Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Nakama, Shigeo; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ochi, Kotaro; Sawahata, Yoshiro*; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-022, 170 Pages, 2025/03
On March 11, 2011, the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake caused a tsunami that led to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, releasing radioactive material into the environment. Since then, Aerial Radiation Monitoring (ARM) using manned helicopters has been employed to measure radiation distribution. As a commissioned project from the Nuclear Regulation Authority, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) utilizes this technology for emergency monitoring during nuclear facility accidents, aiming to provide prompt results by pre-arranging information on background radiation, topography, and control airspaces around nuclear power plants nationwide. In fiscal year 2023, the commissioned project included conducting ARM around the Sendai Nuclear Power Station and preparing related information. To enhance effectiveness during emergencies, ARM and the first domestic training flight of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) were conducted during the FY2023 Nuclear Energy Disaster Prevention Drill. Furthermore, UAVs radiation monitoring technology was advanced by selecting UAVs and investigating their performance. This report summarizes the results and technical issues identified providing insights to improve emergency preparedness.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Nakama, Shigeo; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ochi, Kotaro; Nagakubo, Azusa; Sawahata, Yoshiro*; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-021, 232 Pages, 2025/03
The 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake on March 11, 2011, caused a tsunami that led to the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident, releasing a large amount of radioactive material into the surrounding environment. Since the accident, Aerial Radiation Monitoring (ARM) has been used to quickly and widely measure radiation distribution. As a commissioned project from the Nuclear Regulation Authority, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has continuously conducted ARM around FDNPS using manned and unmanned helicopters. This report summarizes the monitoring results for fiscal year 2023, evaluates changes in dose rate from past results, and discusses the factors contributing to these changes. Additionally, an analysis considering terrain undulation was conducted to improve accuracy for converting ARM data into dose rate. Furthermore, a method to discriminate airborne radon progeny was applied for ARM results to evaluate its impact. Moreover, to perform wide-area monitoring more efficiently, we advanced the development of unmanned airplane monitoring technology.
Muramatsu, Ken; Kubo, Kotaro; Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Takada, Tsuyoshi
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/03
no abstracts in English
Ochi, Kotaro; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ishida, Mutsushi*; Sanada, Yukihisa
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.103 - 107, 2019/01
After the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident, a large amount of radionuclides was spread out all over the world. In our previous study, we developed the aerial radiation monitoring technique using unmanned helicopter for investigating the dose rate derived deposited radionuclides over wide area. In addition, many monitoring techniques were developed for investigating the local distribution of radionuclides using unmanned aerial vehicle, handheld instrument and car within small area. Distinction of these methods depends on desirable position resolution of dose rate. However, the comparison method of the measurement result between different methods is not established. In this study, we attempted to evaluate the some methods of airborne and ground radiation measurement in same extended farm.
 -ray spectra obtained via aerial radiation monitoring using an unmanned helicopter
-ray spectra obtained via aerial radiation monitoring using an unmanned helicopterOchi, Kotaro; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ishida, Mutsushi*; Hamamoto, Shoichiro*; Nishimura, Taku*; Sanada, Yukihisa
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(8), p.926_1 - 926_14, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.21(Environmental Sciences)After the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, the vertical distribution of radiocesium in soil has been investigated to better understand the behavior of radiocesium in the environment. The typical method used for measuring the vertical distribution of radiocesium is troublesome because it requires collection and measurement of the activity of soil samples. In this study, we established a method of estimating the vertical distribution of radiocesium by focusing on the characteristics of  -ray spectra obtained via aerial radiation monitoring using an unmanned helicopter. In this method, the change in the ratio of direct
-ray spectra obtained via aerial radiation monitoring using an unmanned helicopter. In this method, the change in the ratio of direct  rays to scattered
rays to scattered  rays at various depths in the soil was utilized to quantify the vertical distribution of radiocesium. The results show a positive correlation between the abovementioned and the actual vertical distributions of radiocesium measured in the soil samples.
rays at various depths in the soil was utilized to quantify the vertical distribution of radiocesium. The results show a positive correlation between the abovementioned and the actual vertical distributions of radiocesium measured in the soil samples.
 C
C ; Direct observation with resonant X-ray diffraction
; Direct observation with resonant X-ray diffractionTanaka, Yoshikazu*; Inami, Toshiya; Lovesey, S. W.*; Knight, K. S.*; Yakhou, F.*; Mannix, D.*; Kokubun, Jun*; Kanazawa, Masayuki*; Ishida, Kotaro*; Nanao, Susumu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 69(2), p.024417_1 - 024417_11, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:78.94(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Direct evidence of the spatial ordering of Dy 4 quadrupole and hexadecapole moments in DyB
quadrupole and hexadecapole moments in DyB C
C is demonstrated by resonant X-ray diffraction enhanced by an electric quadrupole event (
is demonstrated by resonant X-ray diffraction enhanced by an electric quadrupole event ( 2 resonance) at the Dy L
2 resonance) at the Dy L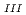 absorption edge. The diffraction data show that the structural phase transition at
absorption edge. The diffraction data show that the structural phase transition at 
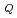 = 24.7 K is accompanied by a reduction in the symmetry of the Dy site to 2/
= 24.7 K is accompanied by a reduction in the symmetry of the Dy site to 2/ , from 4/
, from 4/ , and the spatial ordering of the time-even Dy multipoles with A
, and the spatial ordering of the time-even Dy multipoles with A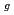 character. Below
character. Below 
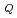 the crystal structure is described by the space group
the crystal structure is described by the space group  4
4 /
/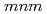 and Dy ions occupy sites (4
and Dy ions occupy sites (4 ). The distortion at T
). The distortion at T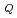 involves the lattice occupied by B and C ions, and it amounts to a buckling of B-C planes that are normal to the two-fold rotation axis of 2/
involves the lattice occupied by B and C ions, and it amounts to a buckling of B-C planes that are normal to the two-fold rotation axis of 2/ . An immediately plausible model of low-energy Dy states correlates data on the specific heat, our X-ray diffraction signals, and magnetic ordering below 15.3 K which has been observed in magnetic neutron diffraction.
. An immediately plausible model of low-energy Dy states correlates data on the specific heat, our X-ray diffraction signals, and magnetic ordering below 15.3 K which has been observed in magnetic neutron diffraction.
 -ray spectra obtained by airborne radiation monitoring
-ray spectra obtained by airborne radiation monitoringOchi, Kotaro; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ishida, Mutsushi*; Sato, Tomohiko*; Hamamoto, Shoichiro*; Nishimura, Taku*; Sanada, Yukihisa
no journal, ,
A large amount of radiocesium ( Cs &
Cs &  Cs) were released into the atmosphere as a result of 2011 Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident. To estimate the impact of the accident to the environment, dose rate around FDNPP have been measured by MEXT. Dose rate nearby FDNPP, however, still stay high even though decontamination work was carried out, which means it is necessary to develop an effective decontamination method promptly. Information of depth profile of radiocesium in soil is required to realize it, though, most of measurement methods have trouble due to collection and measurement of soil samples. As we have developed the radiation measurement techniques using unmanned aerial vehicle to measure dose rate distribution over wide areas for years, we attempt to establish the estimation method of depth profile of radiocesium in soil based on characteristics of
Cs) were released into the atmosphere as a result of 2011 Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident. To estimate the impact of the accident to the environment, dose rate around FDNPP have been measured by MEXT. Dose rate nearby FDNPP, however, still stay high even though decontamination work was carried out, which means it is necessary to develop an effective decontamination method promptly. Information of depth profile of radiocesium in soil is required to realize it, though, most of measurement methods have trouble due to collection and measurement of soil samples. As we have developed the radiation measurement techniques using unmanned aerial vehicle to measure dose rate distribution over wide areas for years, we attempt to establish the estimation method of depth profile of radiocesium in soil based on characteristics of  -ray spectra obtained by airborne radiation monitoring in this paper.
-ray spectra obtained by airborne radiation monitoring in this paper.
Kubo, Kotaro; Muramatsu, Ken; Takito, Kiyotaka; Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Takada, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ochi, Kotaro; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ishida, Mutsushi*; Sanada, Yukihisa
no journal, ,
In previous studies, our group have developed the airborne radiation measurement (ARM) technique. We mounted a radiation detector under an unmanned aerial vehicle to evaluate the deposition of Fukushima accident-derived radiocesium over wide area. In this study, we performed ARM with mounting a LaBr (Ce) detector under an unmanned helicopter. A rapid and simple estimation of depth profile of radiocesium in soil was developed on the basis of the relationship between spectra obtained via ARM and actual depth profile of radiocesium. Our goal is same to series 1 that we attempt to achieve the advancement of airborne radiation measurement technique.
(Ce) detector under an unmanned helicopter. A rapid and simple estimation of depth profile of radiocesium in soil was developed on the basis of the relationship between spectra obtained via ARM and actual depth profile of radiocesium. Our goal is same to series 1 that we attempt to achieve the advancement of airborne radiation measurement technique.
 (Ce) detector for estimating radiocesium distribution in soil
(Ce) detector for estimating radiocesium distribution in soilOchi, Kotaro; Malins, A.; Ishida, Mutsushi*; Yamada, Tsutomu*; Nakasone, Takamasa*; Sanada, Yukihisa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takada, Tsuyoshi; Nishida, Akemi; Choi, B.; Takito, Kiyotaka; Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Muramatsu, Ken; Kubo, Kotaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kubo, Kotaro*; Takito, Kiyotaka; Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Muramatsu, Ken; Takada, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishida, Akemi; Choi, B.; Kubo, Kotaro; Takito, Kiyotaka; Muramatsu, Ken; Takada, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English