Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Yamazaki, Hayato*; Ishibashi, Kozue*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Sando, Kazusa*; Imura, Takumi*; Ono, Takeshi*
Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 226, p.105075_1 - 105075_9, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:49.4(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Simultaneous determination of the U-Pb age of zircon and concentration of titanium in a single analysis spot, using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with laser ablation sample introduction, produces paired age and temperature data of zircon crystallisation, potentially revealing time-temperature ( ) histories for evolved magma. The Kurobegawa granite, central Japan, contains abundant mafic magmatic enclaves (MMEs). We applied this method to evaluate MMEs and their host (enclosing) granites. Cooling behaviour common to both MMEs and host rocks was found between 1.5 and 0.5 Ma. Rapid cooling from the zircon crystallisation temperature to the closure temperature of biotite K-Ar system was within
) histories for evolved magma. The Kurobegawa granite, central Japan, contains abundant mafic magmatic enclaves (MMEs). We applied this method to evaluate MMEs and their host (enclosing) granites. Cooling behaviour common to both MMEs and host rocks was found between 1.5 and 0.5 Ma. Rapid cooling from the zircon crystallisation temperature to the closure temperature of biotite K-Ar system was within  1 million year. Combining the obtained
1 million year. Combining the obtained  paths of MMEs and host rocks with petrological information can provide insights into magma chamber processes. This suggests that MME flotation, migration, and spread through the magma chamber ceased at 1.5-0.5 Ma, indicating the emplacement age of the Kurobegawa granitic pluton, as no large-scale reheating episodes have occurred since then.
paths of MMEs and host rocks with petrological information can provide insights into magma chamber processes. This suggests that MME flotation, migration, and spread through the magma chamber ceased at 1.5-0.5 Ma, indicating the emplacement age of the Kurobegawa granitic pluton, as no large-scale reheating episodes have occurred since then.
 Sb
Sb O
O F
F observed by high-resolution synchrotron and neutron diffraction
observed by high-resolution synchrotron and neutron diffractionShimono, Seiya*; Ishibashi, Hiroki*; Nagayoshi, Yusuke*; Ikeno, Hidekazu*; Kawaguchi, Shogo*; Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Ichihashi, Katsuya*; Nishihara, Sadafumi*; et al.
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 163, p.110568_1 - 110568_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:15.7(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Yuguchi, Takashi*; Ishibashi, Kozue*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ito, Daichi*; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Yagi, Koshi*; Ono, Takeshi*
Lithos, 372-373, p.105682_1 - 105682_9, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.2(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Simultaneous determination of zircon U-Pb age and titanium concentration for a single analysis spot gives both the crystallization age and temperature. The crystallization age and temperature pairs in granitic zircons map the time-temperature ( ) path of granitic magma before its solidification. In laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) analysis, it is challenging to quantitatively analyse a low level of titanium concentration. This study employed two approaches using a Quadrupole mass spectrometer equipped with a collision/reaction cell (CRC). The methods were applied to zircon samples of the Kurobegawa granite (KRG), the Okueyama granite (OKG), the Toki granite (TKG), and the Tono plutonic complex (TPC) and provided U-Pb ages and titanium concentrations consistent with previous studies. The crystallization ages and temperatures collected from individual analysis spots of zircon samples in the KRG, OKG, TKG, and TPC are plotted in the
) path of granitic magma before its solidification. In laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) analysis, it is challenging to quantitatively analyse a low level of titanium concentration. This study employed two approaches using a Quadrupole mass spectrometer equipped with a collision/reaction cell (CRC). The methods were applied to zircon samples of the Kurobegawa granite (KRG), the Okueyama granite (OKG), the Toki granite (TKG), and the Tono plutonic complex (TPC) and provided U-Pb ages and titanium concentrations consistent with previous studies. The crystallization ages and temperatures collected from individual analysis spots of zircon samples in the KRG, OKG, TKG, and TPC are plotted in the  diagrams and enable us to characterize the rapid cooling paths at thermal conditions of zircon crystallization at the sampling sites.
diagrams and enable us to characterize the rapid cooling paths at thermal conditions of zircon crystallization at the sampling sites.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Usami, Akane*; Ishibashi, Masayuki
Heliyon (Internet), 6(8), p.e04815_1 - e04815_6, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.05(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The analysis of the distribution of microfractures and micropores is important to accurately characterise mass transfer within a rock body. In this paper, a new "simultaneous polarization-fluorescence microscopy" method is presented, which can be used to analyse the distribution of microscopic voids, including microfractures and micropores, in granitic rock. In this method, thin sections prepared with fluorescent dye are analysed under a polarizing microscope equipped with a fluorescent reflected light source. Using both the transmitted and the fluorescent light sources, both the distribution of microfractures and micropores, and petrographic characteristics (mineral occurrences) can be determined efficiently and simultaneously. The distribution of microfractures and micropores observed in images of granites obtained using simultaneous polarization-fluorescence microscopy is consistent with the distribution observed in backscattered electron images.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Shobuzawa, Kaho*; Ogita, Yasuhiro*; Yagi, Koshi*; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Nishiyama, Tadao*
American Mineralogist, 104(4), p.536 - 556, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.93(Geochemistry & Geophysics)This study describes the plagioclase alteration process with a focus on the role of micropores, mass transfer and reaction rate in the Toki granitic pluton, central Japan. The plagioclase alteration process involves albitization, K-feldspathization, and the formation of illite, calcite, fluorite and epidote. Such secondary minerals of hydrothermal origin in plagioclase within granitic rocks record the chemical characteristics of the hydrothermal fluid. Our results highlight (1) the nature of micropores such as distribution and volume in plagioclase, (2) the reaction nature of plagioclase alteration inferred by petrography and chemistry, (3) the physical conditions including alteration age and temperature, (4) the sequential variations of the fluid chemistry and (5) the mass transfer rate and reaction rate in the plagioclase alteration.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Iwano, Hideki*; Izumino, Yuya*; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Danhara, Toru*; Sasao, Eiji; Hirata, Takafumi*; Nishiyama, Tadao*
Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 169, p.47 - 66, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:64.05(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)This study presents position-by-position  paths within a granitic pluton based on thermochronological data, and describes their constraints and their relationship with fracture frequency, as an example from the Toki granite, central Japan. The cooling paths have position-specific characteristics; a single
paths within a granitic pluton based on thermochronological data, and describes their constraints and their relationship with fracture frequency, as an example from the Toki granite, central Japan. The cooling paths have position-specific characteristics; a single  path does not represent the cooling behavior of the entire pluton. Such position-specific
path does not represent the cooling behavior of the entire pluton. Such position-specific  paths enable us to evaluate three-dimensional thermal evolution within the granitic pluton, and thus can clarify the detailed formation history of the entire pluton after the incipient intrusion of the granitic magma into the shallow crust. This study reveals the relationship between position-specific
paths enable us to evaluate three-dimensional thermal evolution within the granitic pluton, and thus can clarify the detailed formation history of the entire pluton after the incipient intrusion of the granitic magma into the shallow crust. This study reveals the relationship between position-specific  paths and fracture frequency, and thus provides a criterion for evaluating the fracture population in terms of thermal stress.
paths and fracture frequency, and thus provides a criterion for evaluating the fracture population in terms of thermal stress.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Iwano, Hideki*; Danhara, Toru*; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Nishiyama, Tadao*
Island Arc, 26(6), p.e12219_1 - e12219_15, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:39.42(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The spatial distribution of AFT age in the granitic body is a favorable key to reveal a cooling behavior of the whole pluton. The cooling behavior is attributable to the regional exhumation of the Toki granite related to the regional denudation of the Tono district. Combination of the AERs and AFT inverse model applying to the granite is a powerful procedure for evaluating the cooling and exhumation history of the granitic pluton and thus denudation history of the tectonic region that surrounded the rock body.
Ishibashi, Masayuki; Yuguchi, Takashi*
Oyo Chishitsu, 58(2), p.80 - 93, 2017/06
Mode of granitic rocks is important information for evaluating their formation process, characterizing fracture distribution and understanding mass transfer in the rock matrix. However, previous methods to evaluate the mode of granitic rocks have several issues. Thus, this study provides the new image analysis method (MJPD method) using scanning X-ray analytical microscope for evaluation of mineral distribution and mode including the secondary minerals. The MJPD method can deal with the heterogeneity of elemental distribution in each mineral. For evaluating the applicability of MJPD method, the method was applied to elemental maps of thin sections. As a result, it was found out that the mineral distribution and mode are easily evaluated by MJPD method using the elemental maps measured in approximately 10,000 seconds. In addition, the MJPD method can be potentially applied to the elemental maps obtained by other analytical instrumentation such as EPMA and SEM-EDS.
Ishibashi, Masayuki; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Sasao, Eiji; Yuguchi, Takashi*
Engineering Geology, 208, p.114 - 127, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:76.83(Engineering, Geological)Damage zone (DS) formed by faulting in crystalline rocks can act as significant transport pathway. Therefore, this paper describes the features of WCFs and their long-term behavior associated with faulting based on the results of investigations at the GL -300m and -500m in the MIU. The results of detailed investigations in and around DZ indicate that there are three stages in the development of hydrogeological structures: 1st stage) the formation of background fractures; 2nd stage) the formation of a DZ and corresponding increase in the hydraulic permeability as a result of formation of small fractures; and 3rd stage) the formation of fracture fillings and the hydraulic permeability of the DZ decrease. In the late 3rd stage, unconsolidated clayey fillings formed associated with faulting resulting in decreased permeability of fractures in the DZ. These results underline the importance of understanding the development stages for evaluating the effect of faulting in orogenic belt plutons.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Iwano, Hideki*; Kato, Takenori*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Hattori, Kentaro*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Danhara, Toru*; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; et al.
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 111(1), p.9 - 34, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:54.24(Mineralogy)Zircon growth collected from a granitic pluton shows four (1st - 4th) events with specific mechanisms, crystallization temperatures and U-Pb ages, revealing the sequential formation process from intrusion through emplacement to crystallization / solidification. The events are recognized by: (1) internal structure of zircon based on the cathodoluminescence observation, (2) crystallization temperatures by the Ti-in-zircon thermometer in the internal structure and (3) U-Pb ages in the internal structure.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Kuwabara, Kazumichi; Ueno, Tetsuro; Onuki, Kenji*; Beppu, Shinji; Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-024, 122 Pages, 2015/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technical basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase III, as the Phase II was concluded for a moment with the completion of the excavation of horizontal tunnels at GL-500m level in February 2014. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2014.
Sasao, Eiji; Yuguchi, Takashi*; Ito, Yasuto*; Inoue, Takashi*; Ishibashi, Masayuki
Proceedings of 10th Asian Regional Conference of International Association for Engineering Geology and the Environment (IAEG ARS 2015) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2015/09
Understanding of the fracture network is important for disposal of high-level radioactive waste. We present our hypothesis on the formative mechanism of inhomogeneous distribution of fracture in the Toki Granite. In the Toki Granite, low- and high-angle fractures are abundant at the shallower part, while less at the deeper part where high-angle fracture is dominant. Distribution of the high-angle fracture is inhomogeneous. Thermochronological study revealed that the rapid cooling occurred at the early stage of granite formation. Paleomagnetic directions of the intact granite were dispersed. This suggests granite was plastically deformed during rapid cooling period. The rapid cooling might cause inhomogeneous distribution of cooling strain. When the granite reached to brittle deformation field, inhomogeneous fracture distribution was formed by the inhomogeneous strain. If so, recognition of the cooling history is essential to understand the distribution of the fracture network.
Yuguchi, Takashi; Sasao, Eiji; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Nishiyama, Tadao*
American Mineralogist, 100(5-6), p.1134 - 1152, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:72.97(Geochemistry & Geophysics)This paper describes the biotite chloritization process with a focus on mass transfer in the Toki granitic pluton, Central Japan, and also depicts the temporal variations in chemical characteristics of hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization during the sub-solidus cooling of the pluton. Singular value decomposition (SVD) analysis results in chloritization reaction equations for eight mineral assemblages, leading to the quantitative assessment of mass transfer between the reactant and product minerals, and inflow and outflow of components through the hydrothermal fluid. The matrices for SVD analysis consist of arbitrary combinations of molar volume and closure component in the reactant and product minerals. The eight reactions represent the temporal variations of chemical characteristics of the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization: the progress of chloritization results in gradual increase of silicon, potassium and chlorine and gradual decrease of calcium and sodium in the hydrothermal fluid with temperature decrease. The biotite chloritization involves two essential formation processes: Formation Process 1, small volume decrease from biotite to chlorite and large inflow of metallic ions from the hydrothermal fluid, and Formation Process 2, large volume decrease and large outflow of metallic ions into hydrothermal fluid. Chlorite produced during Formation Process 1 dominates over that of Formation Process 2, resulting in the gradual decrease of metallic components in the hydrothermal fluid with chloritization progress. The combination of continuous reactions based on compositional variations in chlorite together with corresponding continuous Al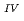 variations gives an indication of the temporal variations in rates of decreasing and increasing concentration of chemical components in the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization.
variations gives an indication of the temporal variations in rates of decreasing and increasing concentration of chemical components in the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Kawamoto, Koji; Yamada, Nobuto; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Sasao, Eiji; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-038, 137 Pages, 2014/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2013. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2013, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Ishibashi, Masayuki; Ando, Tomomi*; Sasao, Eiji; Yuguchi, Takashi; Nishimoto, Shoji*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*
Oyo Chishitsu, 55(4), p.156 - 165, 2014/10
Understanding of long-term history of water-conducting features such as flow-path fractures is key issue to evaluate deep geological environment for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Thus, we conducted study on the geological features and the long-term behavior of flow-path fractures based on the data obtained at -300m levels in the Mizunami Underground research laboratory (MIU), central Japan. Total 1670 fractures were mapped in underground gallery at the -300m levels. Flow-path fractures occupy about 11% of all fractures. The flow-path fractures are divided into grout filling fractures and low inflow-rate fractures. All of the grout filling fractures is filled with calcite as fracture filling minerals without conspicuous host rock alteration around fractures. The low inflow-rate fractures possessed similar geological character with the sealed fractures which are not acted as flow-path. The geological character of fracture filling and host tock alteration around fractures indicates the history of the formation at the time of intrusion and emplacement of host granite (Stage I), then filling at hydrothermal event (Stage II), and finally opening and elongation during exhumation stage (Stage III). In conclusion, the present flow-path fractures were formed by opening and/or elongation of pre-existed fractures, which were filled at the hydrothermal event, at the time of exhumation.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi*; Tanno, Takeo*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Onoe, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-050, 114 Pages, 2014/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2012. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2012, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi; Tanno, Takeo; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-018, 169 Pages, 2013/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in 2011 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2011, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
 -doped YAlO
-doped YAlO in the temperature range from 4.2 to 175 K
in the temperature range from 4.2 to 175 KYasumune, Takashi; Kurihara, Masakazu*; Maehata, Keisuke*; Ishibashi, Kenji*; Yoshikawa, Akira*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 726, p.37 - 40, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.54(Instruments & Instrumentation)Yb -doped yttrium-aluminum perovskites (YAP:Yb) are expected to be scintillator materials with high light yield and short scintillation decay time because of their charge transfer (CT) luminescence. Since the CT luminescence of Yb
-doped yttrium-aluminum perovskites (YAP:Yb) are expected to be scintillator materials with high light yield and short scintillation decay time because of their charge transfer (CT) luminescence. Since the CT luminescence of Yb is strongly affected by thermal quenching, to use YAP:Yb as a scintillator material, it is necessary to measure the scintillation properties of YAP:Yb at low temperatures. Since it is difficult to detect scintillation light at low temperatures, scintillation properties of YAP:Yb characterized by irradiating with
is strongly affected by thermal quenching, to use YAP:Yb as a scintillator material, it is necessary to measure the scintillation properties of YAP:Yb at low temperatures. Since it is difficult to detect scintillation light at low temperatures, scintillation properties of YAP:Yb characterized by irradiating with  -rays or other radiation below 100 K have not been reported. We conducted measurements of the temperature dependence of emission wavelength spectrum of YAP:Yb by irradiating with
-rays or other radiation below 100 K have not been reported. We conducted measurements of the temperature dependence of emission wavelength spectrum of YAP:Yb by irradiating with  -rays from a
-rays from a  Sr/
Sr/ Y source in the temperature range from 4.2 K to 175 K. The emission peak at around 340-350 nm and 500-520 nm were observed in the emission wavelength spectra. The light yield of YAP:Yb was characterized by using an avalanche photodiode in detection of 662 keV
Y source in the temperature range from 4.2 K to 175 K. The emission peak at around 340-350 nm and 500-520 nm were observed in the emission wavelength spectra. The light yield of YAP:Yb was characterized by using an avalanche photodiode in detection of 662 keV  -rays from a
-rays from a  Cs source in the temperature range from 50 K to 175 K. The light yield increased with decreasing temperature and reached 11,000 photons/MeV at a temperature of 4.2 K.
Cs source in the temperature range from 50 K to 175 K. The light yield increased with decreasing temperature and reached 11,000 photons/MeV at a temperature of 4.2 K.
Yuguchi, Takashi; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Morikawa, Keita; Kunimaru, Takanori
JAEA-Data/Code 2013-004, 38 Pages, 2013/06
Tono Geoscientific Research Unit of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is carrying out the Underground Research Laboratory Project, which is a scientific study revealing the deep geological environment as a basis of research and development for geological disposal of high level radioactive wastes. Nowadays, the project is under the Phase II and Phase III. In the 2011 fiscal year, rock specimens accompanied with grout-filling fracture were collected from -300m Access / Research Gallery of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory Construction Site, which were processed into thin sections, and then observed through polarizing microscopy. The grout-filling fracture can be identified as groundwater flow path and thus mass transfer pathway. Investigation methodology and petrological / mineralogical data are basic information for the study of mass transfer in Phase III. This paper presents sampling procedure of rock specimen accompanied with grout-filling fracture and compiles the results of these petrographical observations and analyses.
Kuboshima, Koji; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Tagami, Masahiko*; Yuguchi, Takashi
JAEA-Research 2012-037, 78 Pages, 2013/03
The MIU (Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory) Project has three overlapping phases, Surface-based investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). Currently, the project is under Phase II and Phase III. One of Phase II goals is set up to develop and revise models of the geological environment using the investigation results obtained during excavation, and to determine and assess changes in the geological environment in response to excavation. This report aims compiling results of study on geology and geological structure from the surface to G.L. -300m in the Phase II and provides the fundamental information on the geology and geological structure for future study. The compiling results of this report reflected basic data are utilized in the updating of the geological models in the Phase II.