Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sumita, Takehiro*; Osawa, Takahito; Chiu, I.-H.; Ikeda, Atsushi
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1329, p.343256_1 - 343256_10, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:34.56(Chemistry, Analytical)Kobayashi, Taishi*; Sato, Yutaro*; Tonna, Ryutaro*; Matsumura, Daiju; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Ikeda, Atsushi
Dalton Transactions (Internet), 53(46), p.18616 - 18628, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Aoyagi, Noboru; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Okumura, Masahiko; Ueda, Yuki; Saito, Takumi*; Nishitsuji, Shotaro*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yomogida, Takumi; Sazaki, Gen*; Ikeda, Atsushi
Communications Chemistry (Internet), 7, p.128_1 - 128_13, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Ikeda, Atsushi
Bunseki Kagaku, 73(4.5), p.147 - 159, 2024/04
Factor analysis (FA), one of the multivariate analysis methods that are frequently employed in chemometrics, is a powerful tool to extract physical/chemical information of pure components from the analytical data of the mixture of the components. Although FA has been applied mainly to the quantitative analysis in the field of analytical chemistry, its application to the qualitative analysis has been limited. This article aims at introducing FA to the qualitative analysis for determining the speciation/structure of individual chemical species/compounds by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). The fundamental concept to extract physically/chemically meaningful information from XAS-FA is described, and some reported studies using XAS-FA for the qualitative determination of chemical species/compounds are summarized.
Porcheron, E.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Berlemont, R.*; Bouland, A.*; Lallot, Y.*; Tsubota, Yoichi; Ikeda, Atsushi; Mitsugi, Takeshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/10
Results of the URASOL project aimed at evaluating the generation and dispersion of radioactive aerosols during the cutting of fuel debris, a key issue in the decommissioning of the damaged reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), are presented in this report. Characterization of aerosols generated during heating and mechanical cutting of simulated fuel debris in terms of mass concentration, real-time number density, mass-based particle size distribution, morphology, and chemical properties is reported. In the heating tests, an increase in particle size with increasing temperature was observed, and in terms of particle number density, the case using depleted uranium simulated fuel debris had a smaller number density than the test using Hf-containing simulated fuel debris. In mechanical cleavage, the aerodynamic median mass diameter of the aerosol was almost the same for the radioactive and non-radioactive samples (about 3.7 4.4
4.4  m).
m).
 Sn
Sn S
S -based shandite films
-based shandite filmsLau, Y.-C.*; Ikeda, Junya*; Fujiwara, Kohei*; Ozawa, Akihiro*; Zheng, J.*; Seki, Takeshi*; Nomura, Kentaro*; Du, L.*; Wu, Q.*; Tsukazaki, Atsushi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(6), p.064429_1 - 064429_11, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:72.60(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Gu var, C.*; Testud, V.*; Brackx, E.*; Porcheron, E.*; Bouland, A.*; Berlemont, R.*; Ikeda, Atsushi
var, C.*; Testud, V.*; Brackx, E.*; Porcheron, E.*; Bouland, A.*; Berlemont, R.*; Ikeda, Atsushi
Science Talks (Internet), 6, p.100215_1 - 100215_9, 2023/05
Kitagaki, Toru; Krasnov, V.*; Ikeda, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 576, p.154224_1 - 154224_14, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:60.68(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Fe
Fe O
O grown on Al
grown on Al O
O ; Effects of postdeposition annealing studied by XMCD
; Effects of postdeposition annealing studied by XMCDNonaka, Yosuke*; Wakabayashi, Yuki*; Shibata, Goro; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Ikeda, Keisuke*; Chi, Z.*; Wan, Y.*; Suzuki, Masahiro*; Tanaka, Arata*; Tanaka, Masaaki*; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(4), p.044413_1 - 044413_10, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:47.86(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hirata, Sakiko*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Meiji, Shogo*; Tamekuni, Seita*; Okudera, Kosuke*; Hamada, Shoken*; Sakamoto, Chihiro*; Honda, Takumi*; Matsushita, Kosuke*; Muramatsu, Satoru*; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(1), p.474 - 486, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.89(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear) TaS
TaS with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy; Comparison with Fe
with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy; Comparison with Fe TiS
TiS
Shibata, Goro; Won, C.*; Kim, J.*; Nonaka, Yosuke*; Ikeda, Keisuke*; Wan, Y.*; Suzuki, Masahiro*; Koide, Tsuneharu*; Tanaka, Arata*; Cheong, S.-W.*; et al.
Photon Factory Activity Report 2022 (Internet), 2 Pages, 2023/00
no abstracts in English
 Sn
Sn S
S submicrometer-wide wire devices
submicrometer-wide wire devicesShiogai, Junichi*; Ikeda, Junya*; Fujiwara, Kohei*; Seki, Takeshi*; Takanashi, Koki; Tsukazaki, Atsushi*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(11), p.114203_1 - 114203_9, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sumita, Takehiro; Ikeda, Atsushi
Isotope News, (783), p.28 - 32, 2022/10
no abstracts in English
Porcheron, E.*; Leblois, Y.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Molina, D.*; Suteau, C.*; Berlemont, R.*; Bouland, A.*; Lallot, Y.*; Roulet, D.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/10
One of the important challenges for the decommissioning of the damaged reactors of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) is the fuel debris retrieval. The URASOL project, which is undertaken by a French consortium consisting of ONET Technologies, CEA, and IRSN for JAEA/CLADS, is dedicated to acquiring basic scientific data on the generation and characteristics of radioactive aerosols from the thermal or mechanical processing of fuel debris simulant. Heating process undertaken in the VITAE facility simulates some representative conditions of thermal cutting by LASER. For mechanical cutting, the core boring technique is implemented in the FUJISAN facility. Fuel debris simulants have been developed for inactive and active trials. The aerosols are characterized in terms of mass concentration, real time number concentration, mass size distribution, morphology, and chemical properties. The chemical characterization aims at identifying potential radioactive particles released and the associated size distribution, both of which are important information for assessing possible safety and radioprotection measures during the fuel debris retrieval operations at 1F.
Johansen, M. P.*; Child, D. P.*; Collins, R.*; Cook, M.*; Davis, J.*; Hotchkis, M. A. C.*; Howard, D. L.*; Howell, N.*; Ikeda, Atsushi; Young, E.*
Science of the Total Environment, 842, p.156755_1 - 156755_11, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:39.89(Environmental Sciences) continuous air monitor for the measurement of highly radioactive alpha-emitting particulates (
continuous air monitor for the measurement of highly radioactive alpha-emitting particulates ( -aerosols) under high humidity environment
-aerosols) under high humidity environmentTsubota, Yoichi; Honda, Fumiya; Tokonami, Shinji*; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Ikeda, Atsushi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1030, p.166475_1 - 166475_7, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:52.14(Instruments & Instrumentation)In the long-lasting decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), the dismantling of nuclear fuel debris (NFD) remaining in the damaged reactors is an unavoidable but significant issue with many technical difficulties. The dismantling is presumed to involve mechanical cutting, generating significant concentrations of particulates containing  -radionuclides (
-radionuclides ( -aerosols) that pose significant health risk upon inhalation. In order to minimize the radiation exposure of workers with
-aerosols) that pose significant health risk upon inhalation. In order to minimize the radiation exposure of workers with  -aerosols during the dismantling/decommissioning process at 1F, it is essential to monitor the concentration of
-aerosols during the dismantling/decommissioning process at 1F, it is essential to monitor the concentration of  -aerosols at the point of initial generation, i.e. inside the primary containment vessels (PCV) of the damaged reactors. Toward this end, an
-aerosols at the point of initial generation, i.e. inside the primary containment vessels (PCV) of the damaged reactors. Toward this end, an  monitoring system for
monitoring system for  -aerosols (
-aerosols ( alpha air monitor: IAAM) was developed and its technical performance was investigated under the conditions expected for the actual environments at 1F. IAAM was confirmed to fulfill four technical requirements: (1) steady operation under high humidity, (2) operation without using filters, (3) capability of measuring a high counting rate of
alpha air monitor: IAAM) was developed and its technical performance was investigated under the conditions expected for the actual environments at 1F. IAAM was confirmed to fulfill four technical requirements: (1) steady operation under high humidity, (2) operation without using filters, (3) capability of measuring a high counting rate of  -radiation, and (4) selective measurement of
-radiation, and (4) selective measurement of  -radiation even under high radiation background with
-radiation even under high radiation background with  /
/ -rays. IAAM is capable of selectively measuring
-rays. IAAM is capable of selectively measuring  -aerosols with a concentration of 3.3
-aerosols with a concentration of 3.3  10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm or higher without saturation under a high humid environment (100%-relative humidity) and under high background with
or higher without saturation under a high humid environment (100%-relative humidity) and under high background with  /
/ -radiation (up to 100 mSv/h of
-radiation (up to 100 mSv/h of  -radiation). These results demonstrate promising potential of IAAM to be utilized as a reliable monitoring system for
-radiation). These results demonstrate promising potential of IAAM to be utilized as a reliable monitoring system for  -aerosols during the dismantling of NFD, as well as the whole long-lasting decommissioning of 1F.
-aerosols during the dismantling of NFD, as well as the whole long-lasting decommissioning of 1F.
Uehara, Akihiro*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Ikeda, Atsushi; Numako, Chiya*; Terada, Yasuko*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Ina, Toshiaki*; Takeda-Homma, Shino*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 559, p.153422_1 - 153422_11, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) temperature measurement for lamp-based heating device
temperature measurement for lamp-based heating deviceSumita, Takehiro; Sudo, Ayako; Takano, Masahide; Ikeda, Atsushi
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials; Methods (Internet), 2(1), p.50 - 54, 2022/02
 C
CSumita, Takehiro; Kobata, Masaaki; Takano, Masahide; Ikeda, Atsushi
Materialia, 20, p.101197_1 - 101197_11, 2021/12
 } polyoxo cluster U
} polyoxo cluster U O
O Cl
Cl (MeO)
(MeO)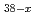 (x = 2.3, MeO = methoxide)
(x = 2.3, MeO = methoxide)Fichter, S.*; Radoske, T.*; Ikeda, Atsushi
Acta Crystallographica Section E; Crystallographic Communications (Internet), 77(8), p.847 - 852, 2021/08