Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsubara, Ryuta*; Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Ishidera, Takamitsu
NUMO-TR-24-03, p.65 - 70, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Koike, Ayaka*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Iwata, Hajime; Fukatsu, Yuta; Taneichi, Yayoi
NUMO-TR-24-03, p.85 - 86, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Sugiura, Yuki; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Saito, Takumi*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 258, p.107476_1 - 107476_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:51.28(Chemistry, Physical)Kimuro, Shingo; Taneichi, Yayoi; Iwata, Hajime; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Kitamura, Akira; Tachi, Yukio; Tanaka, Takeru*; Hirano, Kana*; Hieda, Manami*; Miyabe, Shunsuke*; et al.
Journal of Solution Chemistry, 53(6), p.854 - 868, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
NUMO-TR-24-01, p.87 - 90, 2024/05
no abstracts in English
Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio
NUMO-TR-24-01, p.102 - 103, 2024/05
no abstracts in English
Matsubara, Ryuta*; Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Ishidera, Takamitsu
NUMO-TR-24-01, p.91 - 94, 2024/05
no abstracts in English

McGrady, J.; Kumagai, Yuta; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kimuro, Shingo; Ishidera, Takamitsu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(12), p.1586 - 1594, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ishidera, Takamitsu; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro*; Yamada, Yoshihide*; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Shibutani, Sanae*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(5), p.536 - 546, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)The distribution coefficient ( ) value of radionuclides is an important parameter in the radionuclide migration analysis in the safety assessment of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The
) value of radionuclides is an important parameter in the radionuclide migration analysis in the safety assessment of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The  values must be extensively evaluated especially under conditions where they might be decreased to improve the reliability of safety assessment. In this study, the pH dependence of the
values must be extensively evaluated especially under conditions where they might be decreased to improve the reliability of safety assessment. In this study, the pH dependence of the  values for Sn and Nb on montmorillonite was evaluated using batch sorption experiments at neutral to alkaline pH, which might be caused by the leaching of cementitious materials and the corrosion of carbon steel. The
values for Sn and Nb on montmorillonite was evaluated using batch sorption experiments at neutral to alkaline pH, which might be caused by the leaching of cementitious materials and the corrosion of carbon steel. The  values were determined in the range 8
values were determined in the range 8  pH
pH  12 by the experiments and were found to decrease with increasing pH. A model calculation using a thermodynamic sorption model was conducted on the measured pH dependence of the
12 by the experiments and were found to decrease with increasing pH. A model calculation using a thermodynamic sorption model was conducted on the measured pH dependence of the  values. Two different sorption sites were required to describe the pH dependence of the
values. Two different sorption sites were required to describe the pH dependence of the  values of Sn in the model calculation, whereas one sorption site was considered predominant in the sorption of Nb.
values of Sn in the model calculation, whereas one sorption site was considered predominant in the sorption of Nb.
Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Ishidera, Takamitsu
NUMO-TR-22-02, p.58 - 61, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio
NUMO-TR-22-02, p.88 - 89, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Ichikawa, Nozomi*; Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
NUMO-TR-22-02, p.55 - 57, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Yanagida, Akinobu*; Ura, Yoko*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Kawakita, Ryohei
Nara Bunkazai Kenkyujo Soritsu 70-Shunen Kinen Rombunshu; Bunkazai Ronso 5, p.843 - 856, 2023/03
To investigate chloride salt accumulation inside an iron artifact in soil, non-destructive analysis of three iron artifacts excavated from the Heijo Palace Site was conducted using elemental mapping by X-ray fluorescence analysis, micro-X-ray diffraction analysis, and X-ray computed tomography. Furthermore, the buried environments of the artifacts were presumed based on the previous reports of the environmental investigation at the Heijo Palace site. The results revealed the iron artifact's corrosion behavior was different individually- (1) the iron artifact that was presumed buried under oxidation environments had a goethite/magnetite corrosion layer and contained akageneite inside the corrosion layer. (2) the metal of the other iron artifacts buried under the oxidation environment had eluted absolutely and the artifacts had a rust layer formed by only goethite. (3) the other artifact buried in reduction environments had a rust layer composed of siderite. Accumulation of chloride salts inside an iron artifact was observed only in (1). Because each Cl concentration measured in underground water observation holes at the Heijo Palace Site showed almost the same level concentrations, it was presumed that the accumulation of chloride salts depended on the environmental factor except for Cl
concentration measured in underground water observation holes at the Heijo Palace Site showed almost the same level concentrations, it was presumed that the accumulation of chloride salts depended on the environmental factor except for Cl concentration. Based on these results, there was a possibility that the occurrence of local corrosion attributed to the separation of anodic and cathodic regions through the formation of the goethite/magnetite rust layer caused chloride salts accumulation inside an iron artifact.
concentration. Based on these results, there was a possibility that the occurrence of local corrosion attributed to the separation of anodic and cathodic regions through the formation of the goethite/magnetite rust layer caused chloride salts accumulation inside an iron artifact.
Francisco, P. C. M.; Matsumura, Daiju; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio
Environmental Science & Technology, 56(5), p.3011 - 3020, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.53(Engineering, Environmental)Ishidera, Takamitsu
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 330(1), p.149 - 158, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.79(Chemistry, Analytical)Endo, Takashi*; Tachi, Yukio; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Terashima, Motoki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 20(1), p.9 - 22, 2021/03
Evaluation method of colloid diffusion and filtration in compacted bentonites was developed using dendrimers. Diffusion and filtration behavior of PAMAM dendrimers with the size of 5.7 7.2nm was investigated by the through-diffusion experiment in bentonite compacted to 0.8 Mg/m
7.2nm was investigated by the through-diffusion experiment in bentonite compacted to 0.8 Mg/m and saturated with 0.005
and saturated with 0.005 0.5mol/L NaCl. Effective diffusivities (De) and filtration ratios (Rf) of dendrimers were determined from the breakthrough curves and the depth profiles in compacted bentonite, respectively. The De values of negatively charged dendrimer increased when porewater salinity increased and dendrimer size decreased as influenced by anion exclusion effect in negatively charged clay surfaces. The Rf values increased when porewater salinity decreased and dendrimer size increased, demonstrating significant fractions of dendrimer were filtered by narrow pores in complex pore networks. These trends consistent with the previous studies emphasize the validity of the evaluation method using dendrimer.
0.5mol/L NaCl. Effective diffusivities (De) and filtration ratios (Rf) of dendrimers were determined from the breakthrough curves and the depth profiles in compacted bentonite, respectively. The De values of negatively charged dendrimer increased when porewater salinity increased and dendrimer size decreased as influenced by anion exclusion effect in negatively charged clay surfaces. The Rf values increased when porewater salinity decreased and dendrimer size increased, demonstrating significant fractions of dendrimer were filtered by narrow pores in complex pore networks. These trends consistent with the previous studies emphasize the validity of the evaluation method using dendrimer.
Sugiura, Yuki; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 200, p.105910_1 - 105910_10, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.75(Chemistry, Physical)Tachi, Yukio; Sato, Tomofumi*; Takeda, Chizuko*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Fujiwara, Kenso; Iijima, Kazuki
Science of the Total Environment, 724, p.138097_1 - 138097_10, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:45.76(Environmental Sciences)To understand and predict radiocesium transport behaviors in the environment, sorption and fixation behaviors of radiocesium on river sediments from Ukedo and Odaka rivers around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant were investigated systematically focusing on Cs sorption and fixation mechanisms and their relationship with Cs concentrations and sediment properties including clay mineralogy and organic matter.
Sugiura, Yuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Doi, Reisuke; Francisco, P. C. M.; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Matsumura, Daiju; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Tachi, Yukio
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 324(2), p.615 - 622, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.32(Chemistry, Analytical)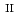 and Si under anoxic and reducing conditions; Structural characteristics of ferrous silicate co-precipitates
and Si under anoxic and reducing conditions; Structural characteristics of ferrous silicate co-precipitatesFrancisco, P. C. M.; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio; Doi, Reisuke; Shiwaku, Hideaki
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 270, p.1 - 20, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:74.11(Geochemistry & Geophysics)