Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 19(11), p.1888 - 1894, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2776, p.012009_1 - 012009_9, 2024/06
Ishida, Takekazu*; Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 214(3-4), p.152 - 157, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied) single crystals based on Bragg-dip analysis using a delay-line superconducting sensor
single crystals based on Bragg-dip analysis using a delay-line superconducting sensorShishido, Hiroaki*; Vu, TheDang*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(4), p.1108 - 1113, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:41.77(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Shishido, Hiroaki*; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Vu, TheDang*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(9), p.2400505_1 - 2400505_5, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.73(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)In this study, we employed a superconducting detector, current-biased kinetic-inductance detector (CB-KID) for neutron imaging using a pulsed neutron source. We employed the delay-line method, and high spatial resolution imaging with only four reading channels was achieved. We also performed wavelength-resolved neutron imaging by the time-of-flight method. We obtained the neutron transmission images of a Gd-Al alloy sample, inside which single crystals of GdAl were grown, using the delay-line CB-KID. Single crystals were well imaged, in both shapes and distributions, throughout the Al-Gd alloy. We identified Gd nuclei via neutron transmissions that exhibited characteristic suppression above the neutron wavelength of 0.03 nm. In addition, the
were grown, using the delay-line CB-KID. Single crystals were well imaged, in both shapes and distributions, throughout the Al-Gd alloy. We identified Gd nuclei via neutron transmissions that exhibited characteristic suppression above the neutron wavelength of 0.03 nm. In addition, the 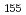 Gd resonance dip, a dip structure of the transmission caused by the nuclear reaction between an isotope and neutrons, was observed even when the number of events was summed over a limited area of 15
Gd resonance dip, a dip structure of the transmission caused by the nuclear reaction between an isotope and neutrons, was observed even when the number of events was summed over a limited area of 15  m
m  12
12  m. Gd selective imaging was performed using the resonance dip of
m. Gd selective imaging was performed using the resonance dip of 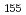 Gd, and it showed clear Gd distribution even with a limited neutron wavelength range of 1 pm.
Gd, and it showed clear Gd distribution even with a limited neutron wavelength range of 1 pm.
Vu, TheDang; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1006, p.165411_1 - 165411_8, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.88(Instruments & Instrumentation)Shishido, Hiroaki*; Vu, TheDang*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1975, p.012023_1 - 012023_8, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Vu, TheDang; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
Superconductor Science and Technology, 34(1), p.015010_1 - 015010_10, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:35.89(Physics, Applied)Shishido, Hiroaki*; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Vu, TheDang*; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Hidaka, Mutsuo*; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1590, p.012033_1 - 012033_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.74(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Vu, TheDang; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Hidaka, Mutsuo*; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1590, p.012036_1 - 012036_9, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:85.96(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Malins, A.; Machida, Masahiko; Vu, TheDang; Aizawa, Kazuya; Ishida, Takekazu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 953, p.163130_1 - 163130_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:49.74(Instruments & Instrumentation)Iizawa, Yuki*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Vu, TheDang*; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Hidaka, Mutsuo*; et al.
Superconductor Science and Technology, 32(12), p.125009_1 - 125009_8, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:58.57(Physics, Applied) B converter
B converterVu, TheDang; Iizawa, Yuki*; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Kojima, Kenji*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Hidaka, Mutsuo*; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1293, p.012051_1 - 012051_9, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:94.99(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) B conversion layer
B conversion layerMiyajima, Shigeyuki*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Narukami, Yoshito*; Yoshioka, Naohito*; Fujimaki, Akira*; Hidaka, Mutsuo*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Arai, Masatoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 842, p.71 - 75, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:72.92(Instruments & Instrumentation) transition edge sensor
transition edge sensorOkayasu, Satoru; Katagiri, Masaki; Hojo, Kiichi; Morii, Yukio; Miki, Shigenobu*; Shimakage, Hisashi*; Wang, Z.*; Ishida, Takekazu*
Physica C, 468(15-20), p.1998 - 2000, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)We have been investigating for neutron detection with the MgB  transition edge sensor (TES). For the purpose, we have been developing a low noise measurement system for neutron detection. To confirm the usefulness of our detecting system, alpha-ray detection from an
transition edge sensor (TES). For the purpose, we have been developing a low noise measurement system for neutron detection. To confirm the usefulness of our detecting system, alpha-ray detection from an  Am source was achieved. To improve the sensitivity, short meander samples with 35
Am source was achieved. To improve the sensitivity, short meander samples with 35  m length and 1
m length and 1  m width is used. Samples are fabricated by the Kansai group. Superconducting transition temperature Tc is 23.3 K. The transition width is sharp enough less than 1 K. The detection was achieved under a constant current condition, and the resistivity changes at the sample due to the alpha-ray irradiation were detected. The bias current is 6
m width is used. Samples are fabricated by the Kansai group. Superconducting transition temperature Tc is 23.3 K. The transition width is sharp enough less than 1 K. The detection was achieved under a constant current condition, and the resistivity changes at the sample due to the alpha-ray irradiation were detected. The bias current is 6  A.
A.
 thin film detector for neutrons
thin film detector for neutronsIshida, Takekazu*; Nishikawa, Masatoshi*; Fujita, Yoshifumi*; Okayasu, Satoru; Katagiri, Masaki*; Sato, Kazuo*; Yotsuya, Tsutomu*; Shimakage, Hisashi*; Miki, Shigehito*; Wang, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 151(3-4), p.1074 - 1079, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:79.24(Physics, Applied)The superconducting neutron detector using high-quality  B-enriched MgB
B-enriched MgB thin films at higher operating temperatures has been proposed, where a resistance change induced by the nuclear reaction of neutron and
thin films at higher operating temperatures has been proposed, where a resistance change induced by the nuclear reaction of neutron and  B in MgB
B in MgB is used to detect a neutron. Cold neutrons from a nuclear research reactor irradiated the MgB
is used to detect a neutron. Cold neutrons from a nuclear research reactor irradiated the MgB detector, and the output voltage was clearly observed through a low-noise amplifier by using a digital oscilloscope. The out-of-equilibrium thermodynamics was investigated by means of the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equations by using the Earth Simulator.
detector, and the output voltage was clearly observed through a low-noise amplifier by using a digital oscilloscope. The out-of-equilibrium thermodynamics was investigated by means of the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equations by using the Earth Simulator.
 neutron detectors
neutron detectorsMachida, Masahiko; Kano, Takuma*; Koyama, Tomio*; Kato, Masaru*; Ishida, Takekazu*
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 151(1), p.58 - 63, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.33(Physics, Applied)We perform large-scale numerical simulations on the non-equilibrium superconducting dynamics after a neutron capture at the superconducting transition edge in MgB by solving the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equation coupled with the Maxwell and the heat diffusion equations. The simulations are carried out under the current-biased condition in order to explain experimental results made in the JAEA reactor JRR-3, and the time scale of the obtained voltage signal is found tobe almost consistent with the experiments. Moreover, the time evolution of the voltage signal is connected with that of the spatial profile of the superconducting order parameter.
by solving the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equation coupled with the Maxwell and the heat diffusion equations. The simulations are carried out under the current-biased condition in order to explain experimental results made in the JAEA reactor JRR-3, and the time scale of the obtained voltage signal is found tobe almost consistent with the experiments. Moreover, the time evolution of the voltage signal is connected with that of the spatial profile of the superconducting order parameter.
Kato, Masaru*; Koyama, Tomio*; Machida, Masahiko; Hayashi, Masahiko*; Ebisawa, Hiromichi*; Ishida, Takekazu*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 403(5-9), p.996 - 998, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)Using the Bogoliubov-de Gennes equation of a tight-binding electron model with attractive on-site and nearest-neighbor sites interactions, we investigate the superconducting structure of nano-structured anisotropic superconductors. Numerical results show that nano-scaled  /4-rotated square d-wave superconductors show various type of uperconductivities depending on the size. Especially,
/4-rotated square d-wave superconductors show various type of uperconductivities depending on the size. Especially,  +
+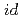 superconductivity, appears when size of superconductors is 10 times of coherence length.
superconductivity, appears when size of superconductors is 10 times of coherence length.
Ishida, Takekazu*; Matsushima, Yoshiaki*; Shimizu, Makoto*; Hayashi, Masahiko*; Ebisawa, Hiromichi*; Sato, Osamu*; Kato, Masaru*; Koyama, Tomio*; Machida, Masahiko; Sato, Kazuo*; et al.
Physica C, 468(7-10), p.576 - 580, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.10(Physics, Applied)The extended Little-Parks effect of superconducting network is known as a periodic 
 variation as a function of magnetic field. Superconducting Pb honeycomb networks of matching field 0.106 G and triangular microhole lattice of Pb of matching field 0.425 G have been fabricated by the combination of electron-beam lithography and a lift-off process of evaporated Pb films. The application of magnetic field corresponds to the vortex filling into superconducting networks. We measured the magnetization of the networks systematically by using a SQUID magnetometer. We found that flux jump appears rather periodically as a function of magnetic field. Flux jumps may be induced by a periodic decrease of the critical current density of the network. To the authors' knowledge, this is for the first time to observe the regular flux jumps due to the critical current modification coming from the extended Little-Parks effect of the superconducting networks.
variation as a function of magnetic field. Superconducting Pb honeycomb networks of matching field 0.106 G and triangular microhole lattice of Pb of matching field 0.425 G have been fabricated by the combination of electron-beam lithography and a lift-off process of evaporated Pb films. The application of magnetic field corresponds to the vortex filling into superconducting networks. We measured the magnetization of the networks systematically by using a SQUID magnetometer. We found that flux jump appears rather periodically as a function of magnetic field. Flux jumps may be induced by a periodic decrease of the critical current density of the network. To the authors' knowledge, this is for the first time to observe the regular flux jumps due to the critical current modification coming from the extended Little-Parks effect of the superconducting networks.
Nakajima, Susumu*; Kato, Masaru*; Koyama, Tomio*; Machida, Masahiko; Ishida, Takekazu*; Nori, F.*
Physica C, 468(7-10), p.769 - 772, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.75(Physics, Applied)A d-dot is a superconducting composite structure of d- and s-wave superconductors, which shows spontaneous half-quantized magnetic fluxes. We developed numerical method to analyze the time development of these spontaneous magnetic fluxes, based on the twocomponents Ginzburg-Landau equation. The d-dot can be used as an element of quantum dot cellular automata logic gates. We show a simulation, which demonstrates the transfer of information between two d-dot's.