Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Kawamoto, Koji; Yamada, Nobuto; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Sasao, Eiji; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-038, 137 Pages, 2014/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2013. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2013, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Kawamoto, Koji; Kuboshima, Koji*; Murakami, Hiroaki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji
JAEA-Research 2014-021, 30 Pages, 2014/11
The MIU (Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory) Project has three overlapping phases, Surface-based investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). Currently, the project is under Phase II and Phase III. One of Phase II goals is set up to develop and revise models of the geological environment using the investigation results obtained during excavation, and to determine and assess changes in the geological environment in response to excavation. This report aims at compiling results of study on geology and geological structure at the -500m Stage in the MIU construction site, investigated in the Phase II and provides the fundamental information on the geology and geological structure for future study and modeling of geological environment.
Kawamoto, Koji; Murakami, Hiroaki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Watanabe, Kazuhiko; Mikake, Shinichiro; Ikeda, Koki
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-014, 27 Pages, 2014/08
This document presents the data of geological investigations at the -500m stage of the MIU from the 2011 fiscal year to the 2013 fiscal year. At the -500m stage of the MIU, although the Cretaceous Toki granite is distributed, pegmatite, aplite and lampropyre dike are distributed partially.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi*; Tanno, Takeo*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Onoe, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-050, 114 Pages, 2014/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2012. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2012, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Katsuyama, Chie*; Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Ishibashi, Tomotaka*; Furuta, Kazuki*; Kinoshita, Takeshi*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Asano, Takahiro*; Sasaki, Yoshito; et al.
FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 86(3), p.532 - 543, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:36.72(Microbiology)Anaerobic microbial activity has a major influence on the subsurface environment, and should be considered in subsurface activities including the construction of radioactive waste repositories. We investigated denitrification and methanogenesis in anoxic groundwater from 140 m depth in two boreholes, where the redox potential fluctuated. The average maximum potential denitrification rates, measured under anaerobic conditions in the two boreholes using an  N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi; Tanno, Takeo; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-018, 169 Pages, 2013/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in 2011 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2011, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Kuboshima, Koji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Mizuno, Takashi; Sato, Toshinori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-028, 31 Pages, 2012/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU project is planned in three overlapping phases; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase I), Construction Phase (Phase II) and Operation Phase (Phase III). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase and the Operation Phase. This document introduces the research and development activities planned for 2012 fiscal year based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010, construction plan and research collaboration plan, etc.
 H
H and F
and F H
H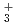
Suzuki, Kimichi*; Ishibashi, Hiroaki*; Yagi, Kiyoshi*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Progress in Theoretical Chemistry and Physics, 26, p.207 - 216, 2012/08
The quantum nature of the strong hydrogen bonds for the F H
H and F
and F H
H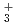 ions and their deuterated isotopomers at the room temperature has been studied using ab initio path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) simulations. It is found that, for both of these ions, the hydrogen-bonded H/D atoms largely fluctuate around the central position of two F atoms. The average FH/FF distances of F
ions and their deuterated isotopomers at the room temperature has been studied using ab initio path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) simulations. It is found that, for both of these ions, the hydrogen-bonded H/D atoms largely fluctuate around the central position of two F atoms. The average FH/FF distances of F H
H and F
and F H
H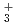 are longer than the average FD/FF distances of F
are longer than the average FD/FF distances of F D
D and F
and F H
H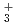 due to the primary/secondary isotope effects, which stem from the difference of the quantum nature of H and D nuclei. These results are compared with the family of Zundel-type ions, O
due to the primary/secondary isotope effects, which stem from the difference of the quantum nature of H and D nuclei. These results are compared with the family of Zundel-type ions, O H
H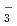 , N
, N H
H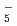 , O
, O H
H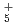 , and N
, and N H
H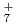 , which have been studied previously with the same ab initio PIMD approach. A comparison is also made with the previous experimental and ab initio vibrational configuration interaction results of F
, which have been studied previously with the same ab initio PIMD approach. A comparison is also made with the previous experimental and ab initio vibrational configuration interaction results of F H
H .
.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Ueno, Takashi; Tokuyasu, Shingo; Daimaru, Shuji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-020, 178 Pages, 2012/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II. And Phase III started in 2010 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2010, as a part of the Phase II based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002.
 H
H
 cation and N
cation and N H
H
 anion by
anion by  path integral molecular dynamics simulation
path integral molecular dynamics simulationIshibashi, Hiroaki*; Hayashi, Aiko*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
ChemPhysChem, 9(3), p.383 - 387, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:64.37(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Michihiro; Miyo, Hiroaki; ; Ishibashi, Yuzo;
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (10), p.43 - 49, 2001/03
None
; Ishibashi, Yuzo; Yoshida, Michihiro; Miyo, Hiroaki; Sukegawa, Yasuhiro*; *; Suzuki, Satoshi*
JNC TN8440 2000-020, 500 Pages, 2000/10
At outside waste storage pits, containers for storage of wastes corroded and were flooded, and it was confirmed on August 26, 1997. Confirmation of contamination of the pits outskirts, installation of sheets to prevent rainwater from flowing into the pits, drawing stay water were executed, promptly. Design and authorization works of the work house and waste treatment devices to take out wastes of the pits were executed too. After construction of the work house, taking out wastes of the pits started, and finished on April 10, 1998. Investigations of the inflow point of rainwater and leak of stay water were executed next. The results were reported to Science and Thechnology Agency (STA), adjoining authorities on December 21, 1998. After decontamination of the pits inner walls to background level of the radioactivity which included general concrete, control area was removed, and the pits were closed by concrete. Measures of closing of the pits were prepared from the middle of August, 1999, and dismantlement of unnecessary instruments started. Decontamination of the pits started from the begining of September, 1999. The above works finished on June 30, 2000. After decontamination of the pits, STA, adjoining authorities confirmed the circumstances. Work pouring concrete into the pits was executed three times (three levels), and finished on August 31, 2000. In addition t0 above, the amount of concrete poured into the pits was about 1,200 m .
.
Ishibashi, Tomotaka*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Katsuyama, Chie*; Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Kato, Kenji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Katsuyama, Chie*; Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Ishibashi, Tomotaka*; Furuta, Kazuki*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Suwa, Yuichi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sasao, Eiji; Yamada, Nobuto; Kuroiwa, Hiroshi; Kuboshima, Koji; Kawamoto, Koji; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Murakami, Hiroaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sasao, Eiji; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Kuboshima, Koji*; Murakami, Hiroaki
no journal, ,
Understanding of a range influenced by fault activity is quite important, because fault activity could lead to form and/or grow crushed zone and to increase water conductivity. We described fracture frequency, fracture filling and alteration along fracture, and then discuss relationship between those features and fault at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. As a result of the study, those features are dominant around faults in the Laboratory. Alteration along fracture and some of the fracture filling suggest inflow of hydrothermal fluid. This implies opening of fracture or reopening of existed fracture. We try to find the evidence of shear fracture in the future study, because fault activity would form shear fracture.
Ishibashi, Masayuki; Kawamoto, Koji; Sasao, Eiji; Murakami, Hiroaki; Yamada, Nobuto
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Sakai, Toshihiro; Murakami, Hiroaki; Ishibashi, Masayuki
no journal, ,
Existing data was analyzed in order to understand Hydrological and Geological Characterization of deep subsurface structures in and around the Main Shaft fault at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. As a result, in response to the low permeability structure of the Main Shaft Fault, fault gouges and alteration parts are found to be continuously distributed in the wall of the Main Shaft. One of the most high-permeable structure was estimated to be constituted by low-angle fractures with a sheet-like calcite. Shear of low angle fractures showed relatively low permeability. It may be possible to understand the permeability structure of these features in a drilling survey of granitic rocks.
Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Sakai, Toshihiro; Murakami, Hiroaki; Ishibashi, Masayuki
no journal, ,
It was carried out research on influences of the faults and fractures distribution and geological environment in granitic rocks, in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project. The geological model was updated based on the information of the distributions of lithofacies and geological structures at a depth 500m research galleries, and besides, the validity of the geological model of the site scale developed in the Phase I is confirmed by comparing with the updated model. The relationship between the permeability and fracture filling materials in granitic rocks was examined. As a result, it is confirmed that the water permeability is different by the kind of filling mineral dominant.
Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Yuguchi, Takashi*; Morikawa, Keita*; Murakami, Hiroaki
no journal, ,
Understanding of matrix diffusion is important for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in terms of retardation of mass transport in deep underground. Micropore is known to act as pathway of matrix diffusion. The authors found that micropore in plagioclase is important for matrix diffusion by the study of the Toki Granite, central Japan. Micropore in plagioclase is ubiquitous in the Toki Granite, while there is not much information in the other granitic rock in Japan. We investigated distribution of micropore in granitic rocks. Though only four samples were investigated at the moment, micropore in plagioclase was ubiquitously observed. Distribution of miecrocrack is heterogeneous in the different rock bodies and between two thin sections of one rock sample. We continue the observation of thin sections to confirm the distribution of micropore, and will perform through-diffusion experiment to understand relationship between micropore and matrix diffusion.