Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Sashida, Sho*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Hawai, Takafumi*; Saito, Hiraku*; Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Sakaki, Koji*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 51(Part A), p.79 - 87, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical) dynamics in the H
dynamics in the H conductors LaH
conductors LaH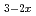 O
O
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Fukui, Keiga*; Iimura, Soshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Tada, Tomofumi*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Kuramoto, Yoshio*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Yamada, Takeshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 107(18), p.184114_1 - 184114_8, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)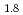 and TiH
and TiH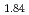 up to 21 GPa by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering
up to 21 GPa by incoherent inelastic neutron scatteringHattori, Takanori; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Iida, Kazuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(13), p.134309_1 - 134309_9, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen vibration excitations of fluorite-type ZrH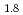 and TiH
and TiH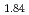 were investigated up to 21 GPa and 4 GPa, respectively, by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering experiments. The first excitation energies increased with pressure, as described by the equations
were investigated up to 21 GPa and 4 GPa, respectively, by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering experiments. The first excitation energies increased with pressure, as described by the equations 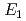 (meV) = 141.4(2) + 1.02(2)
(meV) = 141.4(2) + 1.02(2) (GPa) and
(GPa) and 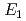 (meV) = 149.4(1) + 1.21(8)
(meV) = 149.4(1) + 1.21(8) (GPa) for ZrH
(GPa) for ZrH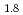 and TiH
and TiH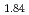 , respectively. Coupling with pressure dependence of lattice parameters, the relations between metal-hydrogen distance (
, respectively. Coupling with pressure dependence of lattice parameters, the relations between metal-hydrogen distance (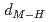 ) and
) and 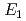 are found to be well described by the equations
are found to be well described by the equations 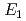 (meV) = 1.62(9)
(meV) = 1.62(9) 10
10
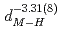 (
(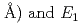 (meV) = 1.47(21)
(meV) = 1.47(21) 10
10
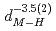 (AA), respectively. The slopes of these curves are much steep compared to the previously reported trend in various fluorite-type metal hydrides at ambient pressure. The hydrogen wave function spreading showed that the local potential field for a hydrogen atom shrinks more intensively than the tetrahedral site. These behavior is likely caused by the rigid metal ion core and the resulting confinement of the hydrogen atom in the narrower potential field at high pressures.
(AA), respectively. The slopes of these curves are much steep compared to the previously reported trend in various fluorite-type metal hydrides at ambient pressure. The hydrogen wave function spreading showed that the local potential field for a hydrogen atom shrinks more intensively than the tetrahedral site. These behavior is likely caused by the rigid metal ion core and the resulting confinement of the hydrogen atom in the narrower potential field at high pressures.
Omasa, Yoshinori*; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Toshima, Kento*; Yokoyama, Kaito*; Endo, Wataru*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033215_1 - 033215_9, 2022/09
Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Majzoub, E. H.*; Machida, Akihiko*; Watanuki, Tetsu*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Mizuno, Masataka*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakamura, Yumiko*
Acta Materialia, 234, p.118055_1 - 118055_10, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:83.6(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Wang, X.*; Tang, X.*; Zhang, P.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; Liu, J.*; Hui, K.*; Wang, Y.*; Dong, X.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 12(50), p.12055 - 12061, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.89(Chemistry, Physical)Substituted polyacetylene is expected to improve the chemical stability, physical properties, and additional functions of the polyacetylene backbones, but its diversity is very limited. Here, by applying external pressure on solid acetylenedicarboxylic acid, we report the first crystalline poly-dicarboxylacetylene with every carbon on the trans-polyacetylene backbone bonded to a carboxyl group, which is very hard to synthesize by traditional methods. This unique structure combines the extremely high content of carbonyl groups and high conductivity of a polyacetylene backbone, which exhibits a high specific capacity and excellent cycling/rate performance as a Li-ion battery (LIB) anode. We present a completely functionalized crystalline polyacetylene and provide a high-pressure solution for the synthesis of polymeric LIB materials and other polymeric materials with a high content of active groups.
 RhSi
RhSiKodama, Katsuaki; Honda, Takashi*; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Shamoto, Shinichi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(7), p.074710_1 - 074710_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.57(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Fe
Fe TiO
TiO
Kodama, Katsuaki; Honda, Takashi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Shamoto, Shinichi; Otomo, Toshiya*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011059_1 - 011059_6, 2021/03
 glasses
glassesHosokawa, Shinya*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Stellhorn, J. R.*; Pusztai, L.*; Blanc, N.*; Boudet, N.*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011070_1 - 011070_7, 2021/03
Local- and intermediate-range atomic order in Ag ion conducting glasses Ag (GeSe
(GeSe )
) with x = 0.15, 0.28, 0.33, and 0.50 were investigated by using a combination of AXS, XRD, ND, and RMC modeling. By adding the ND pdf to AXS and XRD results, reasonable partial structure factors and partial pdf were obtained by the RMC procedure. In contrast to the previous AXS and RMC study, a large number of Ag-Ge and Ge-Ge correlations are observed in the first coordination shell region, which is consistent with an
with x = 0.15, 0.28, 0.33, and 0.50 were investigated by using a combination of AXS, XRD, ND, and RMC modeling. By adding the ND pdf to AXS and XRD results, reasonable partial structure factors and partial pdf were obtained by the RMC procedure. In contrast to the previous AXS and RMC study, a large number of Ag-Ge and Ge-Ge correlations are observed in the first coordination shell region, which is consistent with an  MD simulation. The coordination numbers around the Ge and Se mostly follow the 8-
MD simulation. The coordination numbers around the Ge and Se mostly follow the 8- rule over all Ag concentrations if Ag is not taken into account. With increasing the Ag concentration, the partial coordination numbers with Ge and Se atoms around Ag remarkably increases, while the Ag-Ag coordination number increases only slightly, indicating that the Ag conducting path is formed through the second neighboring Ag-Ag correlations.
rule over all Ag concentrations if Ag is not taken into account. With increasing the Ag concentration, the partial coordination numbers with Ge and Se atoms around Ag remarkably increases, while the Ag-Ag coordination number increases only slightly, indicating that the Ag conducting path is formed through the second neighboring Ag-Ag correlations.
Hosokawa, Shinya*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Pusztai, L.*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(2), p.024601_1 - 024601_12, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Wang, X.*; Gao, D.*; Li, Y.*; Zheng, H.*; Wang, Y.*; Wang, X.*; Fu, R.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 142(41), p.17662 - 17669, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:74.59(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Solid-state topochemical polymerization (SSTP) is a promising method to construct functional crystalline polymeric materials, but in contrast to various reactions that happen in solution, only very limited types of SSTP reactions are reported. Diels-Alder (DA) and dehydro-DA (DDA) reactions are textbook reactions for preparing six-membered rings in solution but are scarcely seen in solid-state synthesis. Here, using multiple cutting-edge techniques, we demonstrate that the solid 1,4-diphenylbutadiyne (DPB) undergoes a DDA reaction under 10-20 GPa with the phenyl as the dienophile. The crystal structure at the critical pressure shows that this reaction is "distance-selected". The distance of 3.2 between the phenyl and the phenylethynyl facilitates the DDA reaction, while the distances for other DDA and 1,4-addition reactions are too large to allow the bonding. The obtained products are crystalline armchair graphitic nanoribbons, and hence our studies open a new route to construct the crystalline carbon materials with atomic-scale control.
between the phenyl and the phenylethynyl facilitates the DDA reaction, while the distances for other DDA and 1,4-addition reactions are too large to allow the bonding. The obtained products are crystalline armchair graphitic nanoribbons, and hence our studies open a new route to construct the crystalline carbon materials with atomic-scale control.
 He neutron spin filter at J-PARC
He neutron spin filter at J-PARCOkudaira, Takuya; Oku, Takayuki; Ino, Takashi*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Kenji; Hiroi, Kosuke; Takahashi, Shingo*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Endo, Hitoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 977, p.164301_1 - 164301_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:79.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)Wu, P.*; Fan, F.-R.*; Hagihara, Masato*; Kofu, Maiko; Peng, K.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Lee, S.*; Honda, Takashi*; Yonemura, Masao*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 22(8), p.083083_1 - 083083_9, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:58.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Thermoelectric material SnSe has aroused world-wide interests in the past years, and its inherent strong lattice anharmonicity is regarded as a crucial factor for its outstanding thermoelectric performance. However, the understanding of lattice anharmonicity in SnSe system remains inadequate, especially regarding how phonon dynamics are affected by this behavior. In this work, we present a comprehensive study of lattice dynamics on Na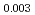 Sn
Sn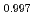 Se
Se S
S by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
 -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, X.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Zhao, E.*; Zhang, Z.*; Guide, T.*; Le, M. D.*; Avdeev, M.*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Kofu, Maiko; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.942_1 - 942_9, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:90.35(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In high-performance thermoelectric materials, there are two main low thermal conductivity mechanisms: the phonon anharmonic and phonon scattering resulting from the dynamic disorder, which have been successfully revealed by inelastic neutron scattering. Using neutron scattering and ab initio calculations, we report here a mechanism of static local structure distortion combined with phonon-anharmonic-induced ultralow lattice thermal conductivity in  -MgAgSb. Since the transverse acoustic phonons are almost fully scattered by the intrinsic distorted rocksalt sublattice in this compound, the heat is mainly transported by the longitudinal acoustic phonons. The ultralow thermal conductivity in
-MgAgSb. Since the transverse acoustic phonons are almost fully scattered by the intrinsic distorted rocksalt sublattice in this compound, the heat is mainly transported by the longitudinal acoustic phonons. The ultralow thermal conductivity in  -MgAgSb is attributed to its atomic dynamics being altered by the structure distortion, which presents a possible microscopic route to enhance the performance of similar thermoelectric materials.
-MgAgSb is attributed to its atomic dynamics being altered by the structure distortion, which presents a possible microscopic route to enhance the performance of similar thermoelectric materials.
 S)
S) (SiS
(SiS )
)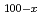 superionic glasses
superionic glassesMori, Kazuhiro*; Iwase, Kenji*; Oba, Yojiro; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Fukunaga, Toshiharu*
Solid State Ionics, 344, p.115141_1 - 115141_10, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:42.81(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Kawamura, Seiko; Hattori, Takanori; Harjo, S.; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Miyata, Noboru*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Watanabe, Masao; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Oku, Takayuki
Neutron News, 30(1), p.11 - 13, 2019/05
In Japanese neutron scattering facilities, some SE equipment that are frequently used at an instrument, such as the closed-cycle refrigerator (CCR), have been prepared for the instrument as standard SE. They are operated for user experiments by the instrument group. The advantage of this practice is that they can optimize the design of the SE for the instrument and can directly respond to users' requests. On the other hand, the SE team in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC has managed commonly used SE to allow neutron experiments with more advanced SE. In this report, recent SE in the MLF is introduced. Highlighted are the SE in BL11, BL19, BL21 and BL17 and other SE recently progressed by the SE team.
Torigoe, Shuhei*; Hattori, Takayuki*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Honda, Takashi*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Abe, Hitoshi*; Murakawa, Hiroshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(13), p.134443_1 - 134443_7, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:52.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) studied by neutron scattering and their relation with thermal conductivities
studied by neutron scattering and their relation with thermal conductivitiesKajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Murai, Naoki; Shamoto, Shinichi; Honda, Takashi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Hata, Hiroto*; Eto, Takahiro*; Noda, Masaaki*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 8(1), p.9651_1 - 9651_8, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.3(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kodama, Katsuaki; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Shamoto, Shinichi; Otomo, Toshiya*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 86(12), p.124708_1 - 124708_8, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:50.08(Physics, Multidisciplinary)