Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 for brittle fracture in ductile-brittle transition temperature region
for brittle fracture in ductile-brittle transition temperature regionHojo, Kiminobu*; Hirota, Takatoshi*; Nagoshi, Yasuto*; Fukahori, Takuya*; Shimizu, Kazuma*; Shimodaira, Masaki; Ogawa, Takuya*; Yashirodai, Kenji*; Ohata, Mitsuru*; Minami, Fumiyoshi*
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/07
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Otani, Masashi*; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; et al.
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.636 - 641, 2022/09
The muon linac project for the precise measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic and electric dipole moments, which is currently one of the hottest issues of the elementary particle physics, is in progress at J-PARC. The muons from the J-PARC muon facility are once cooled to room temperature, then accelerated up to 212 MeV with a normalized emittance of 1.5  mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
Sumi, Kazumichi*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Sue, Yuki*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Otani, Masashi*; Saito, Naohito*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Yoshida, Mitsuhiro*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, p.012038_1 - 012038_6, 2022/07
The disk-loaded structures (DLS) in the muon LINAC are under development for the J-PARC muon g-2/EDM experiment. Four DLSs with an accelerating gradient of 20 MV/m take charge of muon acceleration from 40 MeV to 212 MeV, which corresponds to 70% to 94% of the speed of light. The quasi-constant gradient type TM01-2 /3 mode DLSs with gradually varying disk spacing was designed and it was confirmed that the cumulative phase slip due to the mismatch between muon and phase velocity can be suppressed to less than 2 degrees at the frequency of 2592 MHz. In addition, the optimum synchronous phase and the lattice were investigated to satisfy the requirements of the total emittance less than 1.5
/3 mode DLSs with gradually varying disk spacing was designed and it was confirmed that the cumulative phase slip due to the mismatch between muon and phase velocity can be suppressed to less than 2 degrees at the frequency of 2592 MHz. In addition, the optimum synchronous phase and the lattice were investigated to satisfy the requirements of the total emittance less than 1.5 mm mrad and the momentum spread less than 0.1% in RMS.
mm mrad and the momentum spread less than 0.1% in RMS.
 lepton
leptonInami, Kenji*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 186 of others*
Journal of High Energy Physics (Internet), 2022(4), p.110_1 - 110_13, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:69.46(Physics, Particles & Fields)Hirota, Takatoshi*; Nagoshi, Yasuto*; Hojo, Kiminobu*; Okada, Hiroshi*; Takahashi, Akiyuki*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Ueda, Takashi*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Yashirodai, Kenji*; Ohata, Mitsuru*; et al.
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/07
Inami, Toshiya*; Shobu, Takahisa; Ishii, Kenji*
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 57(3, Part 2), p.6400105_1 - 6400105_5, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Sue, Yuki*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(2), p.022804_1 - 022804_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.23(Physics, Nuclear)A destructive monitor to measure the longitudinal bunch width of a low-energy and low-intensity muon beam was developed. This bunch-width monitor (BWM) employed microchannel plates to detect a single muon with high time resolution. In addition, constant-fraction discriminators were adopted to suppress the time-walk effect. The time resolution was measured to be 65 ps in rms using a picosecond-pulsed laser. This resolution satisfied the requirements of the muon linac of the J-PARC E34 experiment. We measured the bunch width of negative-muonium ions accelerated with a radio-frequency quadrupole using the BWM. The bunch width was successfully measured to be  54
54  11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Otani, Masashi*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Matoba, Shiro*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012067_1 - 012067_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:79.08(Physics, Particles & Fields)Negative muonium atom ( e
e e
e , Mu
, Mu ) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu
) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu were 10
were 10 /s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu
/s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu averaged energy: it was 0.2
averaged energy: it was 0.2 0.1keV.
0.1keV.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.814 - 817, 2019/07
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.55 - 60, 2019/07
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 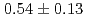 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Otani, Masashi*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.37 - 40, 2019/06
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 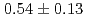 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Sue, Yuki*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Saito, Naohito; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2571 - 2574, 2019/06
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. Further improvement of the measurement system is needed to guarantee the required accuracy. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:99.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
 C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C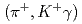 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 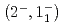 was measured to be
was measured to be 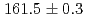 (stat)
(stat)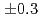 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 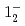 and
and 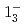 states were measured to be
states were measured to be 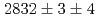 , keV and
, keV and 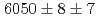 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.
Ishii, Kenji; Jarrige, I.*; Yoshida, Masahiro*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Inami, Toshiya; Murakami, Yoichi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 188, p.127 - 132, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:57.03(Spectroscopy)
Ishii, Kenji; Ishihara, Sumio*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kuzushita, Kaori*; Inami, Toshiya; Owada, Kenji; Yoshida, Masahiro; Jarrige, I.; Tatami, Naka*; et al.
Physical Review B, 83(24), p.241101_1 - 241101_4, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:62.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fujioka, Jun*; Yasue, Toshio*; Miyasaka, Shigeki*; Yamazaki, Yuichi*; Arima, Takahisa*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Inami, Toshiya; Ishii, Kenji; Tokura, Yoshinori*
Physical Review B, 82(14), p.144425_1 - 144425_12, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:85.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) up to 30T
up to 30TInami, Toshiya; Owada, Kenji; Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Ouyang, Z. W.*; Nojiri, Hiroyuki*; Matsumura, Takeshi*; Okuyama, Daisuke*; Murakami, Yoichi*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 211, p.012010_1 - 012010_6, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:74.75(Physics, Applied)Takeuchi, Kenji; Sanyoshi, Hirotaka; Fukuari, Yoshihiro; Inami, Shinichi
Proceedings of 7th International Conference on NDE in relation to Structural Integrity for Nuclear and Pressurized Components (CD-ROM), p.37 - 44, 2010/00
In the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP), lots of blowers are used for enclosing radioactive materials in a controlled area, and pumps are used for circulating cooling water to keep temperature under appropriate conditions of vessels, which contain high-level radioactive liquid waste. These rotating equipments play an important role in safety management of the nuclear facilities, where they are required stable conditions all the time. To improve the reliability of rotating equipments, the condition based maintenance for detecting the deterioration is one of the effective measures. According to the analyses of the past maintenance data obtained in TRP, it has been found that about 90% troubles related to the rotating equipment are caused in the bearing works, in which the lubrication was defective in almost every case. So, it is very important for stable operation of the rotating equipment to monitor the lubrication conditions in bearings. The vibration method facilitates to detect defects and abrasion of bearings by measuring a vibration signal. However, this method has a disadvantage that quantitative management for the lubrication conditions of bearings is not possible. Therefore, the shock pulse method, which is widely used for diagnosis of the bearings, is applied to assess the deterioration of rolling bearing. The shock pulse method can detect the change of the lubrication condition and the presence of defects in bearings, by a pressure wave generated from rotating rolling bearing. The method can also evaluate the oil slick thickness and the condition of deterioration in the bearing. As one of maintenance activities performed after monitoring, replenishment with a suitable amount of oil for a lubricant was able to be conducted with a proper timing. As a result, the number of the troubles on bearings has significantly reduced because proper maintenance for keeping the oil slick thickness can be carried out, which resulted in stable operation of the rotary equipmen
Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Her, J. L.*; Inami, Toshiya; Owada, Kenji; Ouyang, Z. W.*; Okada, Kyoko*; Nojiri, Hiroyuki*; Mitsuda, Akihiro*; Wada, Hirofumi*; Yoshimura, Kazuyoshi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 190, p.012019_1 - 012019_6, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:86.46(Physics, Condensed Matter)