Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kokubun, Yuji; Hosomi, Kenji; Nagaoka, Mika; Seya, Natsumi; Inoue, Kazumi; Koike, Yuko; Uchiyama, Rei; Sasaki, Kazuki; Maehara, Yushi; Matsuo, Kazuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2024-054, 168 Pages, 2025/03
The Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories conducts environmental radiation monitoring around the reprocessing plant in accordance with the "Safety Regulations for Reprocessing Plant of JAEA, Part IV: Environmental Monitoring". This report summarizes the results of environmental radiation monitoring conducted during the period from April 2023 to March 2024 and the results of dose calculations for the surrounding public due to the release of radioactive materials from the plant into the atmosphere and ocean. In the results of the above environmental radiation monitoring, several items were affected by radioactive materials emitted from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Company, Incorporated (changed to Tokyo Electric Power Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016), which occurred in March 2011. In addition, environmental monitoring plan, analysis and measurement methods, monitoring data and their chronological change, meteorological data after statistical processing, status of radioactive waste release and evaluation results of the data over the normal range are included as appendices.
Yoshida, Keisuke; Kato, Shingo; Okuyama, Shinichi; Ishimori, Yuu; Inoue, Mutsuo*
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 24, p.1 - 12, 2024/08
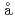 shetta lakes in the Soya Coast region and their paleoenvironmental significance with glacial isostatic adjustment in East Antarctica
shetta lakes in the Soya Coast region and their paleoenvironmental significance with glacial isostatic adjustment in East AntarcticaInoue, Genki*; Honda, Eisuke*; Ito, Keisuke*; Kang, I.*; Seto, Koji*; Tani, Yukinori*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Kashima, Kaoru*; Otani, Shuji*; Yamanaka, Toshiro*; et al.
Quaternary Science Reviews, 338, p.108822_1 - 108822_18, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geography, Physical)We studied Holocene paleolimnological changes inferred from biomarkers and microscopic observation of microalgae and cyanobacteria in sediment cores from Rundv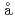 shetta lakes (Maruwanminami-ike and Maruwan o-ike) in the Soya Coast of East Antarctica, along with sedimentary facies and radiocarbon dating. Coastal marine environment: Maruwanminami-ike (147-72.5 cm, 5,010-2,590 cal BP) and Maruwan-oike (226-47.2 cm, 5,700-3,190 cal BP) were characterized by low biological production with the predominance of diatoms. Transition period of stratified brackish lake environment: Maruwanminami-ike (72.5-65.6 cm, 2,590-2,500 cal BP) and Maruwan-oike (47.2-28.8 cm, 3,190-2,890 cal BP) were characterized by stratified conditions with marine water overlain by freshwater, and a chemocline developed together with an anoxic layer in the bottom of photic zone.
shetta lakes (Maruwanminami-ike and Maruwan o-ike) in the Soya Coast of East Antarctica, along with sedimentary facies and radiocarbon dating. Coastal marine environment: Maruwanminami-ike (147-72.5 cm, 5,010-2,590 cal BP) and Maruwan-oike (226-47.2 cm, 5,700-3,190 cal BP) were characterized by low biological production with the predominance of diatoms. Transition period of stratified brackish lake environment: Maruwanminami-ike (72.5-65.6 cm, 2,590-2,500 cal BP) and Maruwan-oike (47.2-28.8 cm, 3,190-2,890 cal BP) were characterized by stratified conditions with marine water overlain by freshwater, and a chemocline developed together with an anoxic layer in the bottom of photic zone.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Oto, Tsutomu; Asano, Norikazu; Kawamata, Takanori; Yanai, Tomohiro; Nishimura, Arashi; Araki, Daisuke; Otsuka, Kaoru; Takabe, Yugo; Otsuka, Noriaki; Kojima, Keidai; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-018, 66 Pages, 2020/11
A collapse event of the cooling tower of secondary cooling system in the JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor) was caused by the strong wind of Typhoon No.15 on September 9, 2019. The cause of the collapse of the cooling tower was investigated and analyzed. As the result, it was identified that four causes occurred in combination. Thus, the soundness of the cooling tower of Utility Cooling Loop (UCL cooling tower), which is a wooden cooling tower installed at the same period as the cooling tower of secondary cooling system, was investigated. The items of soundness survey are to grasp the operation conditions of the UCL cooling tower, to confirm the degradation of structural materials, the inspection items and inspection status of the UCL cooling tower, and to investigate the past meteorological data. As the results of soundness survey of the UCL cooling tower, the improvement of inspection items of the UCL cooling tower was carried out and the replacement and repair of the structural materials of the UCL cooling tower were planned for safe maintenance and management of this facility. And the renewal plan of new cooling tower was created to replace the existing UCL cooling tower. This report is summarized the soundness survey of the UCL cooling tower.
Komura, Keitaro*; Kaneda, Heitaro*; Tanaka, Tomoki*; Kojima, Satoru*; Inoue, Tsutomu*; Nishio, Tomohiro
Geomorphology, 365, p.107214_1 - 107214_22, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:26.47(Geography, Physical)On the basis of pit excavations and sediment cores at an off-fault deep-seated gravitational slope deformation (DGSD) site and a trench excavation across the active Neodani fault at a nearby site, we examined the records of DGSD and surface-rupturing paleoearthquakes of the Neodani fault. We found the four most recent DGSD events and the four most recent surface-rupturing earthquakes, respectively and conclude that the ages of events are overlapped each other. We infer that static crustal strain from repeated seismogenic faulting plays an important role in the occurrence of DGSD events, at least in the immediate vicinity of active faults, although coseismic severe shaking would have at least some effect on them. Our case study suggests that off-fault DGSDs can be used to reconstruct or refine the paleoseismic history of a nearby active fault.
Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Takeyasu, Masanori; Mizutani, Tomoko; Isozaki, Tokuju*; Nagaoka, Mika; Hokama, Tomonori; Yokoyama, Hiroya; Nishimura, Tomohiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-034, 175 Pages, 2016/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2014 to March 2015. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co. in March 2011.
Watanabe, Yasuhiro; Tani, Norio; Inoue, Keigo*
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.628 - 631, 2014/06
no abstracts in English
Tobari, Hiroyuki; Inoue, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Dairaku, Masayuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi; Kuriyama, Masaaki*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(6-8), p.975 - 979, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The HV bushing, one of the ITER NB components, which is to be procured by JADA, is a multi-conductor feed through composed of five-stage double-layered insulator columns with large brazed ceramic ring and fiber reinforced plastic (FRP) ring. The HV bushing is a bulk head between insulation gas at 0.6 MPa and vacuum. The FRP ring is required to sustain the pressure load, seismic load and dead weight. Brazing area of the ceramic ring with Kovar is required to maintain vacuum leak tightness and pressure tightness against the air filled at 0.6 MPa. To design the HV bushing satisfying the safety factor of  3.5, mechanical analyses were carried out. As for the FRP ring, it was confirmed that isotropic fiber cloth FRP rings should be used for sufficient strength against shear stress. Also, shape and fixation area of the Kovar sleeve were modified to lower the stress at the joint area. As a result, a design of the insulator for the HV bushing was established satisfying the requirement.
3.5, mechanical analyses were carried out. As for the FRP ring, it was confirmed that isotropic fiber cloth FRP rings should be used for sufficient strength against shear stress. Also, shape and fixation area of the Kovar sleeve were modified to lower the stress at the joint area. As a result, a design of the insulator for the HV bushing was established satisfying the requirement.
 incident translational energy dependence
incident translational energy dependenceInoue, Keisuke*; Teraoka, Yuden
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 417, p.012034_1 - 012034_6, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:65.77(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)Shibata, Takanori; Terasaki, Ryo*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Inoue, Takashi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Taniguchi, Masaki; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Naotaka; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1515, p.177 - 186, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:92.25(Physics, Applied)In the neutral beam injector in JT-60SA, one of issues is that negative ion beam is partially intercepted at acceleration grids due to a spatial non-uniformity of negative ion production on large extraction area (0.9 0.45m
0.45m ). Previous experiments showed that fast electrons emitted from filament cathodes are transported in a longitudinal direction by
). Previous experiments showed that fast electrons emitted from filament cathodes are transported in a longitudinal direction by 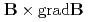 drift and the spatial distribution of electron temperature (
drift and the spatial distribution of electron temperature (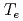 ) strongly relates with the non-uniformity. In this study, a three-dimensional electron transport analysis has been developed. Electron temperature in the analysis agreed well with measurements in JAEA 10A ion source. This study clarified that the bias of
) strongly relates with the non-uniformity. In this study, a three-dimensional electron transport analysis has been developed. Electron temperature in the analysis agreed well with measurements in JAEA 10A ion source. This study clarified that the bias of 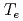 distribution are caused by the following reasons; (1) fast electrons drifted in the longitudinal direction survives near the end wall with energy up to
distribution are caused by the following reasons; (1) fast electrons drifted in the longitudinal direction survives near the end wall with energy up to  = 25-60 eV and (2) they produces thermal electrons by collision with plasma particles there.
= 25-60 eV and (2) they produces thermal electrons by collision with plasma particles there.
 H
H ion beam acceleration at JAEA for the ITER neutral beam injector
ion beam acceleration at JAEA for the ITER neutral beam injectorTobari, Hiroyuki; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Dairaku, Masayuki; Umeda, Naotaka; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Takemoto, Jumpei; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Inoue, Takashi; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 15(2), p.179 - 183, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Vacuum insulation is a common issue for the accelerator and the HV bushing for the ITER NBI. The HV bushing has five-stage structure and each stage consists of double-layered insulators. Hence, several triple points exist around the insulators. To reduce electric field at those points simultaneously, three types of stress ring were developed. In voltage holding test of a full-scale mockup equipped with those stress rings, 120% of rated voltage was sustained and the voltage holding capability required in ITER was verified. In the MeV accelerator, voltage holding capability was not sufficient due to breakdown triggered by electric field concentration at edge and corner on grid components. By extending gap length, 1 MV was sustained in vacuum. Furthermore, with new accelerator grids which compensates beam deflection due to magnetic field and space charge repulsion between beamlets, 980 keV, 185 A/m H
H ion beam acceleration was demonstrated, which was close to ITER requirement.
ion beam acceleration was demonstrated, which was close to ITER requirement.
 molecular beams on Ni(111) surface dependending on kinetic energy
molecular beams on Ni(111) surface dependending on kinetic energyInoue, Keisuke*; Teraoka, Yuden
Protection of Materials and Structures from the Space Environment; Astrophysics and Space Science Proceedings, Vol.32, p.521 - 530, 2013/00
Ono, Shinya*; Inoue, Kei*; Morimoto, Masahiro*; Arae, Sadanori*; Toyoshima, Hiroaki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Ogata, Shoichi*; Yasuda, Tetsuji*; Tanaka, Masatoshi*
Surface Science, 606(21-22), p.1685 - 1692, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:36.69(Chemistry, Physical) nitridation reactions at metal surfaces by molecular beams and their observation via synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy, 2
nitridation reactions at metal surfaces by molecular beams and their observation via synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy, 2Teraoka, Yuden; Inoue, Keisuke*; Jinno, Muneaki*; Harries, J.; Okada, Ryuta; Iwai, Yutaro*; Takaoka, Tsuyoshi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Komeda, Tadahiro*
Dai-56-Kai Nihon Gakujutsu Kaigi Zairyo Kogaku Rengo Koenkai Koen Rombunshu, p.360 - 361, 2012/10
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Yasuhiro; Tani, Norio; Inoue, Keigo*
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.531 - 533, 2012/08
In order to compensate a quadrupole component caused by edge filed in bump magnets, pulsed quadrupole magnets will be installed in the J-PARC RCS. The pulsed quadrupole-magnet power supply is required large voltage and low current ripple. This paper proposes a high-precision and wide dynamic range pulsed power supply.
Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Dairaku, Masayuki; Takemoto, Jumpei; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Kojima, Atsushi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(2), p.02B121_1 - 02B121_3, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:45.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)JAEA has developed the MeV accelerator to demonstrate 1 MeV, 200 A/m H
H ion beam acceleration required for ITER NBI. A key to realize such a high power accelerator is improvement of voltage holding capability. Based on detailed investigation of the voltage holding characteristics, MeV accelerator was modified to reduce electric field concentration by extending gaps between the grid supports and increasing curvature radiuses at the support corners. After the modifications, accelerator succeeded in sustaining -1 MV in vacuum without beam acceleration. Moreover, beam deflection due to the magnetic field for electron suppression and space charge repulsion was compensated by aperture displacement technique. As the result, beam deflection was compensated and voltage holding during the beam acceleration was improved. Beam parameter of the MeV accelerator was increased to 980 keV, 185 A/m
ion beam acceleration required for ITER NBI. A key to realize such a high power accelerator is improvement of voltage holding capability. Based on detailed investigation of the voltage holding characteristics, MeV accelerator was modified to reduce electric field concentration by extending gaps between the grid supports and increasing curvature radiuses at the support corners. After the modifications, accelerator succeeded in sustaining -1 MV in vacuum without beam acceleration. Moreover, beam deflection due to the magnetic field for electron suppression and space charge repulsion was compensated by aperture displacement technique. As the result, beam deflection was compensated and voltage holding during the beam acceleration was improved. Beam parameter of the MeV accelerator was increased to 980 keV, 185 A/m , which is close to the requirement of ITER accelerator.
, which is close to the requirement of ITER accelerator.
 nitridation reactions at metal surfaces by molecular beams and their observation via synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy
nitridation reactions at metal surfaces by molecular beams and their observation via synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopyTeraoka, Yuden; Inoue, Keisuke*; Jinno, Muneaki*; Harries, J.; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Dai-55-Kai Nihon Gakujutsu Kaigi Zairyo Kogaku Rengo Koenkai Koen Rombunshu, p.236 - 237, 2011/10
no abstracts in English
Kashiwagi, Mieko; Inoue, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Umeda, Naotaka; Grisham, L. R.*; Dairaku, Masayuki; Takemoto, Jumpei; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1390, p.457 - 465, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:88.26(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)In a five stage multi-aperture and multi-grid (MAMuG) accelerator in JAEA, beam acceleration tests are in progress toward 1 MeV, 200 A/m H
H ion beams for ITER. The 1 MV voltage holding has been successfully demonstrated for 4000 s with the accelerator of expanded gap length that lowered local electric field concentrations. The led to increase of the beam energy up to 900 keV-level. However, it was found that beamlets were deflected more in long gaps and direct interceptions of the deflected beamlet caused breakdowns. The beamlet deflection and its compensation methods were studied utilizing a three-dimensional multi beamlet analysis. The analysis showed that the 1 MeV beam can be compensated by a combination of the aperture offset of 0.8 mm applied in the electron suppression (ESG) and the metal bar called a field shaping plate with a thickness of 1 mm attached beneath the ESG. The paper reports analytical predictions and experimental results of the MAMuG accelerator.
ion beams for ITER. The 1 MV voltage holding has been successfully demonstrated for 4000 s with the accelerator of expanded gap length that lowered local electric field concentrations. The led to increase of the beam energy up to 900 keV-level. However, it was found that beamlets were deflected more in long gaps and direct interceptions of the deflected beamlet caused breakdowns. The beamlet deflection and its compensation methods were studied utilizing a three-dimensional multi beamlet analysis. The analysis showed that the 1 MeV beam can be compensated by a combination of the aperture offset of 0.8 mm applied in the electron suppression (ESG) and the metal bar called a field shaping plate with a thickness of 1 mm attached beneath the ESG. The paper reports analytical predictions and experimental results of the MAMuG accelerator.
Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Inoue, Takashi; Umeda, Naotaka; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Kojima, Atsushi; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1390, p.449 - 456, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.46(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)At JAEA, MeV accelerator has been developed as a proof-of-principle accelerator for ITER NBI. To achieve the acceleration of 1 MeV, 200 A/m beam required for ITER, improvement of the voltage holding capability is essential. Review of voltage holding results ever obtained with various geometries of the accelerators showed that voltage holding capability was about a half of that for ideal small electrode. This is due to local electric field concentration in the accelerators, such as edge and corner between grids and its support structures. Based on these results, accelerator was modified to reduce the electric field concentration by reshaping the support structures and expanding the gap length. After the modifications, voltage holding capability in vacuum was increased from 835 kV to 1 MV. Voltage holding progressed the energy and current to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m
beam required for ITER, improvement of the voltage holding capability is essential. Review of voltage holding results ever obtained with various geometries of the accelerators showed that voltage holding capability was about a half of that for ideal small electrode. This is due to local electric field concentration in the accelerators, such as edge and corner between grids and its support structures. Based on these results, accelerator was modified to reduce the electric field concentration by reshaping the support structures and expanding the gap length. After the modifications, voltage holding capability in vacuum was increased from 835 kV to 1 MV. Voltage holding progressed the energy and current to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m ).
).