Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishibashi, Atsushi; Masui, Kenji; Goto, Yuichi; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo; Ishikawa, Satoshi*; Ishikawa, Tomoya*
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-19-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.18 - 21, 2023/08
An inner-box typed hot cell for analysis of highly radioactive samples has been operated for about 40 years in Tokai Reprocessing Plant since its installation in 1980. During the operation of analytical hot cell, improvement and upgrades including auxiliary equipment have been performed, in addition to keep the equipment in proper condition through periodic inspections and maintenance. This paper describes about these efforts for analytical hot cell and its results.
 trapped and polarized in a CO
trapped and polarized in a CO matrix
matrixYamakawa, Koichiro; Ishibashi, Atsuki*; Namiyoshi, Toshinobu*; Azuma, Yuichi*; Arakawa, Ichiro*
Physical Review B, 102(4), p.041401_1 - 041401_5, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.9(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)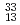 Al
Al ground state
ground stateHeylen, H.*; De Rydt, M.*; Neyens, G.*; Bissell, M. L.*; Caceres, L.*; Chevrier, R.*; Daugas, J. M.*; Ichikawa, Yuichi*; Ishibashi, Yoko*; Kamalou, O.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_5, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:91.78(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Katsuyama, Chie*; Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Ishibashi, Tomotaka*; Furuta, Kazuki*; Kinoshita, Takeshi*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Asano, Takahiro*; Sasaki, Yoshito; et al.
FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 86(3), p.532 - 543, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:36.72(Microbiology)Anaerobic microbial activity has a major influence on the subsurface environment, and should be considered in subsurface activities including the construction of radioactive waste repositories. We investigated denitrification and methanogenesis in anoxic groundwater from 140 m depth in two boreholes, where the redox potential fluctuated. The average maximum potential denitrification rates, measured under anaerobic conditions in the two boreholes using an  N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
Katsuyama, Chie*; Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Ishibashi, Tomotaka*; Furuta, Kazuki*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Suwa, Yuichi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Satoshi; Kinase, Sakae; Saito, Kimiaki; Takahashi, Tomoyuki*; Kurosawa, Naohiro*; Ryufuku, Susumu*; Hayashi, Hiroko*; Ishibashi, Kazufusa*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Nemoto, Hisashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Satoshi; Kinase, Sakae; Saito, Kimiaki; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Ryufuku, Susumu*; Ishibashi, Kazufusa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Satoshi; Kinase, Sakae; Saito, Kimiaki; Takahashi, Tomoyuki*; Kanno, Mitsuhiro*; Hayashi, Hiroko*; Ishibashi, Kazufusa*; Kurosawa, Naohiro*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Nemoto, Hisashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sugiyama, Koichi*; Go, Shintaro*; Tomimatsu, Taro*; Kai, Tamito*; Nagae, Daisuke*; Ishibashi, Yuichi*; Matsunaga, Sotaro*; Nagata, Yuto*; Nishibata, Hiroki*; Washiyama, Kohei*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have successfully performed in-beam gamma-ray spectroscopy using the isomer-scope technique to study excited-state structure of neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei. The neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei were produced in the multinucleon-transfer reactions with a  Cm target and
Cm target and  O projectiles accelerated with the JAEA tandem accelerator. Projectile-like scattered particles were detected with Si E-
O projectiles accelerated with the JAEA tandem accelerator. Projectile-like scattered particles were detected with Si E- E telescopes placed at the backward angle, and target-like scattered particles of isomers were caught by an annular aluminum plate placed at about 60-mm downstream from the target. Four Ge detectors and 4 LaBr detectors were placed at the periphery of the aluminum plate, and detected gamma rays from the isomers. Gamma rays emitted from the actinide isomers were successfully observed with a good sensitivity owing to the tungsten shield placed between the target and the detectors.
E telescopes placed at the backward angle, and target-like scattered particles of isomers were caught by an annular aluminum plate placed at about 60-mm downstream from the target. Four Ge detectors and 4 LaBr detectors were placed at the periphery of the aluminum plate, and detected gamma rays from the isomers. Gamma rays emitted from the actinide isomers were successfully observed with a good sensitivity owing to the tungsten shield placed between the target and the detectors.
Asai, Masato; Ishibashi, Yuichi*; Niwase, Toshitaka*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Ito, Yuta; Sato, Tetsuya; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakaguchi, Satoshi*; Morita, Kosuke*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
Solar cells for power generation can be used as a high-energy heavy-ion detector because it has diode characteristics. To utilize the solar cells for fission-fragment measurements, we have investigated the response (energy resolution and pulse height defect) of a solar cell to heavy ions of various nuclides with several different energies.
 Md
MdAsai, Masato; Ishibashi, Yuichi*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Aoki, Ryota*; Ito, Yuta; Uchibaba, Yuta*; Orlandi, R.; Gong, G.-M.*; Suzaki, Fumi; et al.
no journal, ,
Measurement of mass and total kinetic energy (TKE) distribution for the spontaneous fission (SF) of  Md has been performed to clarify the fission mechanism in the neutron-rich fermium region.
Md has been performed to clarify the fission mechanism in the neutron-rich fermium region.  Md nuclei were produced with the
Md nuclei were produced with the  Es target and
Es target and  O beam, and mass-separated with an on-line isotope separator (ISOL). We discuss the mechanism of fission observed in the SF of
O beam, and mass-separated with an on-line isotope separator (ISOL). We discuss the mechanism of fission observed in the SF of  Md on the basis of the observed mass-TKE distribution.
Md on the basis of the observed mass-TKE distribution.