtained with a 0.25 mm thick Cu metallic sample. These parameters were used to study the impact of the resonance strength and sample thickness, on the accuracy of the areal density derived by NRTA.
Oguri, Hidetomo; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Ao, Hiroyuki; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Kondo, Yasuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.389 - 393, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Kimura, Atsushi; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2014/07
 scintillation detector system for neutron resonance densitometry (NRD)
scintillation detector system for neutron resonance densitometry (NRD)Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Seya, Michio; Kimura, Atsushi; Iimura, Hideki; Becker, B.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2014/07
Harada, Hideo; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Kimura, Atsushi; Seya, Michio; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2014/07
Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Iimura, Soshi*; Kojima, Kenji*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Miao, P.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Miyazaki, Masanori*; et al.
Nature Physics, 10(4), p.300 - 303, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:103 Percentile:95.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Iimura, Hideki; Seya, Michio; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 118, p.502 - 504, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.98(Physics, Nuclear) -ray detector for neutron resonance densitometry
-ray detector for neutron resonance densitometryTsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 729, p.338 - 345, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.63(Instruments & Instrumentation) -ray detector for neutron resonance densitometry
-ray detector for neutron resonance densitometryTsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki
JAEA-Conf 2013-002, p.119 - 124, 2013/10
We have proposed a system to quantify nuclear materials in melted fuels in the reactors of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The system utilizes non destructive techniques combining neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) and neutron resonance capture analysis (NRCA). This is because the melted fuels are though to involve not only nuclear materials but also impurities such as  Hydrogen, Boron, Zirconium, and Iron. Using the combined system, we would be able to identify those non-nuclear materials by NRCA and accurately measure nuclear materials by NRTA. A
Hydrogen, Boron, Zirconium, and Iron. Using the combined system, we would be able to identify those non-nuclear materials by NRCA and accurately measure nuclear materials by NRTA. A  -ray detector for NRCA consists of a cylindrical LaBr
-ray detector for NRCA consists of a cylindrical LaBr scintillation counter and a well-type LaBr
scintillation counter and a well-type LaBr one. The well-type counter is served as a back-catcher detector and individual signals recorded in the two counters are summed to aim at reducing the Compton edge originating from
one. The well-type counter is served as a back-catcher detector and individual signals recorded in the two counters are summed to aim at reducing the Compton edge originating from  Cs that generate intense background for the NRCA measurement. According to GEANT4 simulation, It can be seen that the Compton edge is suppressed by the well-type counter. For example, thanks to the well-type counter, a count at an energy of
Cs that generate intense background for the NRCA measurement. According to GEANT4 simulation, It can be seen that the Compton edge is suppressed by the well-type counter. For example, thanks to the well-type counter, a count at an energy of  B-derived
B-derived  -rays (478 keV) is reduced by
-rays (478 keV) is reduced by  0.15. In this presentation, we show performance of the
0.15. In this presentation, we show performance of the  -ray detector using GEANT4 simulation. In addition, comparing results based on evaluated cross sections of ENDF-VII.0 with those based on JENDL-4.0, we discuss differences in performance expected for the
-ray detector using GEANT4 simulation. In addition, comparing results based on evaluated cross sections of ENDF-VII.0 with those based on JENDL-4.0, we discuss differences in performance expected for the  -ray detector.
-ray detector.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; Kauwenberghs, K.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 8 Pages, 2013/10
We have no established methods to quantify the amount of nuclear materials in particle-like debris of melted fuel derived from a nuclear accident such as the one occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. For this reason, neutron resonance densitometry, combining neutron resonance transmission analysis and neutron resonance capture analysis, is under development. It is expected that such debris have a wide variety of size, shape, and concentration of impurities. Experiments with the Neutron Resonance Transmisson Analysis (NRTA) using three Cu metal disks with different thickness of 0.125 mm, 0.25 mm, and 0.7 mm were made between November 2012 and February 2013 at the Geel Electron LINear Accelerator (GELINA) to investigate sample thickness effect on the transmission analysis. We experimentally derived the areal density for the individual Cu samples with the resonance shape analysis code REFIT, and then compared them with the declared areal density. It was found that the REFIT-evaluated areal density was consistent with declared ones for each sample.
Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Seya, Michio; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 6 Pages, 2013/10
Neutron resonance densitometry (NRD) has been proposed to quantify nuclear materials in particle-like debris of melted fuel formed in severe accidents of nuclear reactors such as Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants. NRD is a method combining NRTA (neutron resonance transmission analysis) and NRCA (neutron resonance capture analysis). It relies on neutron TOF (time of flight) technique using a pulsed white neutron source. The use of a special  -ray spectrometer for NRCA and an evaluation of the achievable accuracy are discussed. The discussion is based on results of Monte Carlo simulations combined experimental data from measurements carried out at GELINA. In this contribution, progress made in the development of NRD for the characterization of nuclear materials mixed with highly radioactive nuclides is presented, together with the basic concept and principles.
-ray spectrometer for NRCA and an evaluation of the achievable accuracy are discussed. The discussion is based on results of Monte Carlo simulations combined experimental data from measurements carried out at GELINA. In this contribution, progress made in the development of NRD for the characterization of nuclear materials mixed with highly radioactive nuclides is presented, together with the basic concept and principles.
Seya, Michio; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Iimura, Hideki; Kureta, Masatoshi; Takamine, Jun; Hajima, Ryoichi; Hayakawa, Takehito; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 10 Pages, 2013/10
The forming of MF in severe accidents of nuclear reactors such as Units 1 - 3 of Fukushima-Daiichi NPP (Nuclear Power Plant) inevitably change the category of the nuclear reactor from "item facility" to "bulk-handling facility". At removal of the MF it is necessary to break chunks of MF into relatively small blocks by using some tools, resulting in debris that consists of cut or small rock-like debris and particle (or grain)-like debris in bulk form. This paper presents a categorization of debris of MF and two possible non-destructive assay (NDA) technologies for precise measurement which could be applied to the NM accountancy of MF debris. One of them is Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) for particle-like (or grain-like) debris, and another is NRF (Nuclear Resonance Fluorescence) NDA using LCS (Laser Compton Scattered)  -rays (mono-energetic
-rays (mono-energetic  -rays) for cut or small rock-like debris. The paper also describes about the recent development of these two technologies.
-rays) for cut or small rock-like debris. The paper also describes about the recent development of these two technologies.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; Kauwenberghs, K.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 54th Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2013/07
Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Seya, Michio; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 54th Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2013/07
In this contribution, progress made in the development of NRD for the characterization of nuclear materials mixed with highly radioactive nuclides is presented, together with the basic concept and principles. The use of a special  -ray spectrometer for NRCA and an evaluation of the achievable accuracy are discussed. The discussion is based on results of Monte Carlo simulations combined experimental data from measurements carried out at GELINA. In addition, a prototype compact NRD system, which will be installed at the JAEA Tokai-site, has been designed and is presented. Other results, such as the impact of the particle size and nuclear data, are presented in other contributions to this symposium.
-ray spectrometer for NRCA and an evaluation of the achievable accuracy are discussed. The discussion is based on results of Monte Carlo simulations combined experimental data from measurements carried out at GELINA. In addition, a prototype compact NRD system, which will be installed at the JAEA Tokai-site, has been designed and is presented. Other results, such as the impact of the particle size and nuclear data, are presented in other contributions to this symposium.