Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsubara, Ryuta*; Ueno, Fuga*; Iwata, Hajime; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Okubo, Takahiro*
NUMO-TR-24-03, p.55 - 61, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Matsubara, Ryuta*; Takubo, Yusaku*; Iwata, Hajime; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Okubo, Takahiro*
NUMO-TR-24-01, p.104 - 108, 2024/05
no abstracts in English
Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Endo, Yoichi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Muroya, Yusa*; Endo, Keita*; Watanabe, Daisuke*; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Ishii, Katsunori; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(3), p.307 - 317, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)A flexible waste management system (FWM) is being developed to apply future MA partitioning and transmutation (P&T) technology to current HLLW. This FWM system will store high-level waste (HLLW) in granular form until MA partitioning and transmutation technology is realized. The feasibility of the main process was essentially confirmed by basic experiments and preliminary thermal analysis for granule production by rotary kiln from simulated HLLW and for temporary storage (50 years) of HLW granules at the HLW storage facility, respectively. The granule production experiments revealed that relatively large particles can be produced by the rotary kiln. The results of the thermal analysis showed that the small diameter canisters could be used to safely store the granules at a higher storage density than vitrified HLW. The effectiveness of the FWM system in terms of potential radiotoxicity and repository area was also evaluated, and it was shown that FWM can reduce these factors and has significant advantages in the disposal of HLW generated in current reprocessing plants. Since LWR fuel is stored for a long period of time in Japan and the operation of a reprocessing plant is expected to start soon, the FWM system is considered to be an effective system for reducing the environmental burden of HLW disposal.
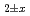 mixed oxides
mixed oxidesVauchy, R.; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154786_1 - 154786_13, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Matsubara, Ryuta*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Okubo, Takahiro*
NUMO-TR-22-02, p.65 - 67, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
 Ln
Ln O
O (Ln = Gd, Er) solid solution
(Ln = Gd, Er) solid solutionPham, V. M.*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 556, p.153189_1 - 153189_9, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The crystal structure change was evaluated for (1-x)UO -xLnO
-xLnO (Ln=Gd or Er; x = 0 to 0.4) samples sintered at 1973 K for 8 h under Ar and Ar-10%H
(Ln=Gd or Er; x = 0 to 0.4) samples sintered at 1973 K for 8 h under Ar and Ar-10%H atmospheres. The effect of LnO
atmospheres. The effect of LnO doping on the crystal structure of UO
doping on the crystal structure of UO was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS). LnO
was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS). LnO doping into UO
doping into UO reduced the lattice parameter of UO
reduced the lattice parameter of UO -LnO
-LnO solid solutions up to 40mol% LnO
solid solutions up to 40mol% LnO . The lattice parameters of these samples were comparable to those of stoichiometric (U,Ln)O
. The lattice parameters of these samples were comparable to those of stoichiometric (U,Ln)O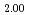 solid solutions, that is, the O/M ratios were close to 2.00. The U L
solid solutions, that is, the O/M ratios were close to 2.00. The U L -edge XANES analysis showed that higher U oxidation states of +5 or +6 formed, in addition to + 4. The EXAFS analysis indicated that the interatomic distances of U-O and Gd-O decreased with increasing x, whereas those of Er-O may not decrease monotonically.
-edge XANES analysis showed that higher U oxidation states of +5 or +6 formed, in addition to + 4. The EXAFS analysis indicated that the interatomic distances of U-O and Gd-O decreased with increasing x, whereas those of Er-O may not decrease monotonically.
Arima, Tatsumi*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*; Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 92, p.286 - 297, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)Diffusion and adsorption behavior of uranyl (UO ) species is important for the performance assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The diffusion behaviors of UO
) species is important for the performance assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The diffusion behaviors of UO , K
, K , CO
, CO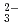 and Cl
and Cl and H
and H O in the aqueous solutions were evaluated by molecular dynamics (MD) calculations. The diffusion coefficient (De) of UO
O in the aqueous solutions were evaluated by molecular dynamics (MD) calculations. The diffusion coefficient (De) of UO is the smallest and is 26% less than the self-diffusion coefficient of H
is the smallest and is 26% less than the self-diffusion coefficient of H O. For the aqueous solution with high concentration of carbonate ions, uranyl carbonate complexes: UO
O. For the aqueous solution with high concentration of carbonate ions, uranyl carbonate complexes: UO CO
CO and UO
and UO (CO
(CO )
) can be observed. For the clay (montmorillonite or illite)-aqueous solution systems, the adsorption and diffusion behaviors of UO
can be observed. For the clay (montmorillonite or illite)-aqueous solution systems, the adsorption and diffusion behaviors of UO and K
and K were evaluated by MD calculations. The distribution coefficients (Kd) increase with the layer charge of clay, and Kd of UO
were evaluated by MD calculations. The distribution coefficients (Kd) increase with the layer charge of clay, and Kd of UO might be smaller than that of K
might be smaller than that of K . Further, their two-dimensional diffusion coefficients were relatively small in the adsorption layer and were extremely small for illite with higher layer charge.
. Further, their two-dimensional diffusion coefficients were relatively small in the adsorption layer and were extremely small for illite with higher layer charge.
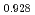 Am
Am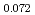 )O
)O at high temperatures
at high temperaturesMatsumoto, Taku; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(10), p.1296 - 1302, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:63.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)The oxygen potentials of (Pu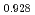 Am
Am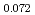 )O
)O were measured at 1873K, 1773K and 1473K by gas equilibrium method. It was shown that following the reduction of Am at the O/M ratio above 1.96, Pu was reduced at the O/M ratio below 1.96.
were measured at 1873K, 1773K and 1473K by gas equilibrium method. It was shown that following the reduction of Am at the O/M ratio above 1.96, Pu was reduced at the O/M ratio below 1.96.
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Watanabe, Koichi; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Sakamaki, Keiko; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 21(2), p.63 - 74, 2014/12
Static leach tests were conducted for simulated HLW glass in CaCl /Ca(OH)
/Ca(OH) solutions to investigate the corrosion behavior of HLW glass under calcium-rich environments induced by cement based materials in geological repositories. Another series of leach tests were conducted in deionized water in the presence of iron to investigate the effects of iron over-pack on the glass corrosion. In Ca solutions, corrosion of the glass was inhibited during the test period compared to that in deionized water, while the corrosion was enhanced at the presence of iron. The enhancement of the glass corrosion was assumed to be accompanied with transformation of silica, a glass network former, into iron silicates.
solutions to investigate the corrosion behavior of HLW glass under calcium-rich environments induced by cement based materials in geological repositories. Another series of leach tests were conducted in deionized water in the presence of iron to investigate the effects of iron over-pack on the glass corrosion. In Ca solutions, corrosion of the glass was inhibited during the test period compared to that in deionized water, while the corrosion was enhanced at the presence of iron. The enhancement of the glass corrosion was assumed to be accompanied with transformation of silica, a glass network former, into iron silicates.
Gin, S.*; Abdelouas, A.*; Criscenti, L.*; Ebert, W.*; Ferrand, K.*; Geisler, T.*; Harrison, M.*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Mueller, K. T.*; et al.
Materials Today, 16(6), p.243 - 248, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:432 Percentile:99.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The nations producing borosilicate glass as a confinement material for high-level waste resulting from spent fuel reprocessing have decided to reinforce scientific collaboration in order to obtain consensus on the mechanisms controlling the long-term dissolution rate of glass. This goal is the most important issue for developing reliable predictive models usable for performance assessment and safety demonstration of geological storage of such materials. This collaboration involves numerous laboratories working either in fundamental or applied research and using all the modern tools available in material science. We present first the situation of the six countries involved in the project regarding their history in nuclear waste vitrification, current policy, and geological disposal project development. This provides an understanding of the common and country specific needs regarding the issue of long-term behavior of glass. Then main proposals and first results are briefly presented.
Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Makigaki, Hikaru; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Noshita, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(4), p.438 - 449, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:78.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Dissolution tests were performed for a simulated HLW glass by using a Micro-Channel Flow-Through (MCFT) test to evaluate the initial dissolution rate, 
 , as a function of pH and temperature. The results indicated that the
, as a function of pH and temperature. The results indicated that the 
 shows a "V-shaped" pH dependence at 25
shows a "V-shaped" pH dependence at 25 C, which is almost consistent with the previous results measured by using other test methods including Single Pass Flow-Through (SPFT) test. At elevated temperatures, however, the
C, which is almost consistent with the previous results measured by using other test methods including Single Pass Flow-Through (SPFT) test. At elevated temperatures, however, the 
 shows a "U-shaped" pH dependence with a flat bottom at neutral pH, which differs from the previous results. The results also indicated that the MCFT provided a higher value of the
shows a "U-shaped" pH dependence with a flat bottom at neutral pH, which differs from the previous results. The results also indicated that the MCFT provided a higher value of the 
 with a steep slope of pH dependence than the SPFT results at basic pH from 8 to 11 at 90
with a steep slope of pH dependence than the SPFT results at basic pH from 8 to 11 at 90 C. With respect to the temperature dependence, the
C. With respect to the temperature dependence, the 
 increases with temperature according to an Arrhenius law at any pH, and the apparent activation energy increases with pH, which suggests that the dissolution mechanism can change depending on pH.
increases with temperature according to an Arrhenius law at any pH, and the apparent activation energy increases with pH, which suggests that the dissolution mechanism can change depending on pH.
Hirano, Fumio; Sato, Seichi*; Kozaki, Tamotsu*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Iwasaki, Tomohiko*; Oe, Toshiaki*; Kato, Kazuyuki*; Kitayama, Kazumi*; Nagasaki, Shinya*; Niibori, Yuichi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(3), p.310 - 319, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal impacts of hull and end piece wastes from the reprocessing of MOX spent fuels burned in LWRs on repository performance were investigated. The heat generation rates in MOX spent fuels and the resulting heat generation rates in hull and end piece wastes change depending on the fuel histories including the burn-up of UO spent fuels, the cooling period before reprocessing, the storage period of fresh MOX fuels. The heat generation rates of hull and end piece wastes from the reprocessing of MOX spent fuels with any of those histories are significantly larger than those from UO
spent fuels, the cooling period before reprocessing, the storage period of fresh MOX fuels. The heat generation rates of hull and end piece wastes from the reprocessing of MOX spent fuels with any of those histories are significantly larger than those from UO spent fuels with burn-ups of 45 GWd/THM. If a temperature below 80
spent fuels with burn-ups of 45 GWd/THM. If a temperature below 80 C is specified for cement-based materials used in waste packages after disposal, the allowable number of canisters containing compacted hull and end pieces in a package for 45 GWd-MOX needs to be limited to a value of 0.7 to 1.6, which is significantly lower than the value of 4.0 for 45 GWd-UO
C is specified for cement-based materials used in waste packages after disposal, the allowable number of canisters containing compacted hull and end pieces in a package for 45 GWd-MOX needs to be limited to a value of 0.7 to 1.6, which is significantly lower than the value of 4.0 for 45 GWd-UO .
.
Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Sakatani, Keiichi*; Yamamura, Yuki*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Noshita, Kenji*; Miura, Yoshiyuki*; Kanehira, Norio*; Ochi, Eiji*; Mukunoki, Atsushi*; Chiba, Tamotsu*
Dai-7-Kai Saishori, Risaikuru Bukai Semina Tekisuto, p.136 - 137, 2011/01
Conventional static test methods are not appropriate to evaluate glass dissolution behavior at an arbitrarily-fixed condition due to compositional change of the solution with glass dissolution. In this study, we applied a newly-devised micro-channel flow-through test method to measurement of the initial dissolution rates of Japanese simulated waste glasses, JAEA-P0798 and JNFL-KMOC, at arbitrarily-fixed conditions and we evaluated temperature and pH dependence of glass dissolution. The results showed that the initial dissolution rate increased with temperature and had "V-shaped" pH dependence at each temperature.
Makigaki, Hikaru*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Noshita, Kenji*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1193, p.307 - 314, 2009/05
By using micro-reactor flow-through test method we measured the initial dissolution rate of P0798 glass at 25 C as a function of pH between 5.6 and 12. The results showed that the initial dissolution rate determined by dissolution rate of Si has "V-shaped" pH dependency similar to R7T7 glass reported by CEA, France. We also measured the initial dissolution rate at pH 5.6 as a function of temperature between 25 and 90
C as a function of pH between 5.6 and 12. The results showed that the initial dissolution rate determined by dissolution rate of Si has "V-shaped" pH dependency similar to R7T7 glass reported by CEA, France. We also measured the initial dissolution rate at pH 5.6 as a function of temperature between 25 and 90 C, and the activation energy was evaluated to be 51 kJ/mol, which value is slightly smaller than that of R7T7 glass at pH 9 reported by CEA. On the basis of these results and comparison, we discussed the dissolution kinetics of P0798 glass.
C, and the activation energy was evaluated to be 51 kJ/mol, which value is slightly smaller than that of R7T7 glass at pH 9 reported by CEA. On the basis of these results and comparison, we discussed the dissolution kinetics of P0798 glass.
Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Makigaki, Hikaru*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Noshita, Kenji*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1193, p.219 - 228, 2009/05
We developed a new flow-through test method using micro-reactor, and applied it to measurement of the dissolution/alteration kinetics for a simulated HLW glass (P0798). In this method, a glass coupon is placed just on a Teflon plate having a micro-channel, and a solution is injected into the inlet of micro-channel by micro-syringe pump at a constant flow rate. The injected solution flows through the micro-channel reacting with the glass to the outlet, and the outlet solution is retrieved at certain intervals to be analyzed for determination of the dissolution/alteration rate. This method has some major features, i.e., simple test apparatus with compact size, high S/V ratio, sensitive/precise measurement of the glass dissolution/alteration rate, adequate glass shape for analysis of reacted glass surface, and so on. By use of this method the dissolution/alteration rate for P0798 was measured as a function of pH, temperature, flow rate, and time, and some available results were obtained to evaluate the dissolution/alteration kinetics.
Inagaki, Yaohiro*
JNC TJ8400 2004-019, 32 Pages, 2005/02
The purpose of this study(fiscal year 2001-2004) is to understand, qualitatively and quantitatively, the glass corrosion and associated elemetal release under assumed disposal conditions for long-term referring to geochemical mechanism in order to establish the validation for long-term corrosion/leaching model. This report(fiscal year 2004) discusses glass size dependence of the glass corrosion rate and leaching of Se from the glass on the basis of the results of corrosion tests performed with P0798 simulated HLW glass with four different sizes. The conclusions are; (1) the glass corrosion rate for the glass with four different sizes can be analyzed by use of hydration model (water diffusion model), and value of the diffusion coefficient is evaluated to be 10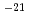 m
m /s at 120
/s at 120 C, (2) Se leaches from the glass congruently with Si, and the leached Se cannot precipitate under the present conditions, (3) the experimental results on glass corrosion rate including previous results of the temperature dependence and the rate in the presence of bentonite can be explained by use of the water diffusion model, which indicates that application of this model is available for confirming validity of the long-term corrosion/leaching model.
C, (2) Se leaches from the glass congruently with Si, and the leached Se cannot precipitate under the present conditions, (3) the experimental results on glass corrosion rate including previous results of the temperature dependence and the rate in the presence of bentonite can be explained by use of the water diffusion model, which indicates that application of this model is available for confirming validity of the long-term corrosion/leaching model.
Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Mitsui, Seiichiro*; Makino, Hitoshi*; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko*; Kamei, Gento*; Kawamura, Kazuhiro*; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Ueno, Kenichi*; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Yui, Mikazu*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu, 10(1-2), p.69 - 84, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Inagaki, Yaohiro*
JNC TJ8400 2003-055, 24 Pages, 2004/02
A large number of studies on aqueous corrosion of HLW glass have shown that the glass reacts with water to form more stable solid phases (alteration-phases or secondary phases). The process of alteration-phase formation is expected to play an important role in the radionuclide release from the glass, because it can affect both the glass dissolution rate and the retention of radionuclides in the phases. However, these processes of alteration and diffusion have not been evaluated in details. Therefore, a sound understanding of the glass corrosion mechanism under disposal conditions for long-term is expected to be essential for validation of the long-term performance. The purpose of this study (fiscal year 2001-2003) is to understand, qualitatively and quantitatively, the glass corrosion and associated elemetal release under assumed disposal conditions for long-term referring to geochemical mechanism in order to establish the validation for long-term corrosion/leaching model. This report (fiscal year 2003) discusses temperature dependence of the glass corrosion rate, effects of bentonite on the glass corrosion, and application of the results to the long-term corrosion model, on the basis of the results of corrosion tests performed with a simulated HLW galss, P0798, under various inditions. The conclusions are; 1) the glass corrosion rate can be analyzed by use of hydration(water diffusion) model, and values of the diffusion coefficient are evaluated to be 2 10
10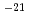 m
m /s (60
/s (60 C) to 5
C) to 5 10
10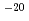 m
m /s (120
/s (120 C) with the activation energy of 52kJ/mol, 2) the presence of bentonite cannot affect the glass corrosion rate, but most of Cs released from the glass are sorbed on bentonite by ion-exchange, 3) application of the hydration (water diffusion) model to the long-term glass corrosion analysis indicates that the glass has higher potential than that evaluated in H12 report and the glass size is one of key parameters.
C) with the activation energy of 52kJ/mol, 2) the presence of bentonite cannot affect the glass corrosion rate, but most of Cs released from the glass are sorbed on bentonite by ion-exchange, 3) application of the hydration (water diffusion) model to the long-term glass corrosion analysis indicates that the glass has higher potential than that evaluated in H12 report and the glass size is one of key parameters.
Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Makino, Hitoshi; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko; Kamei, Gento; Kawamura, Kazuhiro; Maeda, Toshikatsu*
JNC TN8400 2003-036, 53 Pages, 2003/12
Obtain of sufficient data for the performance of high-level radioactive waste(HLW) glass and verification of a model for the radionuclide release from the HLW glass in the disposal condition are required in order to show the objective reliability. In this paper, some reports about performance assessment of HLW glass are reviewed and we clarify the problems to raise reliability comparing these reports.
Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Arima, Tatsumi*
JNC TY8400 2003-001, 72 Pages, 2003/05
None