Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Terauchi, Masami*; Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato
Hyomen Kagaku, 36(4), p.184 - 188, 2015/04
Electron beam induced soft-X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) that uses a grating spectrometer has been introduced to a conventional scanning electron microscope (SEM) for characterizing desired specimen areas of bulk materials. The spectrometer has a grazing-incidence flat-field optics by using aberration corrected (varied-line-spacing) gratings, which has already been applied to transmission electron microscopes. The best resolution was confirmed as 0.13 eV at Mg L-emission (50 eV), which is comparable with that of recent dedicated electron energy-loss spectroscopy instruments. Apparent band structure effects have been observed in Mg-L, Si-L, B-K, and Ti-L emission spectra obtained from bulk materials using SEM-SXES instrument.
Koike, Masato; Imazono, Takashi; Ishino, Masahiko
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 46, p.159 - 166, 2015/03
The demand for the physical-properties research using powerful light sources, such as synchrotron radiation and soft-X-rays laser light, is increasing. When promoting such research, it is required to develop efficient soft-X-ray spectrometers suitable for absorption, emission, and fluorescence which are appeared in an energy rage of 1-8 keV. We describe the development of laminar type diffraction gratings which enhance diffraction efficiency remarkably by use of soft-X-ray multilayers instead of single metal layers.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Faenov, A. Y.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; Koga, J. K.; Mori, Michiaki; Kawase, Keigo*; et al.
RAL-TR-2015-025, P. 22, 2015/00
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato
Thin Solid Films, 571(Part 3), p.513 - 516, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.10(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A laser-driven plasma soft X-ray laser (SXRL) system was constructed in Kansai Photon Science Institute. The SXRL having a 7-ps-duration pulse at a wavelength of 13.9 nm is generated from nickel-like silver plasmas generated by 10 J and ps-duration Nd:glass laser pulse. The polarization state of SXRL is considered to be almost vertically linearly polarized at the end station by the reflections of some Mo/Si multilayer mirrors installed in the SXRL beamline, but it has not been measured experimentally due to the lack of a polarization analysis apparatus. Therefore, we have developed a compact soft X-ray ellipsometer to be able to be installed in the SXRL beamline and evaluated the degree of linear polarization of SXRL with a Mo/Si multilayer polarizer whose polarization property has been characterized by using synchrotron radiation in advance.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Gallegos, P.*; Ahmed, H.*; Ragozin, E. N.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 16(9), p.093003_1 - 093003_30, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:80.06(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Terauchi, Masami*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 20(Suppl.3), p.684 - 685, 2014/08
A novel wavelength dispersive soft X-ray emission spectrometer (SXES) having a X-ray energy range of 50-210 eV has been developed. One feature is that the SXES is parallel detection of the signals so that it can be used like a conventional energy dispersive spectrometer. The other is a high energy resolution, which is about 0.2 eV at Al-L comparable to those revealed by XPS and EELS. These features enable us to obtain meaningful information about chemical bonding in various bulk samples. The SXES can detect Li-K emission spectrum. In the case of an anode electrode of a lithium ion battery (LIB), two types of lithium peaks are observed: one lower energy peak at 50 eV and the other higher energy peak at 54 eV. It was found that the former peak corresponds to the amount of charging, whereas the latter corresponds to the metallic state of lithium.
Terauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Imazono, Takashi; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 20(Suppl.3), p.682 - 683, 2014/08
X-rays originate form electronic transitions from valence bands (VB, bonding electron states) to inner-shell electron levels inform us energy states of bonding electrons. We have developed the SXES spectrometers attaching to TEM, EPMA, and SEM. A spectrometer has an energy range of 50-4000 eV by using four varied-line-spacing gratings. Applications of TEM-SXES instrument to C have revealed characteristic energy distribution of bonding electrons. Carbon K-emission spectra of C
have revealed characteristic energy distribution of bonding electrons. Carbon K-emission spectra of C  crystals showed that both the peak structures in
crystals showed that both the peak structures in  - and
- and  -bands and the characteristic dip structure between the
-bands and the characteristic dip structure between the  - and
- and  -bonding states in monomer-C
-bonding states in monomer-C disappear in the most polymerized-C
disappear in the most polymerized-C crystals. Bulk specimens were examined by applying SXES to a SEM. Al L-emission spectra of intermetallic compounds of Al
crystals. Bulk specimens were examined by applying SXES to a SEM. Al L-emission spectra of intermetallic compounds of Al Au, AlCo, and aluminum showed different intensity distributions due to different band structures originating from different crystal structures.
Au, AlCo, and aluminum showed different intensity distributions due to different band structures originating from different crystal structures.
Terauchi, Masami*; Koshiya, Shogo*; Sato, Futami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Imazono, Takashi; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 20(3), p.692 - 697, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:91.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Electron beam induced soft-X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) by using a grating spectrometer has been introduced to a conventional scanning electron microscope (SEM) for characterizing desired specimen areas of bulk materials. The spectrometer was designed as a grazing-incidence flat-field optics by using aberration corrected (varied-line-spacing) gratings and a multi-channel-plate detector combined with a charge-coupled-device camera, which has already applied for a transmission electron microscope. The best resolution was confirmed as 0.13 eV at Mg L-emission (50 eV), which value is comparable to that of recent dedicated electron energy-loss spectroscopy instruments. This SXES-SEM instrument presents density of states of simple metals of bulk Mg and Li. Apparent band structure effects have been observed in Si L-emission of Si-wafer, P L-emission of GaP-wafer, and Al L-emissions of intermetallic compounds of AlCo, AlPd, Al Pt, and Al
Pt, and Al Au.
Au.
Imazono, Takashi
Oyo Butsuri, 83(4), p.288 - 292, 2014/04
We have developed a soft X-ray flat-field spectrograph capable to detect soft X-ray emissions in 50-4000 eV with high spectral resolution. The spectrograph in combination with an electron microscope such as transmission electron microscope (TEM) and electron probe micro-analyzer (EPMA) makes it possible to simultaneously perform not only the structural and elemental analyses of such functional materials as lithium-ion batteries and solar cells, but also chemical-bonding states analysis in the nano-scale area. In this article, the development of the soft X-ray flat-field spectrograph and preliminary experimental results measured by the spectrograph installed in EPMA and TEM are described.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Kaihori, Takeshi; Morita, Toshimasa; Sasaki, Akira; Terakawa, Kota*; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2012; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.147, p.117 - 120, 2014/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We have developed the femto-second laser pump and soft X-ray laser probe system in order to observe the dynamical processes of the femto-second laser ablation. By using this system, we succeed to obtain the temporal evolution of the soft X-ray reflectivity from the laser induced Pt surface. The results lead that the rate of decrease in the reflectivity of the probe beam has a non-linear relation with the pump laser fluence.
Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Terauchi, Masami*; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2013-001, p.13 - 15, 2013/09
A very unique high performance soft X-ray emission spectrometer (SXES) has successfully been developed which can be attached not only to transmission electron microscopes (TEMs), but also to scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) as well as electron probe microanalyzers (EPMAs). To extend the analyzed energy ranges, a newly designed laminar-type varied-line-spacing (VLS) grating JS50XL, for a lower energy range, 50-170 eV, and a multilayered VLS grating JS4000, for a higher energy range, 2000-4000 eV, have been developed and installed to this spectrometer. Application software has also been developed for a commercial use of SXES in several fields such as battery materials, steel and alloys, and electron devices. The appearance of this spectrometer attached to EPMA and a few results acquired are shown in the following figures. This development has been conducted as one of the projects of Collaborative Development of Innovative Seeds (Practicability verification stage) by Japan Science and Technology Agency.
Terauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2013-001, p.77 - 80, 2013/09
We have been developing a soft X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) instrument for electron microscopes (TEM, EPMA/SEM) with an extension of detectable energy range to 50-4000 eV. An introduction of valence electron spectroscopy with microscopy will supply fruitful information on bonding electrons, which cannot be obtained by EELS and EDS. For extend the lowest (or highest) detection energy upto 50 eV (or 4000 eV), a new laminar-type varied-line-spacing (VLS) grating, JS50XL, (or JS4000) has designed and manufactured. JS50XL and JS4000 having 1200 and 2400 lines/mm as well as coated by Au and a new multilayer-structure of W/B C for a wide-band energy region of 2000-3800 eV, respectively. Those gratings were installed and tested in a SXES spectrometer attached to a TEM. The extension in lowest detection energy was confirmed by Mg-L emission (JS50XL). The energy resolution was 0.2 eV at Fermi edge of 49.5 eV. It can be also seen a sharp Fermi edge for Li-K emission spectrum of metal-Li. The high energy resolution was confirmed by Te-La emission at 3.8 keV (JS4000). The full width at half maximum of the peak was 27 eV. The detection energy range was successfully extended by using the two new VLS-gratings.
C for a wide-band energy region of 2000-3800 eV, respectively. Those gratings were installed and tested in a SXES spectrometer attached to a TEM. The extension in lowest detection energy was confirmed by Mg-L emission (JS50XL). The energy resolution was 0.2 eV at Fermi edge of 49.5 eV. It can be also seen a sharp Fermi edge for Li-K emission spectrum of metal-Li. The high energy resolution was confirmed by Te-La emission at 3.8 keV (JS4000). The full width at half maximum of the peak was 27 eV. The detection energy range was successfully extended by using the two new VLS-gratings.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.8848, p.884812_1 - 884812_14, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:95.42(Optics)We have developed an objective soft X-ray flat-field spectrograph to be able to attach to electron microscopes. This spectrograph has two attractive features. One is that it is designed to cover a wide energy range of 50-4000 eV by using four varied-line-spacing holographic gratings optimized for 50-200 eV, 155-350 eV, 300-2200 eV, and 2000-4000 eV. They can be accommodated in the single spectrograph. The other is a newly invented W/B C multilayer coating covering the 2000-4000 eV range. It can enhance the diffraction efficiency above a practical level of
C multilayer coating covering the 2000-4000 eV range. It can enhance the diffraction efficiency above a practical level of 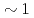 % at a constant incidence angle in the whole energy range.
% at a constant incidence angle in the whole energy range.
Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Terauchi, Masami*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 19(Suppl.2), p.1258 - 1259, 2013/08
A new wavelength dispersive soft X-ray emission spectrometer (WD-SXES) consisting of newly developed diffraction gratings has been developed for soft X-ray emission spectroscopy. The WD-SXES with two types of diffraction gratings nominally covering an energy range between 50 and 210 eV has been installed to electron probe X-ray microanalyzers, JEOL JXA-8100, for commercial use. The energy resolution of this WD-SXES is nominally 0.3 eV, which is one order of magnitude better than that of conventional WDSs with layered dispersion elements. It is to be noted that the corresponding edge of Al B is shifted to higher energy side by about 1 eV. One of the energy range was selected from 72 to 73.5 eV whereas the other was from 73.5 to 75 eV. The contrast in the former map is reversed in the later map as expected even though the energy difference between two maps is only 1.5 eV. The study confirms the high potential for the characterization especially for chemical state mapping.
B is shifted to higher energy side by about 1 eV. One of the energy range was selected from 72 to 73.5 eV whereas the other was from 73.5 to 75 eV. The contrast in the former map is reversed in the later map as expected even though the energy difference between two maps is only 1.5 eV. The study confirms the high potential for the characterization especially for chemical state mapping.
Terauchi, Masami*; Koshiya, Shogo*; Sato, Futami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Imazono, Takashi; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 19(Suppl.2), p.1278 - 1279, 2013/08
We have been developed and tested soft-X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) instruments by attaching to TEM and EPMA. The spectrometer has an energy range form 50-4000 eV by using four varied-line-spacing (aberration corrected) gratings. This SXES spectrometer inform us energy states of valence electrons (bonding electrons) form an identified specimen area by electron microscopy, which cannot be obtained by EELS and EDS. This provides not only the probing method for the energy states of valence electrons but also a sensitive tool for elemental and chemical identification. The spectrometer has applied also to a SEM (JEOL JSM-6480LV). As SEM can use a larger probe current and excitation volume of specimen than those of TEM, the detection time is about one order shorter than that of TEM. The energy resolution evaluated at AL-L edge is 0.16 eV. The spectrum of LaB
edge is 0.16 eV. The spectrum of LaB shows apparent intensity corresponds to B-K Fermi edge, showing chemical state of boron.
shows apparent intensity corresponds to B-K Fermi edge, showing chemical state of boron.
 and Sn-L
and Sn-L emissions of indium tin oxide
emissions of indium tin oxideTerauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy, 62(3), p.391 - 395, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.35(Microscopy)A new multilayer-coated varied line-spaced grating, JS4000, was fabricated and tested for extending the upper limit of a grating X-ray spectrometer for electron microscopy. This grating was designed for 2-3.8 keV at a grazing incidence angle of 1.35 deg. It was revealed that this new multilayer structure enables us to take soft-X-ray emission spectra continuously from 1.5 keV to 4 keV at the same optical setting. The full-width at half maximum of Te-L
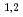 (3.8 keV) emission peak was 27 eV. Sn-L
(3.8 keV) emission peak was 27 eV. Sn-L (3444 eV) and In-L
(3444 eV) and In-L
 (3487 eV) peaks, which cannot be resolved by a widely used energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer.
(3487 eV) peaks, which cannot be resolved by a widely used energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; Terauchi, Masami*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 425(15), p.152008_1 - 152008_4, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:83.74(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed a flat-field spectrograph equipped with a wide-band multilayer grating and prefocusing mirror for the 2-4 keV range. To realize a spectrograph without any mechanical movement, the multilayer has a newly invented layer structure to uniformly enhance the diffraction efficiency (or reflectivity) of the grating (or prefocusing mirror) at a fixed angle of incidence in the whole energy region. The multilayer structure consisting of W and B C layers has been deposited by ion beam sputtering method on a varied-line-spacing laminar-type holographic grating. Also the same multilayer has been done on a spherical substrate. The average diffraction efficiency (or reflectivity) of the multilayer grating (or spherical mirror) is in excess of 3% at 88.65
C layers has been deposited by ion beam sputtering method on a varied-line-spacing laminar-type holographic grating. Also the same multilayer has been done on a spherical substrate. The average diffraction efficiency (or reflectivity) of the multilayer grating (or spherical mirror) is in excess of 3% at 88.65 (or 4% at 88.00
(or 4% at 88.00 ) in the 2.1-3.8 keV range. The throughput of the spectrograph with multilayer optics can be evaluated to be 2-5000 times higher than that with conventional optics coated by a gold layer.
) in the 2.1-3.8 keV range. The throughput of the spectrograph with multilayer optics can be evaluated to be 2-5000 times higher than that with conventional optics coated by a gold layer.
Ishino, Masahiko; Faenov, A.*; Tanaka, Momoko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Pikuz, S.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Skobelev, I.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.236 - 240, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:62.11(Physics, Applied)We irradiated the focusing soft X-ray laser pulses having a wavelength of 13.9 nm and the duration of 7 ps to aluminum surface. After the irradiation process, the irradiated surface was observed with a scanning electron microscope. The surface modifications caused by soft X-ray laser single pulse exposure were clearly seen. In addition, it was found that the conical structures having around 100 nm in diameters were formed in the shallow features. The nano-meter size modified surface structures on aluminum induced by the soft X-ray laser pulse is interesting as the newly surface structure. Hence, the soft X-ray laser beam would be a candidate for a tool of micromachining. We also provide a thermomechanical modeling of the soft X-ray laser interaction with aluminum briefly to explain the surface modification.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.33 - 37, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:83.24(Physics, Applied)Esirkepov, T. Z.; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Gallegos, P.*; Ahmed, H.*; Ragozin, E. N.*; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.172 - 180, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)The bow wave induced mechanism of high-order harmonics generation was discovered using simulations and catastrophe theory. This mechanism feasibility was successfully demonstrated in 3D and 2D PIC simulations. The mechanism and the simulations explained high-order harmonics in the XUV spectral region seen in recent experiments with terawatt lasers. Development of new XUV light and X-ray source based on the high-order harmonics generation mechanism is proposed.