Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:156 Percentile:99.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Oshima, Katsumi; Oda, Yasuhisa; Takahashi, Koji; Terakado, Masayuki; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Moriyama, Shinichi; Kajiwara, Ken; Sakamoto, Keishi
JAEA-Technology 2015-061, 65 Pages, 2016/03
In JAEA, an ITER relevant control system for ITER gyrotron was developed according to Plant Control Design Handbook. This control system was developed based on ITER CODAC Core System and implemented state machine control of gyrotron operation system, sequential timing control of gyrotron oscillation startup, and data acquisition. The operation of ITER 170 GHz gyrotron was demonstrated with ITER relevant power supply configuration. This system is utilized for gyrotron operation test for ITER procurement. This report describes the architecture of gyrotron operation system, its basic and detailed design, and recent operation results.
Kobayashi, Takayuki; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Oda, Yasuhisa; Wada, Kenji; Hinata, Jun; Yokokura, Kenji; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
Proceedings of 40th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz 2015) (USB Flash Drive), 3 Pages, 2015/08
A gyrotron for electron cyclotron heating and current drive (ECH/CD) has been developed for JT-60SA (Super-Advanced). In high-power, long-pulse operations, oscillations of 1 MW/100 s have been demonstrated at both 110 GHz and 138 GHz, for the first time. These results fully satisfied the requirements for JT-60SA. Moreover, it was experimentally shown that the higher power operation at each frequency is expected to be acceptable for this gyrotron from the viewpoint of heat load at the cavity resonator, collector, and stray radiation absorbers. An oscillation at 82 GHz, which is an additional frequency, has been demonstrated up to 2 s at the output power of 0.4 MW, so far. High power experiments toward higher power of 1.5 MW (110/138 GHz) and 1 MW (82 GHz) are ongoing.
Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Yokokura, Kenji; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Wada, Kenji; Sato, Yoshikatsu; Hinata, Jun; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(6), p.063008_1 - 063008_8, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:75.46(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A gyrotron enabling high-power, long-pulse oscillations at both 110 GHz and 138 GHz has been developed for electron cyclotron heating (ECH) and current drive (CD) in JT-60SA. Oscillations of 1 MW for 100 s have been demonstrated at both frequencies, for the first time as a gyrotron operating at two frequencies. The optimization of the anode voltage, or the electron pitch factor, using a triode gun was a key to obtain high power and high efficiency at two frequencies. It was also confirmed that the internal losses in the gyrotron were sufficiently low for expected long pulse operation at the higher power level of  1.5 MW. Another important result is that an oscillation at 82 GHz, which enables to use fundamental harmonic waves in JT-60SA while the other two frequencies are used as second harmonics waves, was demonstrated up to 0.4 MW for 2 s. These results of the gyrotron development significantly contribute to enhancing operation regime of the ECH/CD system in JT-60SA.
1.5 MW. Another important result is that an oscillation at 82 GHz, which enables to use fundamental harmonic waves in JT-60SA while the other two frequencies are used as second harmonics waves, was demonstrated up to 0.4 MW for 2 s. These results of the gyrotron development significantly contribute to enhancing operation regime of the ECH/CD system in JT-60SA.
Oda, Yasuhisa; Oshima, Katsumi; Nakamoto, Takashi*; Hashimoto, Yasunori*; Yamamoto, Tsuyoshi; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Takahashi, Koji; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 90(7), p.365 - 373, 2014/07
no abstracts in English
Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Iimura, Soshi*; Kojima, Kenji*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Miao, P.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Miyazaki, Masanori*; et al.
Nature Physics, 10(4), p.300 - 303, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:108 Percentile:95.07(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Moriyama, Shinichi; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Wada, Kenji; Sato, Yoshikatsu; Hinata, Jun; Yokokura, Kenji; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
no journal, ,
Long pulse operation of the dual frequency gyrotron was started for JT-60SA ECH system. Pulse length of 2 s at 0.4 MW output, and 1 s at 0.7 MW were obtained at both 110 GHz and 138 GHz, so far. Typical oscillation efficiency is about 30%. Diffraction loss was acceptable for long pulse 1 MW output. The first high power test of the "power and beam profile monitor" featuring a fast movable Si N
N disk in the waveguide slit was successfully demonstrated.
disk in the waveguide slit was successfully demonstrated.
Oda, Yasuhisa; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
 n eigenmode damping
n eigenmode dampingMatsunaga, Go; Toi, Kazuo*; Ikeda, Ryosuke*; Takeuchi, Masaki*; Takechi, Manabu; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oda, Yasuhisa; Oshima, Katsumi; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Takahashi, Koji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oda, Yasuhisa; Kajiwara, Ken; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Oshima, Katsumi; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Purohit, D.*; Gandini, F.*; Omori, Toshimichi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Takahashi, Koji; Abe, Ganji; Isozaki, Masami; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Oda, Yasuhisa; Kajiwara, Ken; Sakamoto, Keishi; Kobayashi, Noriyuki*; Iida, Hiromasa*; Komatsuzaki, Manabu*; et al.
no journal, ,
It was analytically obtained that electron cyclotron current drive efficency at  =0.4
=0.4 0.6 can be doubled modifying the steering function of millimeter wave launching from the equatorial port from toroidally to poloidally. The design modification of the ITER equatorial launcher enhancing ECCD function is implemented. The millimeter wave design satisfying transmission efficiency more than 99% with the required ploidal beam steering capability is successfully obtained and reflected to the launcher structural design. The millimeter wave design optimization, BSM design modification to allow the required polidal beam steering capability and so on are reported in detail at the conference.
0.6 can be doubled modifying the steering function of millimeter wave launching from the equatorial port from toroidally to poloidally. The design modification of the ITER equatorial launcher enhancing ECCD function is implemented. The millimeter wave design satisfying transmission efficiency more than 99% with the required ploidal beam steering capability is successfully obtained and reflected to the launcher structural design. The millimeter wave design optimization, BSM design modification to allow the required polidal beam steering capability and so on are reported in detail at the conference.
Ikeda, Ryosuke; Oda, Yasuhisa; Kajiwara, Ken; Takahashi, Koji; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
Long pulse gyrotrons for ITER are under development. At present, output power of 1.2 MW for 2 s pulse operation and long pulse operation of 1000 s at 0.5 MW were achieved in experiments of TE31,11 mode gyrotron. Moreover, a transmission efficiency of 91% was obtained in 40 m transmission experiment. Recently, development of TE31,9 mode gyrotron was started. 1 MW with oscillation efficiency of 33% was realized in 1 ms operation without depressed collector voltage. And, 0.61 MW with total electric efficiency 51 % was achieved in 10 s operation with depressed collector voltage.
Takahashi, Koji; Abe, Ganji; Isozaki, Masami; Kobayashi, Noriyuki*; Shidara, Hiroyuki; Oda, Yasuhisa; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
An ITER equatorial EC launcher has been designed to inject a 170 GHz, 20 MW millimeter wave beam to plasma with poloidal steering functionality in order to obtain more driven current at the peripheral region of plasma. The millimeter wave design to accomplish the high transmission efficiency more than 99% and to compliant with the requirement on heat load on the mirror s and beam size at the resonance location of plasma has been successfully developed. The mock-up to simulate the millimeter wave propagation in the launcher based on the design modification of the beam path is fabricated and the low power experiment is in progress. The field pattern measurement at the mock-up outlet indicates the validity of the design optimization of mirror's and the waveguide set-up. The design of the millimeter wave beam path for poloidal steering launcher and the experiments of the launcher mock-up are reported in detail at the workshop.
Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Isayama, Akihiko; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Wada, Kenji; Sato, Yoshikatsu; Hinata, Jun; Yokokura, Kenji; et al.
no journal, ,
A high-power long-pulse dual-frequency gyrotron, which can be operated at both 110 GHz and 138 GHz independently, was successfully developed for electron cyclotron heating and current drive in JT-60SA. The output power of 1 MW and the pulse length of 100 s were obtained at both frequencies with the high oscillation efficiency (not including an efficiency enhancement by collector potential depression) of 34% (110 GHz) and 32% (138 GHz), respectively, for the first time. The target of the JT-60SA gyrotron was fully satisfied by this gyrotron. An optimization of the electron pitch factor was a key to obtain the high efficiencies, and oscillation characteristics of the gyrotron were experimentally confirmed.
Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Oda, Yasuhisa; Takahashi, Koji; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
TE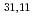 mode gyrotron has advantages for multi-frequency oscillation. Oscillations of 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz at TE
mode gyrotron has advantages for multi-frequency oscillation. Oscillations of 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz at TE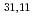 , TE
, TE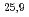 and TE
and TE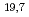 modes, respectively are excited by varying the magnetic field strength. In high power experiments, the output power, the oscillation efficiency and the electric efficiency for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation achieved 1.2 MW / 27% / 43%, 810 kW / 25% / 40% and 720 kW / 25% / 38%. In long pulse operation, 900 kW / 100 s, 800 kW / 224 s and 650 kW / 433 s for 170 GHz oscillation are obtained. HE
modes, respectively are excited by varying the magnetic field strength. In high power experiments, the output power, the oscillation efficiency and the electric efficiency for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation achieved 1.2 MW / 27% / 43%, 810 kW / 25% / 40% and 720 kW / 25% / 38%. In long pulse operation, 900 kW / 100 s, 800 kW / 224 s and 650 kW / 433 s for 170 GHz oscillation are obtained. HE mode purity of 91%, 88% and 95% for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation is obtained at the exit of a 40 m transmission line.
mode purity of 91%, 88% and 95% for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation is obtained at the exit of a 40 m transmission line.
Moriyama, Shinichi; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Wada, Kenji; Sato, Yoshikatsu; Hinata, Jun; Yokokura, Kenji; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
no journal, ,
Long pulse operation of the dual frequency gyrotron was started for JT-60SA ECH system. Pulse lengths of 10 s with output power of 1MW were obtained at both 110 GHz and 138 GHz, so far. Typical oscillation efficiency is approximately 30%. Diffraction loss was acceptable for long pulse 1 MW output. The first high power test of the "power / beam profile monitor" featuring a fast movable Si 3N
3N disk in the waveguide slit was successfully demonstrated.
disk in the waveguide slit was successfully demonstrated.
Oda, Yasuhisa; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Oshima, Katsumi; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Purohito, D.*; Henderson, M.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Takayuki; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Wada, Kenji; Sato, Yoshikatsu; Hinata, Jun; Yokokura, Kenji; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Takahashi, Koji; et al.
no journal, ,
Developments of a dual frequency (110 GHz and 138 GHz) electron cyclotron heating and current drive system for JT-60SA are required. In a long pulse operation of a dual-frequency gyrotron, oscillations of 1 MW for 10 s at both frequencies were obtained, so far. Out gas in the gyrotron has been decreased shot by shot, and conditioning of the gyrotron is in progress. Oscillation efficiencies of higher than 30% were obtained for both frequencies. Measured internal diffraction loss was almost the same level of the previously developed 110 GHz long pulse gyrotron. From the above results, it is expected that further pulse length expansion is possible by continuing conditioning operations. Moreover, optical characteristics of an antenna, which is used to inject high-power millimeter waves into tokamak, was confirmed for dual frequency operation. It was found that the beam width for the 138 GHz wave is narrower than that for the 110 GHz wave.
Kobayashi, Takayuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Hiranai, Shinichi; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Wada, Kenji; Sato, Yoshikatsu; Hinata, Jun; Yokokura, Kenji; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
no journal, ,
An original design of the toroidal injection angle range of electron cyclotron waves in JT-60SA was -15 degree to +15 degree for effective use of 110 GHz wave. However, the modification of the toroidal angle range has been discussed since the frequency of 138 GHz is considered to be a second frequency by the use of a dual frequency gyrotron. We report newly calculated available steering range of the launcher on both poloidal and toroidal angles with and without tilting angle of the second mirror, which is considered to obtain large toroidal injection angle. Moreover calculated beam divergences for various curvature radiuses of the first and second mirrors are shown. The decision of the target injection angle range for JT-60SA initial plasma will be made by the JT-60SA physics team by taking into account the above calculation results.