Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Ono, Takehiro; Itami, Kiyoshi
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(1), p.013503_1 - 013503_7, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Itami, Kiyoshi
Journal of Computational Physics, 292, p.208 - 214, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:37.19(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Itami, Kiyoshi
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 90(11), p.743 - 747, 2014/11
no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Itami, Kiyoshi
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Itami, Kiyoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori
Nuclear Fusion, 54(1), p.013012_1 - 013012_8, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper proposes a new method to calculate a safety factor,  , profile from gridded data of a poloidal flux,
, profile from gridded data of a poloidal flux, 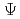 , efficiently and accurately. Difficulties of calculating
, efficiently and accurately. Difficulties of calculating  are derived from a difficulty of specifying a contour line of
are derived from a difficulty of specifying a contour line of 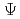 and a singularity at a magnetic axis. In order to solve the first difficulty, the proposed method interpolates knots, which are located on a target
and a singularity at a magnetic axis. In order to solve the first difficulty, the proposed method interpolates knots, which are located on a target 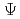 , by utilizing a normalized arc length and constraints expressed by a magnetic field. Regarding the second difficulty, the proposed method identifies
, by utilizing a normalized arc length and constraints expressed by a magnetic field. Regarding the second difficulty, the proposed method identifies  by extrapolating
by extrapolating  profile around a magnetic axis with a constraint of
profile around a magnetic axis with a constraint of 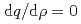 at the magnetic axis. Accuracy assessments of the proposed method are carried out by utilizing Solov'ev type equilibrium. The results show the validity and high performance of the proposed method.
at the magnetic axis. Accuracy assessments of the proposed method are carried out by utilizing Solov'ev type equilibrium. The results show the validity and high performance of the proposed method.
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(12), p.123507_1 - 123507_5, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.96(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 54(5), p.055005_1 - 055005_7, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:31.61(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori
Nuclear Fusion, 51(11), p.113022_1 - 113022_8, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:69.20(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We have developed the new method for identifying the  -profile from data, whose accuracy is determined in ITER, in order to assess the necessary measurement accuracy of the poloidal polarimeter. We have adopted the finite element method to calculate the ideal MHD equilibrium. Assuming that all measurement data has no error, we have shown the Importance of using the measurement data of the electron temperature,
-profile from data, whose accuracy is determined in ITER, in order to assess the necessary measurement accuracy of the poloidal polarimeter. We have adopted the finite element method to calculate the ideal MHD equilibrium. Assuming that all measurement data has no error, we have shown the Importance of using the measurement data of the electron temperature, 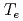 , and the ellipticity angle,
, and the ellipticity angle,  , of the polarization state in the inductive operation scenario II (S2), and the non-inductive operation scenario IV (S4).
, of the polarization state in the inductive operation scenario II (S2), and the non-inductive operation scenario IV (S4). 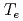 is used to calculate the relativistic effect on the polarization state. When the relativistic effect has not been included in the
is used to calculate the relativistic effect on the polarization state. When the relativistic effect has not been included in the  -profile identification, the error of
-profile identification, the error of  -profile identification has exceeded 7.7
-profile identification has exceeded 7.7 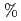 and 15
and 15 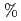 in S2 and S4, respectively.
in S2 and S4, respectively.  is mainly related to the Cotton-Mouton effect, which is an obstacle in measurement of a pure Faraday effect. Taking into account
is mainly related to the Cotton-Mouton effect, which is an obstacle in measurement of a pure Faraday effect. Taking into account  reduced the error of
reduced the error of  -profile identification by 0.5
-profile identification by 0.5 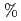 . Finally, we have assessed the necessary accuracy of the orientation angle,
. Finally, we have assessed the necessary accuracy of the orientation angle, 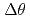 , and the ellipticity angle,
, and the ellipticity angle, 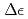 . The polarimetric measurements with accuracy of
. The polarimetric measurements with accuracy of 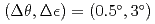 have satisfied the measurement requirement for the
have satisfied the measurement requirement for the  -profile identification (
-profile identification (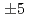
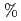 ) in case of that viewing chords are via both equatorial and upper ports.
) in case of that viewing chords are via both equatorial and upper ports.
Ishikawa, Masao; Kawano, Yasunori; Imazawa, Ryota; Sato, Satoshi; Vayakis, G.*; Bertalot, L.*; Yatsuka, Eiichi; Hatae, Takaki; Kondoh, Takashi; Kusama, Yoshinori
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(6-8), p.1286 - 1289, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)The nuclear heating rates of the optical mirrors of the poloidal polarimeter installed in the equatorial port plug of ITER are calculated. Since the system cannot have a sufficiently labyrinthine structure and the second mirrors are located nearly as close to the plasma as the first mirrors due to limited space, the nuclear heating rate of the second mirrors is as high as that of the first mirrors. However, it is possible to reduce the nuclear heating rates of the mirrors if the blanket shield module provides a sufficient degree of neutron shielding.
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Ono, Takehiro; Kusama, Yoshinori
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 6(Sp.1), p.2402032_1 - 2402032_5, 2011/08
This paper describes results from the first integrated analysis on the feasibility of a retro-reflector (RR) installed in the ITER vacuum vessel. We make thermal and structural analyses of passively-cooled RR and terrace retro-reflector array (TERRA) by using heat load conditions on ITER. In the case of RR, the temperature reaches over 600 C, and the flatness of deformed mirror surface forming RR is approximately 80
C, and the flatness of deformed mirror surface forming RR is approximately 80  m. Although the maximal displacement of mirror surface is large, 69% of the incident-laser power returns to a diagnostic room, disturbance of phase is
m. Although the maximal displacement of mirror surface is large, 69% of the incident-laser power returns to a diagnostic room, disturbance of phase is 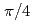 and rotation angle of polarization plane is less than 0.06
and rotation angle of polarization plane is less than 0.06  . On the other hand, the temperature of TERRA is approximately 350
. On the other hand, the temperature of TERRA is approximately 350 C, and the flatness of the deformed mirror surface is less than 10
C, and the flatness of the deformed mirror surface is less than 10  m. The flatness of the mirror surface of the deformed TERRA is much smaller than laser wavelength (118
m. The flatness of the mirror surface of the deformed TERRA is much smaller than laser wavelength (118  m), but the global shape is curved to ruin the coherent phase of laser light. The curvature radius of TERRA is 21 m, and 49% of the incident-laser power returns to the diagnostic room, disturbance of phase is
m), but the global shape is curved to ruin the coherent phase of laser light. The curvature radius of TERRA is 21 m, and 49% of the incident-laser power returns to the diagnostic room, disturbance of phase is 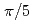 , and rotation angle of polarization plane is less than 0.06
, and rotation angle of polarization plane is less than 0.06 . Since the optimized incident angles of flat and curved TERRA are different, a real-time feedback control of the incident angle is necessary for applying TERRA to ITER poloidal polarimeter.
. Since the optimized incident angles of flat and curved TERRA are different, a real-time feedback control of the incident angle is necessary for applying TERRA to ITER poloidal polarimeter.
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Ono, Takehiro; Kusama, Yoshinori
Review of Scientific Instruments, 82(2), p.023116_1 - 023116_5, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.30(Instruments & Instrumentation)Sato, Kazuyoshi; Imazawa, Ryota; Ono, Takehiro; Kawano, Yasunori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Ono, Takehiro; Kawano, Yasunori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Itami, Kiyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawano, Yasunori; Kondoh, Takashi; Ishikawa, Masao; Hatae, Takaki; Yatsuka, Eiichi; Imazawa, Ryota; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Sugie, Tatsuo; Takeuchi, Masaki; Sato, Kazuyoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
Recent progress in development of ITER diagnostic systems in Japan is presented as briefly shown below. (1) Microfission Chamber: A prototyping of vacuum feedthrough showed that the vacuum leak rate satisfies that of ITER requirement. (2) Thomson scattering (edge): A new method proposed for the measurement of anisotropic electron temperature was presented. (3) Poloidal Polarimeter: Measurement accuracy of the poloidal polarimeter was evaluated so that the accuracy of resultant current profile can satisfy the ITER measurement requirement. (4) Impurity influx monitor (divertor): By improvement of the design of equatorial port optics, expected detected light was 16 times increased in comparison with that of the previous design. (5) Divertor thermocouples (outer target): Investigation was started about the fixation method of the thermocouple on the side of divertor outer target. (6) Divertor IR thermography: Conceptual design activity was started for equatorial port optics.
Imazawa, Ryota; Ono, Takehiro; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawano, Yasunori; Imazawa, Ryota; Ono, Takehiro; Ishikawa, Masao; Hayashi, Toshimitsu; Sato, Kazuyoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori; Ebisawa, Katsuyuki*; Wakabayashi, Kuniaki*; Katsumata, Takahito*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawano, Yasunori; Ishikawa, Masao; Sato, Kazuyoshi; Imazawa, Ryota; Kusama, Yoshinori; Hayashi, Toshimitsu; Ono, Takehiro; Ebisawa, Katsuyuki*; Wakabayashi, Kuniaki*; Hiramatsu, Miho*; et al.
no journal, ,