Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Hasegawa, Makoto*; Kishimoto, Tadafumi*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/05
From the viewpoint of energy security in Japan and reduction of the environmental load, continuous operation of light water reactors is essential. Since a pH adjuster with enriched Li-7 ions is required for water quality control on PWR, the development of Li-7 enrichment technology is one of the key issues. The multi-channel counter-current electrophoresis (MCCCE) method has been developed as the technology with a low environmental load. To put this method into practical use, it is necessary to understand Li-7 ion behavior in the channel flow and optimize the experimental condition to separate Li-7 and its isotope. In this paper, to understand Li-7 ion behavior in a single channel of the experimental apparatus, a numerical simulation method based on a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) code with a particle tracking method, TPFIT-LPT, was developed. In the method, the motion of multiple ions under the electric field was simulated as a particle with an added velocity by the electric field. The difference in the isotopes was represented by changing of the magnitude of the added velocity. We also considered that although it is impossible to measure the behavior of each ion, it is important to measure the flow velocity of the bulk fluid for the validation of the numerical simulation. We developed a lab-scale experimental apparatus in which the single channel of the actual apparatus was simplified to measure the flow velocity by Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV). We set a pulsation flow condition on the lab-scale experiment, which is one of difficult conditions for the numerical simulation, and measured the velocity. As the result, we confirmed that the pulsation flow was reproduced. We set the measured data as the inlet boundary condition of the numerical simulation and conducted it. As the numerical result, we confirmed the ions affected by the electric field moved upstream with pulsation. We also confirmed the effect of the electric field on the motion of the isotope.
Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Umetsu, Rie*; Kuroda, Fumiaki*; Miyawaki, Jun*; Kashiuchi, Toshiyuki*; Nishimoto, Kohei*; Nagai, Kodai*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Irizawa, Akinori*; Takeda, Yukiharu; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.18654_1 - 18654_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Yonomoto, Taisuke; Nakashima, Hiroshi*; Sono, Hiroki; Kishimoto, Katsumi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Kinase, Masami; Osa, Akihiko; Ogawa, Kazuhiko; Horiguchi, Hironori; Inoi, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-056, 51 Pages, 2021/03
A group named as "The group for investigation of reasonable safety assurance based on graded approach", which consists of about 10 staffs from Sector of Nuclear Science Research, Safety and Nuclear Security Administration Department, departments for management of nuclear facility, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness, aims to realize effective graded approach (GA) about management of facilities and regulatory compliance of JAEA. The group started its activities in September, 2019 and has had discussions through 10 meetings and email communications. In the meetings, basic ideas of GA, status of compliance with new regulatory standards at each facility, new inspection system, etc were discussed, while individual investigation at each facility were shared among the members. This report is compiled with expectation that it will help promote rational and effective safety management based on GA by sharing contents of the activity widely inside and outside JAEA.
Iketani, Shotaro; Yokobori, Tomohiko; Ishikawa, Joji; Yasuhara, Toshiyuki*; Kozawa, Toshiyuki*; Takaizumi, Hirohide*; Momma, Takeshi*; Kurosawa, Shingo*; Iseda, Hirokatsu; Kishimoto, Katsumi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2018-016, 46 Pages, 2018/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) adopts melting process for the waste processing and packaging method of radioactive miscellaneous solid waste in NSRI because melting process is effective in radioactivity evaluation, volume reduction, and stabilization treatment. Metal melting processing facilities, Incinerator, and Nonmetal melting processing facilities (hereinafter referred to as melting process facilities) have taken lots of safety measures, including measures for preventing the recurrence of the fire accidents. To exchange opinions and discuss the validity of these measures and so on with internal personnel and external experts, "Discussions on Melting Process Facilities" was held. As a document collection, this paper summarizes presentation materials of discussion meetings. Presentation materials describe "Outline of AVRF", "Safety measures in the melting facilities in WVRF", "Operation management of the melting facilities in WVRF", "Comparison of the past accident cases between facilities in and outside Japan and WVRF", and "Introduction of past accident cases and safety measures in other facilities from each committee".
Ogoshi, Yurie; Satoyama, Tomonori; Kishimoto, Katsumi; Nanri, Tomohiro; Suzuki, Takeshi; Tomioka, Osamu; Takaizumi, Hirohide*; Kanno, Tomoyuki*; Maruyama, Tatsuya*
JAEA-Technology 2017-017, 152 Pages, 2017/08
At Nuclear Science Research Institute, clearance works for about 4,000 tons of extremely low-level radioactive concrete debris, which were generated from the modification activities of JRR-3 from FY 1985 to FY 1989 and stored in the waste storage facility NL, carried out. First of this clearance works, method for measuring and evaluating radioactivity concentration was approved by Minister of MEXT on July 25, 2008. And then, clearance works were started from FY 2009. Measuring and evaluating radioactivity concentration was achieved by using the approved method, and was confirmed by government. And then, clearance works were completed in FY 2014. The clearance concrete was recycled as a material for restoration works of the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake. This report summarizes the results of measuring and evaluating radioactivity concentration, achievement of confirmation by government, recycling of cleared concrete and cost for clearance works.
Ishihara, Keisuke; Yokota, Akira; Kanazawa, Shingo; Iketani, Shotaro; Sudo, Tomoyuki; Myodo, Masato; Irie, Hirobumi; Kato, Mitsugu; Iseda, Hirokatsu; Kishimoto, Katsumi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2016-024, 108 Pages, 2016/12
Radioactive isotope, nuclear fuel material and radiation generators are utilized in research institutes, universities, hospitals, private enterprises, etc. As a result, various low-level radioactive wastes (hereinafter referred to as non-nuclear radioactive wastes) are produced. Disposal site for non-nuclear radioactive wastes have not been settled yet and those wastes are stored in storage facilities of each operator for a long period. The Advanced Volume Reduction Facilities (AVRF) are built to produce waste packages so that they satisfy requirements for shallow underground disposal. In the AVRF, low-level beta-gamma solid radioactive wastes produced in the Nuclear Science Research Institute are mainly treated. To produce waste packages meeting requirements for disposal safely and efficiently, it is necessary to cut large radioactive wastes into pieces of suitable size and segregate those depending on their types of material. This report summarizes activities of pretreatment to dispose of non-nuclear radioactive wastes in the AVRF.
Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Masui, Tomomi*; Mashita, Ryo*; Kishimoto, Hiromichi*; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Kumada, Takayuki; Takata, Shinichi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Junichi*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 49(6), p.2036 - 2045, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.58(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Ishibashi, Masayuki; Ando, Tomomi*; Sasao, Eiji; Yuguchi, Takashi; Nishimoto, Shoji*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*
Oyo Chishitsu, 55(4), p.156 - 165, 2014/10
Understanding of long-term history of water-conducting features such as flow-path fractures is key issue to evaluate deep geological environment for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Thus, we conducted study on the geological features and the long-term behavior of flow-path fractures based on the data obtained at -300m levels in the Mizunami Underground research laboratory (MIU), central Japan. Total 1670 fractures were mapped in underground gallery at the -300m levels. Flow-path fractures occupy about 11% of all fractures. The flow-path fractures are divided into grout filling fractures and low inflow-rate fractures. All of the grout filling fractures is filled with calcite as fracture filling minerals without conspicuous host rock alteration around fractures. The low inflow-rate fractures possessed similar geological character with the sealed fractures which are not acted as flow-path. The geological character of fracture filling and host tock alteration around fractures indicates the history of the formation at the time of intrusion and emplacement of host granite (Stage I), then filling at hydrothermal event (Stage II), and finally opening and elongation during exhumation stage (Stage III). In conclusion, the present flow-path fractures were formed by opening and/or elongation of pre-existed fractures, which were filled at the hydrothermal event, at the time of exhumation.
Abe, Hiroshi; Orimo, Satoshi; Kishimoto, Masahiko*; Aone, Shigeo*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Oshima, Takeshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 307, p.218 - 220, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.54(Instruments & Instrumentation)We investigated the structure changes of a hydrogen storage alloy by ion irradiations, and its absorption property in order to obtain basic data and to elucidate relevant mechanisms of hydrogen absorption by the influence of the irradiation. In previous studies, the induction of vacancies in a hydrogen absorption alloy was found to be effective to increase in the hydrogen absorption rate. As well known, the rate of hydrogen absorption strongly depends upon the surface state of a hydrogen storage alloy because the dissociation of hydrogen molecules or water molecules needs electron change with the surface in the H gas or electrochemical reaction process. In this study, ion irradiations were made at a room temperature using the laser driven proton beam method, at Kansai Photon Science Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The beam treatment has several unique properties such as short pulse duration, high peak current, low transverse emittance, and wide energy range from KeV to MeV. The irradiation was used to modify the alloy surface using this equipment. From obtained results, the initial hydrogen absorption rate was found improved by the laser driven proton beam rather more effectively than a mono-energetic proton beam. Discussion is made on the correlation among proton irradiation (laser driven proton or mono-energetic proton) and the initial hydrogen absorption rate of the alloy. We argue about the usefulness of an energy spread beam.
gas or electrochemical reaction process. In this study, ion irradiations were made at a room temperature using the laser driven proton beam method, at Kansai Photon Science Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The beam treatment has several unique properties such as short pulse duration, high peak current, low transverse emittance, and wide energy range from KeV to MeV. The irradiation was used to modify the alloy surface using this equipment. From obtained results, the initial hydrogen absorption rate was found improved by the laser driven proton beam rather more effectively than a mono-energetic proton beam. Discussion is made on the correlation among proton irradiation (laser driven proton or mono-energetic proton) and the initial hydrogen absorption rate of the alloy. We argue about the usefulness of an energy spread beam.

Tokunaga, Yo; Saito, Yo*; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Sanada, Naoyuki*; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Suzuki, Kazuya*; Kawasaki, Yu*; Kishimoto, Yutaka*
Physical Review B, 84(21), p.214403_1 - 214403_7, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:36.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report NMR studies of TbCoGa , which has the tetragonal HoCoGa
, which has the tetragonal HoCoGa structure and exhibits two antiferromagnetic (AF) transitions at
structure and exhibits two antiferromagnetic (AF) transitions at 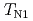 =36.2 K and
=36.2 K and 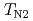 =5.4 K. From a symmetry analysis of internal magnetic fields at orthorhombic Ga sites, we have successfully determined the magnetic structures in the AF-I (
=5.4 K. From a symmetry analysis of internal magnetic fields at orthorhombic Ga sites, we have successfully determined the magnetic structures in the AF-I (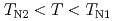 ) and AF-II (
) and AF-II (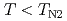 ) phases. The AF-I phase is a collinear AF order with a propagation vector
) phases. The AF-I phase is a collinear AF order with a propagation vector ![$$q=[1/2, 0, 1/2]$$](/search/images/ERYT0WZRF2ZCYIBQFQQDCLZSLUSA.gif) and ordered moments parallel to the [001] direction. In the AF-II phase, on the other hand, we found a non-collinear AF structure described by double propagation vectors
and ordered moments parallel to the [001] direction. In the AF-II phase, on the other hand, we found a non-collinear AF structure described by double propagation vectors ![$$q_1=[1/2, 0, 1/2]$$](/search/images/ERYV4MJ3LMYS4MRMEAYCYIBRF2ZF0JA.gif) and
and ![$$q_{2}=[0, 1/2, 1/2]$$](/search/images/ERYV44ZSPU4VWMBMEAYS4MRMEAYS4MS3EQ.gif) , where the moments tilt away from the [001] direction toward [100], keeping a constant value along the [001] direction. In the context of these results we discuss the possible presence of magnetic frustration in this system.
, where the moments tilt away from the [001] direction toward [100], keeping a constant value along the [001] direction. In the context of these results we discuss the possible presence of magnetic frustration in this system.
Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Kishimoto, Maki; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Momoko; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2010; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.136, p.15 - 24, 2011/12
This paper reviews recent improvement in the source development of laser-driven X-ray lasers and the applications in the research fields of material science, laser processing, X-ray imaging, and radiation damage in biological cells. In the application for material science, we have firstly observed temporal correlation between the domain structures of ferro-electric substance under the Curie temperature. In the laser processing, new X-ray laser interferometer reveals us the nano-scale surface distortion of substance pumped by a femto-second optical pulse. In the X-ray diffraction image, we have taken several static images of micro-structure of samples: now we are trying to extend the objective to nano-scale dynamics using pump and probe method. In the radiation damage of biological cells, we observed double strand break in DNA using X-ray laser exposure; this results are compared with the case using incoherent several KeV X-ray exposure.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Terakawa, Kota*; Tomita, Takuro*; Yamamoto, Minoru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Imazono, Takashi; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2010; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.136, p.353 - 358, 2011/12
The understanding of the dynamics of the initial process is important for the micro processing and welding by the ultra-short laser pulse. The X-ray laser is suitable for probing this initial process because it has short wavelength (Ni-like Ag, 13.9 nm) and short duration (7 ps). For this investigation, the origin of time of the pumping pulse is quite important. In this study, we used the scintillation plate and the plasma gate technique to realize the spatial and temporal synchronization of the pump and probe pulses. For the spatial alignment, a CsI scintillation plate that was set at the sample position was illuminated by both the X-ray laser pulse, and the fluorescence light were detected by the CCD camera. For the temporal synchronization, we set a thin foil at the sample position. We measured the transmission of the X-ray laser while changing a temporal delay of the pumping laser with respect to the time of X-ray laser pulse to obtain the origin of the irradiation time.
Nozawa, Takashi; Ogiwara, Hiroyuki*; Kannari, Jun*; Kishimoto, Hirotatsu*; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(9-11), p.2512 - 2516, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:71.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)A hot isostatic press (HIP) process is a key technology to fabricate a first wall of the blanket system utilizing a reduced-activation ferritic/martensitic (RAFM) steel such as F82H. A primary objective of this study is to characterize interfacial properties of HIPed F82H joints by torsion to identify the feasibility of this test method. It is apparent that the absorption energies of the HIP joints varied by the processing conditions, although the maximum shear strength was not much different. According to the fracture surfaces, it is indicated that the reduction of the absorption energy was due to the oxide formed on the interface of the HIP joint and this was consistent with the results of charpy impact tests. In conclusion, the torsion test method enables to precisely evaluate the shear properties of the HIPed joint interface and becomes one of promising powerful techniques for inspection of the HIP joints.
Nakamura, Takahiro; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Teshima, Minoru*; Kasagi, Toshio*; Kishimoto, Munemaru*; Deguchi, Tomonori*; Makuuchi, Ayumu*
JAEA-Research 2010-006, 68 Pages, 2010/06
The present document is to report the result of geophysical survey by electric survey around a site proposed for the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project at Horonobe-cho, Hokkaido by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This Electric survey using pole-pole array in Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Area was the third survey. Resistivity distribution near surface was about 20 
 m and it become to about 2
m and it become to about 2 
 m as the depth increasing. Resistivity distribution was good agreement with existing survey results and existing electrical resistivity log data. By comparing resistivity model with hydrology model, it was confirmed that resistivity reflected the density of salinity. The range and distribution trends of apparent resistivity in this year were similar to the results of last year. It is thought that the data in which reproducibility is high is acquired in this survey. The influence on the underground water flow by construction is not admitted now.
m as the depth increasing. Resistivity distribution was good agreement with existing survey results and existing electrical resistivity log data. By comparing resistivity model with hydrology model, it was confirmed that resistivity reflected the density of salinity. The range and distribution trends of apparent resistivity in this year were similar to the results of last year. It is thought that the data in which reproducibility is high is acquired in this survey. The influence on the underground water flow by construction is not admitted now.
Ishino, Masahiko; Kado, Masataka; Nishikino, Masaharu; Shinohara, Kunio*; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Yasuda, Keiko*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kishimoto, Maki; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kawachi, Tetsuya
Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.7589, p.75891B_1 - 75891B_8, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.8(Engineering, Biomedical)Soft X-ray microscopes operating in the water window are capable of imaging living hydrated biological specimens. Laser produced plasmas are attractive soft X-ray sources, because of their short duration time. Based on the minimum dose calculation, soft X-ray photons more than 10 photons/
photons/ m
m at the sample surface are needed to acquire an image of the biological specimens with spatial resolution up to 100 nm. The observations of soft X-ray emissions from laser produced plasmas using ultra thin film targets have been carried out. Au thin films were irradiated by a high contrast Nd:glass laser pulses. The spectral properties of emitted soft X-rays were monitored by an X-ray spectrograph from the rear side with respect to the surface of laser irradiation. The observed emission intensities had an obvious dependence on the film thickness, and the most intense emissions were obtained at the thickness of 28 nm. The experimental results have suggested that the most of the laser energy irradiated is absorbed by the film target, and it is resulted an efficient energy deposition from laser to X-rays.
at the sample surface are needed to acquire an image of the biological specimens with spatial resolution up to 100 nm. The observations of soft X-ray emissions from laser produced plasmas using ultra thin film targets have been carried out. Au thin films were irradiated by a high contrast Nd:glass laser pulses. The spectral properties of emitted soft X-rays were monitored by an X-ray spectrograph from the rear side with respect to the surface of laser irradiation. The observed emission intensities had an obvious dependence on the film thickness, and the most intense emissions were obtained at the thickness of 28 nm. The experimental results have suggested that the most of the laser energy irradiated is absorbed by the film target, and it is resulted an efficient energy deposition from laser to X-rays.
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Oba, Toshiyuki; Tanaka, Momoko; Kishimoto, Maki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Nagashima, Keisuke; Sugiyama, Akira
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 48(12), p.120212_1 - 120212_3, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:73.52(Physics, Applied)We have demonstrated the fully spatial coherent 13.9-nm laser with output energy of submicroJoule by means of the double target geometry by using new driver system. The power amplifiers providing tow beams with 10-J energy and picoseconds duration at the repetition rate of 0.1 Hz. The obtained 13.9-nm laser pulse with 10 coherent photons will enable us to make single-shot pump-probe observation of non-periodic ultrafast phenomena.
coherent photons will enable us to make single-shot pump-probe observation of non-periodic ultrafast phenomena.
Kimura, Akihiko*; Kasada, Ryuta*; Iwata, Noriyuki*; Kishimoto, Hirotatsu*; Zhang, C. H.*; Isselin, J.*; Dou, P.*; Lee, J. H.*; Muthukumar, N.*; Okuda, Takanari*; et al.
Proceedings of 2009 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '09) (CD-ROM), p.9220_1 - 9220_8, 2009/05
Cladding material development is essential for realization of highly efficient high burn-up operation of next generation nuclear systems, where high performance is required for the materials, that is, high strength at elevated temperature, high resistance to corrosion and high resistance to irradiation. Oxide dispersion strengthening (ODS) ferritic steels are considered to be most adequate for the cladding material because of their high strength at elevated temperature. In this work, "Super ODS steel" that has better corrosion resistance than 9Cr-ODS steel, has been developed for application to cladding of a variety of next generation nuclear systems. In the following ten papers, the recent experimental results of "Super ODS steel" R&D will be presented, indicating that many unexpected preferable features were found in the mechanical properties of nano-sized oxide dispersion high-Cr ODS ferritic steel. A series of paper begins with alloy design of "Super ODS steel". Corrosion issue requires Cr concentration more than 14wt.%, but aging embrittlement issue requires less than 16wt.%. An addition of 4wt.%Al is effective to improve corrosion resistance of 16wt.%Cr-ODS steel in supercritical water (SCW) and lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE), while it is detrimental to high-temperature strength. Additions of 2wt.%W and 0.1wt.%Ti are necessary to keep high strength at elevated temperatures. An addition of small amount of Zr or Hf results in a significant increase in creep strength at 700  C in Al added ODS steels. Tube manufacturing was successfully done for the super ODS steel candidates. "Super ODS steel" is promising for the fuel cladding material of next generation nuclear systems, and the R&D is now ready to proceed to the next stage of empirical verification.
C in Al added ODS steels. Tube manufacturing was successfully done for the super ODS steel candidates. "Super ODS steel" is promising for the fuel cladding material of next generation nuclear systems, and the R&D is now ready to proceed to the next stage of empirical verification.
Lee, J. H.*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Kasada, Ryuta*; Iwata, Noriyuki*; Kishimoto, Hirotatsu*; Zhang, C. H.*; Isselin, J.*; Dou, P.*; Muthukumar, N.*; Okuda, Takanari*; et al.
Proceedings of 2009 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '09) (CD-ROM), p.9223_1 - 9223_6, 2009/05
Corrosion is a critical issue for cladding materials, especially, in sever corrosion environment as supercritical pressurized water (SCPW). In this work, the effects of alloy elements on the corrosion behavior in SCPW were investigated for a series of oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steels to design alloy compositions for corrosion resistant super ODS ferritic steels. Corrosion tests were carried out for the ODS steels with different concentrations of Cr and Al in SCPW at 773 K at 25 MPa with 8 ppm of dissolved oxygen. The corrosion rate of SUS430, which contained 16wt.%Cr, was much higher than 16Cr-ODS steel. This suggests that nano-sized oxide particles dispersion and very fine grains play an important role in suppression of the corrosion. The corrosion of the ODS steel was reduced by an addition of Al in 16wt.%Cr-ODS steel but not in 19Cr-ODS steel. FE-EPMA chemical analysis clearly indicated that the surface of the Al added ODS steels was covered by alumina which suppresses the corrosion in SCPW. It is considered that an adequate combination of the contents of Cr and Al is ranging (14-16)Cr and (3.5-4.5)Al.
Nakamura, Takahiro; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Teshima, Minoru*; Kishimoto, Munemaru*; Matsuo, Koichi*
JAEA-Research 2008-102, 58 Pages, 2009/03
The present document is to report the result of geophysical survey by electric survey around a site proposed for the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project at Horonobe-cho, Hokkaido by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This Electric survey using pole-pole array in Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Area was the second survey. Resistivity distribution near surface was about 20 ohm-m and it become to about 2 ohm-m as the depth increasing. Resistivity distribution was good agreement with existing survey results and existing electrical resistivity log data. By comparing resistivity model with hydrology model, it was confirmed that resistivity reflected the density of salinity. The range and distribution trends of apparent resistivity in this year were similar to the results of last year. It is thought that the data in which reproducibility is high is acquired in this survey. The influence on the underground water flow by construction is not admitted now.
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tanaka, Momoko; Kishimoto, Maki; Oba, Toshiyuki
X-Ray Lasers 2008; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.130, p.161 - 166, 2009/00