Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kang, Z.; Okuda, Yukihiko; Nishida, Akemi; Tsubota, Haruji; Li, Y.
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/03
Most studies conducted till now on local damage of reinforced concrete (RC) slab structures subjected to projectile impact are about normal impact, while few research related to oblique impact can be found. The objective of this study is to carry out impact tests under different impact conditions including oblique impacts, to confirm the different impact behaviors of the RC slab structure, to develop an analysis method by investigating the test results and analytical conditions, and to validate the analysis method through comparison with the test results. This study focuses on the scabbing damage which is one of the local damage modes of RC slab. Based on oblique impact test results due to soft projectile with hemispherical nose shape, we investigate the relationship between the criterion related to the concrete fracture and the occurrence of scabbing damage.
Okuda, Yukihiko; Kang, Z.; Nishida, Akemi; Tsubota, Haruji; Li, Y.
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/03
The outer walls of nuclear facility buildings consist of reinforced concrete (RC) panels. When a projectile collides with a nuclear facility building, local damages such as penetration, scabbing, and perforation can occur in the RC panels. Numerical simulation using finite element analysis (FEA) is generally employed to assess these damage conditions. However, the impact analysis by FEA modelled with continuum elements is difficult to address phenomena such as scattering fragments of concrete because the elements deletion method for large deformation is used to prevent interruption of numerical calculations. Recently, a numerical method known as Smooth Particles Hydrodynamics (SPH), one of the particle methods, has been employed to address discontinuous phenomena. In this paper, we focus on the scabbing damages to RC panels and report on the findings obtained through the validation of the numerical analysis using the SPH method.
Ishida, Takekazu*; Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 214(3-4), p.152 - 157, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Applied)Tsuru, Tomohito; Han, S.*; Matsuura, Shutaro*; Chen, Z.*; Kishida, Kyosuke; Lobzenko, I.; Rao, S.*; Woodward, C.*; George, E.*; Inui, Haruyuki*
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1706_1 - 1706_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0Refractory high-entropy alloys (RHEAs) have attracted attention because of their potential for use in ultrahigh-temperature applications. Unfortunately, their body-centered-cubic (BCC) crystal structures make them more brittle than the ductile and fracture-resistant face-centered-cubic (FCC) HEAs. RHEAs also display significantly lower creep strengths than a leading Ni-base superalloy and its FCC matrix. To overcome these drawbacks and develop RHEAs into viable structural materials, improved fundamental understanding is needed of factors that control strength and ductility. Here we investigate two model RHEAs, TiZrHfNbTa and VNbMoTaW, and show that the former is plastically compressible down to 77 K, whereas the latter is not below 298 K. We find that hexagonal close-packed (HCP) elements in TiZrHfNbTa lower its dislocation core energy, increase its lattice distortion, and lower its shear modulus relative to VNbMoTaW whose elements are all BCC, leading to the formers higher ductility and modulus-normalized yield strength. Consistent with our yield strength models, primarily screw dislocations are present in TiZrHfNbTa after deformation, but equal numbers of edge and screw segments in VNbTaMoW. Dislocation cores are compact in VNbTaMoW and extended in TiZrHfNbTa, and different macroscopic slip planes are activated in the two RHEAs, which we attribute to the concentration of HCP elements. Our findings demonstrate how electronic structure changes related to the ratio of HCP to BCC elements can be used to control strength, ductility, and slip behavior to develop the next generation of high-temperature materials for more efficient power plants and transportation.
Okuda, Yukihiko; Takito, Kiyotaka; Nishida, Akemi; Li, Y.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/00
After the Great East Japan earthquake and the accident at the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Stations in March 2011, the regulation for nuclear power plants (NPPs) has been enhanced to take countermeasures against beyond-design-basis events. To improve the seismic safety of nuclear facilities against earthquakes that exceed the design input ground motion, the importance of seismic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) has drawn much attention. It is essential to evaluate the realistic seismic response of the equipment and piping in NPPs for fragility assessment in seismic PRA. In particular, since piping systems have plant-specific complex route geometries, it is known that the arrangement and stiffness of piping support structures have a significant impact on seismic response characteristics of the entire piping system. To construct a realistic seismic response analysis method for excessive input ground motion exceeding the elastic response, it is desired to develop an elastic-plastic response analysis method that can estimate the realistic response of piping systems including pipe support structures. In this study, the applicability of the method is confirmed by the simulation analysis of the elasto-plastic response for the piping support structure loading test previously reported. Moreover, based on the good correlation between the ductility factor and the damage status obtained from the test results and simulation analysis results, it is shown that the ductility factor is effective as a damage evaluation index for piping support structures.
 single crystals based on Bragg-dip analysis using a delay-line superconducting sensor
single crystals based on Bragg-dip analysis using a delay-line superconducting sensorShishido, Hiroaki*; Vu, TheDang*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(4), p.1108 - 1113, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) cuprates
cupratesIwasawa, Hideaki*; Sumida, Kazuki; Ishida, Shigeyuki*; Le F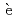 vre, P.*; Bertran, F.*; Yoshida, Yoshiyuki*; Eisaki, Hiroshi*; Santander-Syro, A.*; Okuda, Taichi*
vre, P.*; Bertran, F.*; Yoshida, Yoshiyuki*; Eisaki, Hiroshi*; Santander-Syro, A.*; Okuda, Taichi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.13451_1 - 13451_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Takito, Kiyotaka; Okuda, Yukihiko; Nishida, Akemi; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/07
In probabilistic risk assessment against earthquakes (seismic PRA) for nuclear power plants, the development of a realistic response analysis method for the fragility assessment of piping systems considering input seismic motions exceeding design assumptions is one of the important issues. Usually, piping systems exhibit complex three-dimensional shapes. The arrangement and stiffness of the piping support structures significantly affect the response characteristics of the entire piping system. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a realistic response analysis method of piping systems including piping support structures. In this study, a method for modeling the elasto-plastic hysteresis characteristics of piping support structures is developed to establish a seismic response analysis method of piping systems including piping support structures. First, we formulate an elatsto-plastic spring model that can express the elasto-plastic hysteresis characteristics of a piping support structure. Subsequently, we perform a simulation analysis for the loading test of a piping support structure using this model. As the analysis results and test results were in good agreement, we confirmed the effectiveness of the formulation of the model. The main contents, such as the formulation of the elasto-plastic spring model, the simulation analysis of the loading test, and the comparison between the analysis results and the test results, and the results of this study are reported in this paper.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Nishida, Naoki; Kobayashi, Daisuke; Nemoto, Ryo*; Hayashi, Hiroyuki*; Kitao, Takahiko; Kuno, Takehiko
JAEA-Technology 2023-004, 30 Pages, 2023/06
Glove-box gloves, that are used for handling nuclear fuel materials at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, have an expiration date by internal rules. All gloves are replaced at a maximum of every 4-year. However, degrees of glove deterioration varies depending on its usage environment such as frequency, chemicals, and radiation dose. Therefore, physical properties such as tensile strength, elongation, hardness of gloves are measured and technical evaluation method for the glove life-time is established. It was found that gloves without any defects in its appearance have enough physical properties and satisfies the acceptance criteria values of new gloves. Thus, it was considered that the expired gloves could be used for total of 8-year, by adding 4-year of new glove life-time. In addition, the results of extrapolation by plotting the glove's physical properties versus the used years showed that the physical properties at 8-year is on the safer side than the reported physical properties of broken glove. Also, the data are not significantly different from the physical properties of the long-term storage glove (8 and 23 years). Based on these results, life-time of gloves at TRP is set to be 8-year. The frequency of glove inspections are not changed, and if any defects is found, the glove is promptly replaced. Thus, the risk related to glove usage is not increased. The cost of purchasing gloves, labor for glove replacement, and the amount of generated waste can be reduced by approximately 40%, respectively, resulting in more efficient and rationalized glove management.
Okuda, Yukihiko; Kang, Z.; Nishida, Akemi; Tsubota, Haruji; Li, Y.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 10(3), p.22-00370_1 - 22-00370_12, 2023/06
Many experimental studies have been reported on the impact resistance of reinforced concrete (RC) structures. However, most formulas were derived from impact tests based on normal impact to target structures using rigid projectiles that do not deform during impact. Therefore, this study develops a local damage evaluation method considering the rigidity of projectiles and oblique impacts that should be considered in realistic projectile impact phenomena. Specifically, we focused on scabbing, defined as the peeling off the back face of the target opposite the impact face, and conducted impact tests on RC panels to clarify the scabbing limit by changing the impact velocity in an oblique impact. The effects of the projectile rigidity and oblique impact on the scabbing limit were investigated based on the test results. This work presents the test conditions, equipment, results, and the scabbing limit on the local damage to RC panels subjected to oblique impacts.
Okuda, Yukihiko; Takito, Kiyotaka; Nishida, Akemi; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
After the Great East Japan earthquake and the accident at the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Stations in March 2011, the regulation for nuclear power plants (NPPs) has been enhanced to take countermeasures against beyond-design-basis events. To improve the seismic safety of nuclear facilities against earthquakes that exceed the design input ground motion, the importance of seismic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) has drawn much attention. It is essential to evaluate the realistic seismic response of the equipment and piping in NPPs for fragility assessment in seismic PRA. In particular, since piping systems have plant-specific complex route geometries, it is known that the arrangement and stiffness of piping support structures have a significant impact on seismic response characteristics of the entire piping system. In contrast, the current seismic design procedure adopts an evaluation method assuming an elastic response. To construct a realistic seismic response analysis method for excessive input ground motion exceeding the elastic response, it is desired to develop an elastic-plastic response analysis method that can estimate the realistic response of piping systems including pipe support structures. In this study, the applicability of the method is confirmed by the simulation analysis of the elasto-plastic response for the piping support structure loading test previously reported. Moreover, based on the good correlation between the ductility factor and the damage status obtained from the test results and simulation analysis results, it is shown that the ductility factor is effective as a damage evaluation index for piping support structures.
Kang, Z.; Okuda, Yukihiko; Nishida, Akemi; Tsubota, Haruji; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
Most studies conducted till now on local damage of reinforced concrete (RC) slab structures subjected to projectile impact are about normal impact, while few research related to oblique impact can be found. The objective of this study is to carry out impact tests under different impact conditions including oblique impacts, to confirm the different impact behaviors of the RC slab structure, to develop an analysis method by investigating the test results and analytical conditions, and to validate the analysis method through comparison with the test results. This study focuses on the scabbing damage which is one of the local damage modes of RC slab. Based on oblique impact test results due to soft projectile with hemispherical nose shape, we investigate the relationship between the criterion related to the concrete fracture and the occurrence of scabbing damage.
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Tsujimura, Norio; Kunugita, Naoki*; Nishida, Kazutaka*; Ezaki, Iwao*; Kato, Masahiro*; Okubo, Hideki*
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 99(4), p.604 - 619, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.69(Biology)In April 2011, the International Commission on Radiological Protection recommended reducing the occupational equivalent dose limit for the lens. Such a new occupational lens dose limit has thus far been implemented in many countries, and there are extensive discussions toward its regulatory implementation in other countries. In Japan, discussions in the Japan Health Physics Society (JHPS) began in April 2013 and in Radiation Council in July 2017, and the new occupational lens dose limit was implemented into regulation in April 2021. To share our experience, we have published a series of papers summarizing situations in Japan: the first paper based on information available by early 2017, and the second paper by early 2019. This paper (our third paper of this series) aims to review updated information available by mid-2022, such as regarding regulatory implementation of the new occupational lens dose limit, recent discussions by relevant ministries based on the opinion from the council, establishment process of safety and health management systems, the JHPS guidelines on lens dose monitoring and radiation safety, voluntary countermeasures of the licensees, development of lens dose calibration method, and recent studies on exposure of the lens in nuclear workers and biological effect on the lens.
Okuda, Yukihiko; Nishida, Akemi; Kang, Z.; Tsubota, Haruji; Li, Y.
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 9(2), p.021801_1 - 021801_12, 2023/04
Most empirical formulas were proposed to evaluate the local damage to reinforced concrete (RC) structures based on impact tests conducted with a rigid projectile at an impact angle normal to the target structure. Only a few impact tests were performed involving a soft projectile. Therefore, in this study, we conducted a series of impact tests to evaluate the local damage to RC panels subjected to normal and oblique impacts by rigid and soft projectiles. This paper presents the test conditions, test equipment, test results, and obtained knowledge on local damage to RC panels subjected to normal and oblique impacts.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Tokiyoshi, Masanori*; Nishiyama, Kyohei*; Sato, Rina; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Funaki, Hironori; Abe, Tomohisa; Ishida, Mutsushi*; Nagamine, Haruo*; Fujisaka, Motoyuki*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(2), p.87 - 96, 2023/04
Since the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, many decontamination works have been carried out, but it is difficult to say that much data on workers' exposure has necessarily been analyzed in detail. In this paper, based on the GPS location information carried by the workers together with their personal dosimeters, the air dose rate in the work area and the characteristics of each type of work were analyzed. The results showed that more than 50% of the measured actual doses were more than twice the median planned dose calculated from the air dose rate and actual working hours. Furthermore, as a result of the analysis by work type, it was found that the exposure doses of demolition workers tended to be high, and that this was due to the fact that most of the work was carried out before the work was carried out to reduce the dose at the work site. In addition, when the conversion from air dose to effective dose was taken into account, there were many cases of underestimation where the planned values were lower than the measured values, and it is considered important for management to set appropriate working factor.
Nakada, Akira; Kanai, Katsuta; Kokubun, Yuji; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei*; Kubota, Tomohiro; Hirao, Moe; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2022-079, 116 Pages, 2023/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2021. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Nishida, Masayuki*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Yamashita, Takayuki*; Gong, W.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(1), p.8_1 - 8_15, 2023/03
Kang, Z.; Okuda, Yukihiko; Nishida, Akemi; Tsubota, Haruji; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/08
Most of the empirical formulas that have been proposed seeking to quantitatively investigate local damage to reinforced concrete (RC) structures caused by a rigid projectile impact. These formulas have been derived based on impact tests performed normal to the target structure, while only a few impact tests involving soft projectile to the target structure have been studied. The purpose of this study is to develop a local damage evaluation method that takes into account the oblique impact due to soft projectile, which should be considered in realistic impact conditions. In this paper, we compare the test results with the analytical results to examine and validate the parameter setting of analytical method for evaluating local damage in RC panel. The obtained knowledge is presented.
Kobayashi, Daisuke; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Nishida, Naoki; Miyoshi, Ryuta; Nemoto, Ryo*; Hayashi, Hiroyuki*; Kato, Keisuke; Nishino, Saki; Kuno, Takehiko; Kitao, Takahiko; et al.
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-18-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.237 - 240, 2022/07
All gloves attached to glove-box in Tokai Reprocessing Plant have a fixed expiration date and have to be replaced every 4-year. However, degrees of glove deterioration are different depending on its usage environment (frequency, chemicals, radiation, etc.), because of rubber products. Therefore, physical properties such as tensile strength, elongation, hardness of gloves are measured, and the life-time of gloves are estimated. As a result, gloves without any defects in its appearance have enough physical property for acceptance criteria of new glove. The extrapolated physical property of glove is sufficiently larger than the reported values of damaged glove. No deterioration in physical properties of gloves, that are periodically replaced without any defects in its appearance, is observed and the usable life-time of the glove is estimated to be 8 years.
Kang, Z.; Okuda, Yukihiko; Nishida, Akemi; Tsubota, Haruji; Li, Y.
Transactions of the 26th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-26) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/07
So far, studies on local damage to reinforced concrete (RC) panels subjected to projectile impact have mainly focused on collisions that occur at an angle normal to the structure, while research on oblique impact is scarce. In this research, we conducted a series of impact tests to confirm validity of the analytical method based on the investigation on local damage behavior of RC panel due to projectile impact under various impact conditions covering impact angles, projectile types (rigid and soft) and RC panel's thickness. In part 2, we concentrate on the investigation to the penetration damage and scabbing damage of RC panels subjected to normal and oblique impact by rigid and soft projectiles. Based on the analysis of experimental results, the obtained knowledge will be presented.