Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Endo, Shunsuke; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Ino, Takashi*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kawamura, Shiori*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kobayashi, Ryuju*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 60(8), p.166_1 - 166_10, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)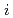 - and
- and  -processes following
-processes following  -process in the collapsar jet
-process in the collapsar jetHe, Z.*; Kajino, Toshitaka*; Kusakabe, Motohiko*; Zhou, S.-G.*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Chiba, Satoshi*; Li, H.*; Lin, Y.*
Astrophysical Journal Letters, 966(2), p.L37_1 - L37_7, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.74(Astronomy & Astrophysics)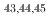 Cl via
Cl via 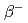 and
and 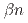 decay
decayTripathi, V.*; Bhattacharya, S.*; Rubino, E.*; Benetti, C.*; Perello, J. F.*; Tabor, S. L.*; Liddick, S. N.*; Bender, P. C.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Carroll, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.044320_1 - 044320_15, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Koyama, Shinichi; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Mitsugi, Takeshi; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Tsai, T.-H.; Takano, Masahide; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Satoshi; et al.
Hairo, Osensui, Shorisui Taisaku Jigyo Jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 216 Pages, 2023/11
In FY 2021 and 2022, JAEA perfomed the subsidy program for "the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy, Thermal Bahavior Estimation, and Simplified Analysis of Fuel Debris)" started in FY 2021. This presentation material summarized the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning, Contaminated Water and Treated Water Management.
Su, Y. H.; Oikawa, Kenichi; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Horino, Takashi*; Idohara, Osamu*; Misaka, Yoshitaka*; Tomota, Yo*
International Journal of Fatigue, 174, p.107729_1 - 107729_12, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:88.52(Engineering, Mechanical)Zhang, T.*; Tajima, Hiroyuki*; Sekino, Yuta*; Uchino, Shun; Liang, H.*
Communications Physics (Internet), 6, p.86_1 - 86_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.15(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically propose the laser-induced Andreev reflection between two-component Fermi superfluid and normal states via spatially-uniform Rabi couplings. By analyzing the tunneling current between the superfluid and normal states up to the fourth order in the Rabi couplings, we find that the Andreev current exhibits unconventional non-Ohmic transport at zero temperature. Remarkably, the Andreev current gives the only contribution in the synthetic junction system at zero detunings regardless of the ratio of the chemical potential bias to the superfluid gap, which is in sharp contrast to that in the conventional superconductor-normal metal junction. Our result may also pave a way for understanding the black hole information paradox through the Andreev reflection as a quantum-information mirror.
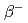 decay of exotic P and S isotopes with neutron number near 28
decay of exotic P and S isotopes with neutron number near 28Tripathi, V.*; Bhattacharya, S.*; Rubino, E.*; Benetti, C.*; Perello, J. F.*; Tabor, S. L.*; Liddick, S. N.*; Bender, P. C.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Carroll, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064314_1 - 064314_14, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:52.14(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Garc a-Tecocoatzi, H.*; Giachino, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Santopinto, E.*; Takeuchi, Sachiko*; Takizawa, Makoto*
a-Tecocoatzi, H.*; Giachino, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Santopinto, E.*; Takeuchi, Sachiko*; Takizawa, Makoto*
Few-Body Systems, 62(3), p.33_1 - 33_7, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.54(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the hidden-charm pentaquarks as hadronic molecules of 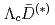 and
and 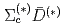 coupled to a
coupled to a 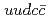 compact core by employing an interaction satisfying the heavy quark and chiral symmetries. Our model can consistently explain the masses and decay widths of
compact core by employing an interaction satisfying the heavy quark and chiral symmetries. Our model can consistently explain the masses and decay widths of 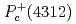 ,
, 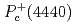 and
and 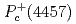 with spin parity assignments
with spin parity assignments 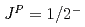 ,
, 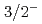 and
and 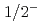 , respectively. We find that the mass ordering is dominantly determined by the short-range interaction given by coupling to the compact core, while the decay widths by the tensor force of the one-pion exchange.
, respectively. We find that the mass ordering is dominantly determined by the short-range interaction given by coupling to the compact core, while the decay widths by the tensor force of the one-pion exchange.
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.80(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:76.09(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Su, Y. H.; Oikawa, Kenichi; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Horino, Takashi*; Idohara, Osamu*; Misaka, Yoshitaka*; Tomota, Yo*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11, p.4155_1 - 4155_14, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:77.95(Multidisciplinary Sciences) pentaquarks with chiral tensor and quark dynamics
pentaquarks with chiral tensor and quark dynamicsYamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Garc a-Tecocoatzi, H.*; Giachino, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Santopinto, E.*; Takeuchi, Sachiko*; Takizawa, Makoto*
a-Tecocoatzi, H.*; Giachino, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Santopinto, E.*; Takeuchi, Sachiko*; Takizawa, Makoto*
Physical Review D, 101(9), p.091502_1 - 091502_7, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:94.98(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the hidden-charm pentaquarks as hadronic molecules of 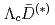 and
and 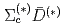 coupled to a
coupled to a 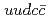 compact core by employing an interaction satisfying the heavy quark and chiral symmetries. Our model can consistently explain the masses and decay widths of
compact core by employing an interaction satisfying the heavy quark and chiral symmetries. Our model can consistently explain the masses and decay widths of 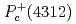 ,
, 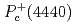 and
and 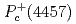 with spin parity assignments
with spin parity assignments 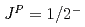 ,
, 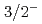 and
and 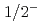 , respectively. We find that the mass ordering is dominantly determined by the short-range interaction given by coupling to the compact core, while the decay widths by the tensor force of the one-pion exchange.
, respectively. We find that the mass ordering is dominantly determined by the short-range interaction given by coupling to the compact core, while the decay widths by the tensor force of the one-pion exchange.
 s isomeric state in
s isomeric state in 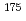 Ir
IrGillespie, S. A.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Al Monthery, M.*; Barton, C. J.*; Antalic, S.*; Auranen, K.*; Badran, H.*; Cox, D.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; O'Donnell, D.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(6), p.064310_1 - 064310_6, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27.77(Physics, Nuclear)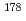 Hg
HgM ller-Gatermann, C.*; Dewald, A.*; Fransen, C.*; Auranen, K.*; Badran, H.*; Beckers, M.*; Blazhev, A.*; Braunroth, T.*; Cullen, D. M.*; Fruet, G.*; et al.
ller-Gatermann, C.*; Dewald, A.*; Fransen, C.*; Auranen, K.*; Badran, H.*; Beckers, M.*; Blazhev, A.*; Braunroth, T.*; Cullen, D. M.*; Fruet, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054325_1 - 054325_7, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:70.85(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Cs from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident; Simulations based on identical input data
Cs from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident; Simulations based on identical input dataSato, Yosuke*; Takigawa, Masayuki*; Sekiyama, Tsuyoshi*; Kajino, Mizuo*; Terada, Hiroaki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Kondo, Hiroaki*; Uchida, Junya*; Goto, Daisuke*; Qu lo, D.*; et al.
lo, D.*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 123(20), p.11748 - 11765, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:84.51(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)A model intercomparison of the atmospheric dispersion of  Cs emitted following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident was conducted by 12 models to understand the behavior of
Cs emitted following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident was conducted by 12 models to understand the behavior of  Cs in the atmosphere. The same meteorological data, horizontal grid resolution, and an emission inventory were applied to all the models to focus on the model variability originating from the processes included in each model. The multi-model ensemble captured 40% of the observed
Cs in the atmosphere. The same meteorological data, horizontal grid resolution, and an emission inventory were applied to all the models to focus on the model variability originating from the processes included in each model. The multi-model ensemble captured 40% of the observed  Cs events, and the figure-of-merit in space for the total deposition of
Cs events, and the figure-of-merit in space for the total deposition of  Cs exceeded 80. Our analyses indicated that the meteorological data were most critical for reproducing the
Cs exceeded 80. Our analyses indicated that the meteorological data were most critical for reproducing the  Cs events. The results also revealed that the differences among the models were originated from the deposition and diffusion processes when the meteorological field was simulated well. However, the models with strong diffusion tended to overestimate the
Cs events. The results also revealed that the differences among the models were originated from the deposition and diffusion processes when the meteorological field was simulated well. However, the models with strong diffusion tended to overestimate the  Cs concentrations.
Cs concentrations.
 is not a prerequisite for the core/shell ion tracks or ion shaping
is not a prerequisite for the core/shell ion tracks or ion shapingAmekura, Hiroshi*; Kluth, P.*; Mota-Santiago, P.*; Sahlberg, I.*; Jantunen, V.*; Leino, A. A.*; Vazquez, H.*; Nordlund, K.*; Djurabekova, F.*; Okubo, Nariaki; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 2(9), p.096001_1 - 096001_10, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:32.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)When a swift heavy ion (SHI) penetrates amorphous SiO , a core/shell (C/S) ion track is formed due to vaporization, where the ion track consists of a lower-density core and a higher-density shell. Here we reexamine this hypothesis. The MD simulations indicate that the vaporization is not induced under 50-MeV Si irradiation (
, a core/shell (C/S) ion track is formed due to vaporization, where the ion track consists of a lower-density core and a higher-density shell. Here we reexamine this hypothesis. The MD simulations indicate that the vaporization is not induced under 50-MeV Si irradiation (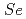 = 3 keV/nm), but the C/S tracks and the ion shaping of nanoparticles are nevertheless induced. Thus, the vaporization is not a prerequisite for the C/S tracks and the ion shaping.
= 3 keV/nm), but the C/S tracks and the ion shaping of nanoparticles are nevertheless induced. Thus, the vaporization is not a prerequisite for the C/S tracks and the ion shaping.
Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Marlow, J. B.*; Makino, Risa; Nakamura, Hironobu
LA-UR-17-23474, 28 Pages, 2017/04
The Inventory Verification Sample system (INVS) has been used for IAEA verification measurement at the Plutonium Conversion Development Facility for MOX powder and Pu solution samples (measurement uncertainty: about 3-5%). If the measurement uncertainty can be improved (to  1%), it is expected that the range of usage can be extended and it could reduce the number of destructive analyses. In order to improve the measurement uncertainty for solution samples, we conducted three different types of calibration method that are passive calibration curve method, known-
1%), it is expected that the range of usage can be extended and it could reduce the number of destructive analyses. In order to improve the measurement uncertainty for solution samples, we conducted three different types of calibration method that are passive calibration curve method, known- method and multiplicity method after optimization of detector parameter and sample position. In the range of concentration of typical solution samples, a good correlation was found between measured doubles and
method and multiplicity method after optimization of detector parameter and sample position. In the range of concentration of typical solution samples, a good correlation was found between measured doubles and  Pu effective mass in the three methods. Especially, the result of the conventional calibration curve method and known-
Pu effective mass in the three methods. Especially, the result of the conventional calibration curve method and known- method met our target uncertainty within 1% (22 hours measurement). Since it is thought that background singles change may affect measurement uncertainty, an additional shielding was installed around the INVS to reduce those effects. This shielding improved measurement uncertainty in known-
method met our target uncertainty within 1% (22 hours measurement). Since it is thought that background singles change may affect measurement uncertainty, an additional shielding was installed around the INVS to reduce those effects. This shielding improved measurement uncertainty in known- method. The results with this shielding suggests passive calibration method and known-
method. The results with this shielding suggests passive calibration method and known- method could achieve the target uncertainty within 1% less than 1 hour measurement time.
method could achieve the target uncertainty within 1% less than 1 hour measurement time.
 Es and
Es and  Bk
BkKonki, J.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Uusitalo, J.*; Greenlees, P. T.*; Auranen, K.*; Badran, H.*; Block, M.*; Briselet, R.*; Cox, D. M.*; Dasgupta, M.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 764, p.265 - 270, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:81.50(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Kraus, H.; Simin, D.*; Fuchs, F.*; Onoda, Shinobu; Makino, Takahiro; Dyakonov, V.*; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 11th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-11) (Internet), p.176 - 179, 2015/11