Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Nakayoshi, Akira; Arai, Yoichi; Sato, Takumi; Ohgi, Hiroshi; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamaguchi, Yukako; Morishita, Kazuki; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-005, 418 Pages, 2023/12
For safe and steady decommissioning of Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), information concerning composition and physical/chemical properties of fuel debris generated in the reactors should be estimated and provided to other projects conducting the decommissioning work including the retrieval of fuel debris and the subsequent storage. For this purpose, in FY2021, samples of contaminants (the wiped smear samples and the deposits) obtained through the internal investigation of the 1F Unit 2 were analyzed to clarify the components and to characterize the micro-particles containing uranium originated from fuel (U-bearing particles) in detail. This report summarized the results of analyses performed in FY2021, including the microscopic analysis by SEM and TEM, radiation analysis, and elemental analysis by ICP-MS, as a database for evaluating the main features of each sample and the probable formation mechanism of the U-bearing particles.
 Pb and
Pb and  Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeV
Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeVIwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Sugihara, Kenta*;  elik, Y.*; et al.
elik, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 544, p.165107_1 - 165107_15, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:71.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The lack of double-differential cross-section (DDX) data for neutron production below the incident proton energy of 200 MeV hinders the validation of spallation models in technical applications, such as research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs). The present study aims to obtain experimental DDX data for ADS spallation target materials in this energy region and identify issues related to the spallation models by comparing them with the analytical predictions. The DDXs for the (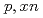 ) reactions of
) reactions of  Pb and
Pb and  Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30
Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30 to 150
to 150 using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Shibata, Daisuke*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Hasegawa, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Fukaya, Akane*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2023-004, 45 Pages, 2023/09
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the chemical state regarding boron (B), silicon (Si) and waste elements of iron (Fe), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. To understand the chemical stability of simulated waste glasses, XANES spectra of B K-edge, Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO
-edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO ) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO
) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO ) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L
) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na
-edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
 and O
and O in a reaction cell in triple quadrupole inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
in a reaction cell in triple quadrupole inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryKazama, Hiroyuki; Konashi, Kenji*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Koyama, Shinichi; Maeda, Koji; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Onishi, Takashi; Abe, Chikage*; Shikamori, Yasuyuki*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 38(8), p.1676 - 1681, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:60.75(Chemistry, Analytical)Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01023_1 - 01023_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron, lead, and bismuth have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics. The measured TTNYs and DDXs were compared with calculations by the Monte Carlo transport code PHITS with its default physics model of INCL version 4.6 combined with GEM and those with the JENDL-4.0/HE nuclear data library.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.435 - 449, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) for Fe, Pb, and Bi targets induced by 107-MeV protons were measured using the fixed-field alternating gradient accelerator at Kyoto University for research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs) and fundamental ADS reactor physics research at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). Note that TTNYs were obtained with the time-of-flight method using a neutron detector system comprising eight neutron detectors; each detector has a small NE213 liquid organic scintillator and photomultiplier tube. The TTNYs obtained were compared with calculation results using Monte Carlo-based spallation models (i.e., INCL4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, JQMD/GEM, and JQMD/SMM/GEM) and the evaluated high-energy nuclear data library, i.e., JENDL-4.0/HE, implemented in the particle and heavy iontransport code system (PHITS). All models, including JENDL-4.0/HE, failed to predict high-energy peaks at a detector angle of 5 . Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of
. Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of  20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.404 - 409, 2023/01
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2022-001, p.129 - 133, 2022/11
For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors composed of the NE213 liquid organic scintillators and photomultiplier tubes, which were connected to a multi-channel digitizer mounted with a field-programmable gate array (FPGA), for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination applying the gate integration method to the FPGA. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2022-008, 37 Pages, 2022/10
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, borosilicate glass frit and simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the chemical state regarding boron (B), silicon (Si) and waste elements of iron (Fe), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass surfaces after immersion test to investigate the long chemical stability. (1) As the leaching time of glass samples in immersion test passed, the Cs M , M
, M -edge XANES spectra disappeared and the Fe L
-edge XANES spectra disappeared and the Fe L , L
, L -edge spectra changed. (2) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and these changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. However, it became difficult to obtain a clear B K-edge XANES spectrum by forming a compound on glass surfaces. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits with different Na
-edge spectra changed. (2) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and these changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. However, it became difficult to obtain a clear B K-edge XANES spectrum by forming a compound on glass surfaces. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits with different Na O content were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na
O content were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The intensity of the Si K-edge peak is maximum when the Na
O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The intensity of the Si K-edge peak is maximum when the Na O content in glass frits was about 7wt%.
O content in glass frits was about 7wt%.
Kobayashi, Aine*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nakamura, Takeshi*; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Ishi, Koji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1031, p.166515_1 - 166515_12, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The beam power of the main ring of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) is currently being increased. For high-power beam realization, it is essential to suppress the beam instability that limits the beam power and to estimate and enact countermeasures against the beam coupling impedance of individual devices. The fast-extraction (FX) septum magnet will be replaced with another magnet that copes with higher numbers of repetition cycles. Despite their different structures, both septa demonstrated a large impedance in estimates performed by the CST studio suite wake-field solver. The widely used taper impedance-reduction method would be effective but receives spatial constraints. By attaching a copper plate and SiC to the flange of the septum magnet, we could effectively reduce the impedance. The copper plate on the flange reduces the impedance below the cut-off frequency. Moreover, when SiC was loaded, the remaining impedance was three times lower than when using the copper plate alone. After applying this method to the new septum magnet, the maximum longitudinal impedance was reduced to 1% of the value without countermeasures, largely improving the beam stability condition. We also estimated the required thickness of SiC and the calorific value. This method saves space and is installed by simple attachment to the flange, regardless of the shape of the beam pipe. Therefore, it is also applicable to other devices.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Ota, Toshiaki*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2021-010, 62 Pages, 2022/01
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, borosilicate glass frit and simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the local structure and chemical state regarding boron(B), oxygen(O), silicon(Si) and waste elements of iron(Fe), cesium(Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of prepared glass frit and simulated waste glass samples: (1) The effect of Na O concentration on B-O coordination structure is greater than that of the waste elements concentration. (2) The height of pre-edge by O K-edge spectrum depends on the concentration of first transition elements such as Fe in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate the long chemical stability. (1) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. (2) Cs on the sample surface after immersion test dissolves into the leaching solution. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits and simulated waste glass samples included lanthanides oxide were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na
O concentration on B-O coordination structure is greater than that of the waste elements concentration. (2) The height of pre-edge by O K-edge spectrum depends on the concentration of first transition elements such as Fe in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate the long chemical stability. (1) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. (2) Cs on the sample surface after immersion test dissolves into the leaching solution. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits and simulated waste glass samples included lanthanides oxide were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The peak height of the K-edge of Si differs depending on the kind of lanthanide.
O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The peak height of the K-edge of Si differs depending on the kind of lanthanide.
Abe, Yuta; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oishi, Yuji*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Nagae, Yuji; Sato, Ikken
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011075_1 - 011075_6, 2021/03
Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Abe, Yuta; Oishi, Yuji*; Kai, Tetsuya; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Harada, Masahide; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011074_1 - 011074_6, 2021/03
In the decommissioning of the Fukushima-Daiichi (1F) Nuclear Power Plant, it is essential to understand characteristics of the melted core materials. The estimation of boride in the real debris is of great importance to develop safe debris removal plans. Hence, it is required to investigate the amount of boron in the melted core materials with nondestructive methods. Prompt gamma-ray activation analysis (PGAA) is one of the useful techniques to determine the amount of borides by means of the 478 keV prompt gamma-ray from neutron absorption reaction of boron. Moreover, it is well known that the width of the 478 keV gamma-ray peak is typically broadened due to the Doppler effect. The degree of the broadening is affected by coexisting materials, and can be recognized by the width of the prompt gamma-ray peak. As a feasibility study, the prompt gamma-ray from boride samples were measured using the ANNRI, NOBORU, and RADEN beamlines at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of Japan Proton Accelerator Complex (J-PARC).
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Ota, Toshiaki*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2020-009, 48 Pages, 2020/09
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in waste glass varies with its chemical composition. In this study, borosilicate glass frit and simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the local structure and chemical state regarding boron (B), oxygen (O), and waste elements of cerium (Ce), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of prepared glass frit and simulated waste glass samples: (1) The existence ratio of four coordinate sp structure (BO
structure (BO ) tends to increase with increasing Na
) tends to increase with increasing Na O content in glass samples. (2) The height of a pre-edge which appears by K-edge XANES spectrum of O is so high that the Fe content in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate long chemical stability. (1) The existence ratio of four coordinate sp
O content in glass samples. (2) The height of a pre-edge which appears by K-edge XANES spectrum of O is so high that the Fe content in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate long chemical stability. (1) The existence ratio of four coordinate sp structure (BO
structure (BO ) increases by immersion test. (2) Ce which exists in the surface layer is oxidized by immersion test, and much of Cs in surface layer is lost after leach testing. Even if the glass frit form (fiber cartridge or beads) and manufacturing method were changed and a glass sample of the similar chemical composition was prepared, these observed Raman spectra of samples were different.
) increases by immersion test. (2) Ce which exists in the surface layer is oxidized by immersion test, and much of Cs in surface layer is lost after leach testing. Even if the glass frit form (fiber cartridge or beads) and manufacturing method were changed and a glass sample of the similar chemical composition was prepared, these observed Raman spectra of samples were different.
Abe, Yuta; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oishi, Yuji*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Nagae, Yuji; Sato, Ikken
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
Nagai, Takayuki; Sasage, Kenichi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Ota, Toshiaki*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*; Takahashi, Tomoe*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-003, 94 Pages, 2019/09
The local structures of glass-forming elements and waste elements would change by the chemical composition of waste glass including those elements. In this study, simulated waste glass samples were prepared from borosilicate glass frit including phosphorus (P) or vanadium (V), and we investigated local structures of boron, sodium, and waste elements in these P glass and V glass samples by using synchrotron XAFS measurements in soft and hard X ray region.
 Np and
Np and  Am by accelerator-driven system at Kyoto University Critical Assembly
Am by accelerator-driven system at Kyoto University Critical AssemblyPyeon, C. H.*; Yamanaka, Masao*; Oizumi, Akito; Fukushima, Masahiro; Chiba, Go*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Endo, Tomohiro*; Van Rooijen, W. G.*; Hashimoto, Kengo*; Sakon, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(8), p.684 - 689, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:72.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study demonstrates, for the first time, the principle of nuclear transmutation of minor actinide (MA) by the accelerator-driven system (ADS) through the injection of high-energy neutrons into the subcritical core at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly. The main objective of the experiments is to confirm fission reactions of neptunium-237 ( Np) and americium-241 (
Np) and americium-241 ( Am), and capture reactions of
Am), and capture reactions of  Np. Subcritical irradiation of
Np. Subcritical irradiation of  Np and
Np and  Am foils is conducted in a hard spectrum core with the use of the back-to-back fission chamber that obtains simultaneously two signals from specially installed test (
Am foils is conducted in a hard spectrum core with the use of the back-to-back fission chamber that obtains simultaneously two signals from specially installed test ( Np or
Np or  Am) and reference (uranium-235) foils. The first nuclear transmutation of
Am) and reference (uranium-235) foils. The first nuclear transmutation of  Np and
Np and  Am by ADS soundly implemented by combining the subcritical core and the 100 MeV proton accelerator, and the use of a lead-bismuth target, is conclusively demonstrated through the experimental results of fission and capture reaction events.
Am by ADS soundly implemented by combining the subcritical core and the 100 MeV proton accelerator, and the use of a lead-bismuth target, is conclusively demonstrated through the experimental results of fission and capture reaction events.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Yoshida, Makoto*; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 61st ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity and High-Brightness Hadron Beams (HB 2018) (Internet), p.116 - 121, 2018/07
The radiation damage model in the radiation transport code PHITS has been developed to calculate the basic data of the radiation damage including the energy of the target Primary Knock on Atom (PKA). For the high-energy proton incident reactions, a target PKA created by the secondary particles was more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile. To validate the radiation damage model in metals irradiated by  100 MeV protons, we developed a proton irradiation device with a Gifford-McMahon cryocooler to cryogenically cool wire samples. By using this device, the defect-induced electrical resistivity changes related to the DPA cross section of copper and aluminum were measured under irradiation with 125 and 200 MeV protons at cryogenic temperature. A comparison of the experimental data with the calculated results indicates that the DPA cross section with defect production efficiencies provide better quantitative descriptions.
100 MeV protons, we developed a proton irradiation device with a Gifford-McMahon cryocooler to cryogenically cool wire samples. By using this device, the defect-induced electrical resistivity changes related to the DPA cross section of copper and aluminum were measured under irradiation with 125 and 200 MeV protons at cryogenic temperature. A comparison of the experimental data with the calculated results indicates that the DPA cross section with defect production efficiencies provide better quantitative descriptions.
Sato, Yuji*; Tsukamoto, Masahiro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Yamashita, Yoshihiro*; Yamagata, Shuto*; Nishi, Takaya*; Higashino, Ritsuko*; Okubo, Tomomasa*; Nakano, Hitoshi*; Abe, Nobuyuki*
Applied Physics A, 124(4), p.288_1 - 288_6, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:61.68(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dynamics of titanium (Ti) melted by laser irradiation was investigated in a synchrotron radiation experiment. As an indicator of wettability, the contact angle between a selective laser melting (SLM) baseplate and the molten Ti was measured by synchrotron X-rays at 30 keV during laser irradiation. As the baseplate temperature increased, the contact angle decreased, down to 28 degrees at a baseplate temperature of 500 C. Based on this result, the influence of wettability of a Ti plate fabricated by SLM in a vacuum was investigated. It was revealed that the improvement of wettability by preheating suppressed sputtering generation, and a surface having a small surface roughness was fabricated by SLM in a vacuum.
C. Based on this result, the influence of wettability of a Ti plate fabricated by SLM in a vacuum was investigated. It was revealed that the improvement of wettability by preheating suppressed sputtering generation, and a surface having a small surface roughness was fabricated by SLM in a vacuum.
Naito, Fujio*; Anami, Shozo*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Uota, Masahiko*; Ouchi, Toshikatsu*; Onishi, Takahiro*; Oba, Toshiyuki*; Obina, Takashi*; Kawamura, Masato*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1244 - 1246, 2016/11
The proton linac installed in the Ibaraki Neutron Medical Research Center is used for production of the intense neutron flux for the Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). The linac consists of the 3-MeV RFQ and the 8-MeV DTL. Design average beam current is 10mA. Target is made of Beryllium. First neutron production from the Beryllium target was observed at the end of 2015 with the low intensity beam as a demonstration. After the observation of neutron production, a lot of improvement s was carried out in order to increase the proton beam intensity for the real beam commissioning. The beam commissioning has been started on May 2016. The status of the commissioning is summarized in this report.