Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Balois-Oguchi, M. V.*; Hayazawa, Norihiko*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Ikeda, Katsuyoshi*; Nguyen, T. Q.*; Esca o, M. C.*; Tanaka, Takuo*
o, M. C.*; Tanaka, Takuo*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(12), p.5982 - 5990, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:62.48(Chemistry, Physical)Micrometer-sized wrinkles in graphene are known to affect the electronic properties of graphene due to their shape and the strain variations they create. Here, we analyze the strain distribution and doping of a graphene wrinkle having 1.9 nm width using tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) in ambient conditions. We found a strong correlation between the TERS images of the graphene wrinkle and the electronic Raman scattering (eRS) of the Au(111) substrate. Our work demonstrates that the as-fabricated physical and electronic properties of nanometer-sized features, such as wrinkles, can be probed and studied in detail with TERS which is essential for nanodevice characterization.
 Be(p,xn) reaction for new nuclear data library JENDL-5
Be(p,xn) reaction for new nuclear data library JENDL-5Kunieda, Satoshi; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Konno, Chikara; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Ikeda, Yujiro*
Journal of Neutron Research, 24(3-4), p.329 - 335, 2023/01
We have evaluated double-differential cross-sections (DDX) of the  Be(p,xn) reaction based on the function proposed by Wakabayashi et al. up to 12 MeV. Through compilation in the ENDF-6 format file, data processing, and neutronics analysis with MC simulation codes MCNP and PHITS to thick target yield (TTY) measurements, the function was re-confirmed to give more reasonable DDX data than those in our previous library JENDL-4.0/HE and ENDF/B-VIII.0. We finally decided to reduce the absolute cross-sections by 15% for our new nuclear data library JENDL-5 since the prediction ability of neutronics simulation was much better than that based on the original function. Through comprehensive comparisons of the simulation results on TTY at different proton energies and neutron emission angles, we conclude that JENDL-5 gives the best estimation in the world.
Be(p,xn) reaction based on the function proposed by Wakabayashi et al. up to 12 MeV. Through compilation in the ENDF-6 format file, data processing, and neutronics analysis with MC simulation codes MCNP and PHITS to thick target yield (TTY) measurements, the function was re-confirmed to give more reasonable DDX data than those in our previous library JENDL-4.0/HE and ENDF/B-VIII.0. We finally decided to reduce the absolute cross-sections by 15% for our new nuclear data library JENDL-5 since the prediction ability of neutronics simulation was much better than that based on the original function. Through comprehensive comparisons of the simulation results on TTY at different proton energies and neutron emission angles, we conclude that JENDL-5 gives the best estimation in the world.
Teshigawara, Makoto; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Yan, M.*; Muramatsu, Kazuo*; Sutani, Koichi*; Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Saruta, Koichi; Otake, Yoshie*
Nanomaterials (Internet), 13(1), p.76_1 - 76_9, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:66.71(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)To enhance neutron intensity below cold neutrons, it is proposed that nanosized graphene aggregation could facilitate neutron coherent scattering under particle size conditions similar to nanodiamond. It might also be possible to use it in high neutron radiation conditions due to graphene's strong sp2 bonds. Using the RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron source and iMATERIA at J-PARC, we performed neutron measurement experiments, total neutron cross-section, and small-angle neutron scattering on nanosized graphene aggregation. The measured data revealed, for the first time, that nanosized graphene aggregation increased the total cross-sections and small-angle scattering in the cold neutron energy region, most likely due to coherent scattering, resulting in higher neutron intensities, similar to nanodiamond.
 O
O with electrochemical Li
with electrochemical Li intercalation
intercalationMurase, Satoshi*; Yoshikawa, Yumi*; Fujiwara, Kosuke*; Fukada, Yukimasa*; Teranishi, Takashi*; Kano, Jun*; Fujii, Tatsuo*; Inada, Yasuhiro*; Katayama, Misaki*; Yoshii, Kenji; et al.
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 162, p.110468_1 - 110468_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We report a trial of the valence control for mixed valence iron triangular oxide YbFe O
O in order to develop an effective technique to control the frustration of charges in strongly correlated electron systems. The electro-chemical doping of Li
in order to develop an effective technique to control the frustration of charges in strongly correlated electron systems. The electro-chemical doping of Li into YbFe
into YbFe O
O was examined on the cell type sample similar to the Li-ion secondary battery cell. Systematic change of the lattice constant, Fe-Fe and Fe-Yb distance were observed with Li doping. Maximum value of the doping was over 300 mAh/g. An EXAFS experiment indicated that Li positioned between Yb octahedron layer (U-layer) and Fe-bipyramidal layer (W-layer). However, detailed change of iron valence state of YbFe
was examined on the cell type sample similar to the Li-ion secondary battery cell. Systematic change of the lattice constant, Fe-Fe and Fe-Yb distance were observed with Li doping. Maximum value of the doping was over 300 mAh/g. An EXAFS experiment indicated that Li positioned between Yb octahedron layer (U-layer) and Fe-bipyramidal layer (W-layer). However, detailed change of iron valence state of YbFe O
O was not clearly observed because of the superimpose of the signal from iron metal nano particles in XANES observation. The results indicate that the electrochemical method might be one of the potential technique to control the frustration of charges in YbFe
was not clearly observed because of the superimpose of the signal from iron metal nano particles in XANES observation. The results indicate that the electrochemical method might be one of the potential technique to control the frustration of charges in YbFe O
O .
.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:96.99(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 Se
Se epitaxial thin films
epitaxial thin filmsNakano, Masaki*; Wang, Y.*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; Matsuoka, Hideki*; Majima, Yuki*; Ikeda, Keisuke*; Hirata, Yasuyuki*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Wadachi, Hiroki*; Kohama, Yoshimitsu*; et al.
Nano Letters, 19(12), p.8806 - 8810, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:92.26(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kawamura, Shunsuke; Naoe, Takashi; Ikeda, Tsubasa*; Tanaka, Nobuatsu*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Advanced Experimental Mechanics, 4, p.33 - 37, 2019/08
A mercury enclosure vessel made of stainless steel is used as a spallation target in the pulsed spallation neutron source at J-PARC. It is severely damaged by the cavitation induced with pressure waves in association with the pulsed proton beam injection. A double-walled structure with a narrow mercury channel was adopted in the front end of the target vessel to reduce the cavitation damage. It has been experimentally demonstrated that the cavitation damage could be mitigated in the narrow channel but its mechanism has been unclarified yet. In this study, we investigated the cavitation from growing to collapsing through visualizing the spark-induced cavitation bubbles under flow field using a high-speed video camera. Furthermore, we measured the wall vibration due to the cavitation bubble collapse with changing flow velocity parametrically. It was found that the microjet collided perpendicular to the wall in the stagnant flow condition while it collided with an inclined angle from the perpendicular direction, suggesting that the collision pressure on the wall was reduced by flowing.
Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Iimura, Soshi*; Kojima, Kenji*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Miao, P.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Miyazaki, Masanori*; et al.
Nature Physics, 10(4), p.300 - 303, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:103 Percentile:95.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kuboyama, Satoshi*; Mizuta, Eiichi*; Ikeda, Naomi*; Abe, Hiroshi; Oshima, Takeshi; Tamura, Takashi*
Proceedings of 10th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-10) (Internet), p.138 - 141, 2012/12
no abstracts in English
Wada, Ken*; Hyodo, Toshio*; Yagishita, Akira*; Ikeda, Mitsuo*; Osawa, Satoshi*; Shidara, Tetsuo*; Michishio, Koji*; Tachibana, Takayuki*; Nagashima, Yasuyuki*; Fukaya, Yuki; et al.
European Physical Journal D, 66(2), p.37 - 40, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:85.09(Optics)no abstracts in English
Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Harada, Erika*; Yamasaki, Shigeto*; Ikeda, Kenichi*; Hata, Satoshi*; Nakashima, Hideharu*; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji
Kashika Joho Gakkai-Shi, 31(122), p.98 - 103, 2011/07
no abstracts in English
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.86(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
Machida, Akihiko; Watanuki, Tetsu; Omura, Ayako*; Ikeda, Tomohiro*; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Nakano, Satoshi*; Takemura, Kenichi*
Solid State Communications, 151(5), p.341 - 345, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:41.83(Physics, Condensed Matter)The compressibility of lanthanum (La) metal and its hydrides were measured at room temperature by high pressure synchrotron X-ray diffraction. La metal pressurized in a hydrogen medium forms a hydride with an fcc metal lattice, which likely contains hydrogen at a concentration close to 3.0. Equations of state have been determined by helium compression experiments for LaH with tetrahedral interstitial sites fully occupied with hydrogen atoms and for LaH
with tetrahedral interstitial sites fully occupied with hydrogen atoms and for LaH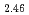 with octahedral interstitial sites partially occupied with hydrogen atoms and tetrahedral sites fully occupied. Both hydrides possess fcc metal lattices. These values are three times larger than that of La metal and are very close to each other despite the difference in hydrogen occupation states. The hardening of the metal lattice by hydrogenation is attributed predominantly to hydrogen-metal interactions at the tetrahedral sites and is most pronounced for La, which has the largest ionic radius among rare-earth metals.
with octahedral interstitial sites partially occupied with hydrogen atoms and tetrahedral sites fully occupied. Both hydrides possess fcc metal lattices. These values are three times larger than that of La metal and are very close to each other despite the difference in hydrogen occupation states. The hardening of the metal lattice by hydrogenation is attributed predominantly to hydrogen-metal interactions at the tetrahedral sites and is most pronounced for La, which has the largest ionic radius among rare-earth metals.
Kuboyama, Satoshi*; Maru, Akifumi*; Ikeda, Naomi*; Hirao, Toshio; Tamura, Takashi*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 57(6), p.3257 - 3261, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:72.11(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Naomi*; Kuboyama, Satoshi*; Maru, Akifumi*; Hirao, Toshio; Abe, Hiroshi; Tamura, Takashi*
Proceedings of 9th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-9), p.163 - 166, 2010/10
The trench structure showed an anomalously large degradation by heavy ion irradiation. For the trench structure, ions irradiated normal to the chip surface traverse the gate oxide along the entire length of the channel. Therefore, there is a possibility that the trapped holes resulting from the ion traverse introduce the anomalously large leakage current path. This phenomenon is apparently attributable to the microdose effect. In the previous report, the microdose effect was identified on both trench and planner type of power MOSFETs by real-time measurement of the threshold voltage shift during the heavy ion irradiation with very long range. In this study, detailed characterization of the microdose effects was carried out with several in species. As a result, several damage parameters introduced in the gate oxide by a single ion, such as physical damage size and trapped hole density in the damage region were estimated.
Maekawa, Fujio; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Teshigawara, Makoto; Kai, Tetsuya; Meigo, Shinichiro; Oi, Motoki; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Takada, Hiroshi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 620(2-3), p.159 - 165, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:74 Percentile:97.61(Instruments & Instrumentation)The J-PARC 1-MW pulsed spallation neutron source JSNS was successfully launched on 30th of May 2008. To demonstrate the unique features of the moderator design and the neutronic performance of JSNS the neutron spectral intensity, absolute neutron flux, and time structure of the neutron pulse shapes etc have been measured using several neutron instruments since then. The measured energy spectra clearly revealed the feature of the para-hydrogen, as expected when designing the moderator. The measured neutron flux below 0.4 eV agreed with the corresponding design value within  20%, thus suggesting that the JSNS design calculations to have been reliable. World-class high-resolution diffraction data could be recorded due to the suitability of design of the moderators and the instruments. Another world-class high-intensity neutron flux was also capable of being demonstrated due to the unique design of the large cylindrical coupled moderator.
20%, thus suggesting that the JSNS design calculations to have been reliable. World-class high-resolution diffraction data could be recorded due to the suitability of design of the moderators and the instruments. Another world-class high-intensity neutron flux was also capable of being demonstrated due to the unique design of the large cylindrical coupled moderator.
Harada, Masahide; Meigo, Shinichiro; Ito, Manabu; Dantsuji, Eiji; Takagiwa, Katsunori; Takada, Hiroshi; Maekawa, Fujio; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.87 - 90, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)In MLF of J-PARC, since weights of a building and shields are considerably heavy as 130,000 tons and 80,000 tons, respectively, large settlement of the MLF building is expected. The 3NBT line with 300 m in length is similar. To achieve a precise alignment under the large settlement, we conducted periodical survey measurements at the MLF building and 3NBT. At the completion of construction of the MLF building in December 2005, the settlement was about 40 mm. By extrapolating this result with weights to be added in the future for neutron beam line shields, we predicted that the MLF building settled in about 68mm at the completion of all neutron instrument construction. We decided that the muon target should be installed 5 mm higher than the neutron target with expecting future uneven settlement of the MLF building. The validation in the end of 2007 indicated that the measured level difference came up to the expected value.
Oikawa, Kenichi; Takada, Hiroshi; Maekawa, Fujio; Harada, Masahide; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Ikeda, Yujiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600, p.84 - 86, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron beam shutter system of JSNS at J-PARC has been designed under a particular precondition that every shutter should be controlled and maintained independently. This is very important from viewpoints of usability and interlock system of JSNS. The biggest challenge we faced was that to meet a single shutter design on asymmetric and narrow angular intervals of JSNS beam-lines; 6.7 in minimum and 12.7
in minimum and 12.7 in maximum. To realize this precondition, a compact ball screw jack system sustaining a shutter gate with two shafts was designed. Rotating motion during open/close stroke is absorbed by a couple of oilless bearings (OILES corp.) fitted in every shaft guide. The assembly is driven by an electric servomotor.
in maximum. To realize this precondition, a compact ball screw jack system sustaining a shutter gate with two shafts was designed. Rotating motion during open/close stroke is absorbed by a couple of oilless bearings (OILES corp.) fitted in every shaft guide. The assembly is driven by an electric servomotor.
Oyama, Yukio; Ikeda, Yujiro; Arai, Masatoshi; Morii, Yukio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 51(1), p.14 - 19, 2009/01
, 51(1), p.14 - 19, 2009/01
The beam commissioning of the J-PARC facilities of which the construction was started in 2001 is now progressed toward completion at the end of JFY2008. Of the J-PARC facilities, especially the pulsed neutron source with the world highest performance is able to open a new era of neutron application research. In this article, the outline of J-PARC, the pulsed neutron source which will start the user operation on December 2008, and their neutron instruments which is under construction are introduced. The neutron research is one of the important applications of quantum beam technology and expected to expand to broad research area such as bio-science, materials science, industrial use, etc. by start of J-PARC utilization. The latest achievement of neutron research mostly conducted at the JRR-3 research reactor in operation and future prospect are overviewed.
Futakawa, Masatoshi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Naoe, Takashi; Ida, Masato; Haga, Katsuhiro; Wakui, Takashi; Tanaka, Nobuatsu*; Matsumoto, Yoichiro*; Ikeda, Yujiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(10), p.1041 - 1048, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:87.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)The life time of mercury target will be reduced by the cavitation damage induced by pressure waves. Micro-bubble injection into mercury is one of prospective technologies to mitigate the pressure waves. We have carried out damage tests using mercury loop with an impact generator to evaluate the bubbling effect on the pressure response and cavitation damage. The impulsive pressure was hardly changed but the damage was reduced remarkably by the micro-bubble injection. Numerical simulation was performed to investigate the bubbling effects. It was understandable that micro bubbles suppressed cavitation inception.