Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Methanoperedenaceae
MethanoperedenaceaeNishimura, Hiroki*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Fukuda, Akari*; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Suzuki, Yohei*
Environmental Microbiology Reports (Internet), 15(3), p.197 - 205, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:39.44(Environmental Sciences)The family  Methanoperedenaceae archaea mediate anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM). We newly developed a high-pressure laboratory incubation system and investigated groundwater from 214- and 249-m deep boreholes at Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan, where the high and low abundances of
Methanoperedenaceae archaea mediate anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM). We newly developed a high-pressure laboratory incubation system and investigated groundwater from 214- and 249-m deep boreholes at Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan, where the high and low abundances of  Methanoperedenaceae archaea have been revealed, respectively. We incubated the samples amended with or without amorphous Fe(III) and
Methanoperedenaceae archaea have been revealed, respectively. We incubated the samples amended with or without amorphous Fe(III) and  C-labelled methane at an in-situ pressure of 1.6 MPa. After three to seven-day incubation, AOM activities were not detected from the 249-m sample but from the 214-m sample. The AOM rates were 93.7
C-labelled methane at an in-situ pressure of 1.6 MPa. After three to seven-day incubation, AOM activities were not detected from the 249-m sample but from the 214-m sample. The AOM rates were 93.7 40.6 and 27.7
40.6 and 27.7 37.5 nM/day with and without Fe(III) amendment. Suspended particulates were not visible in the 249-m sample on the filter, while they were abundant and contained amorphous Fe(III) and Fe(III)-bearing phyllosilicates in the 214-m sample. This supports the in-situ activity of Fe(III)-dependent AOM in the deep subsurface borehole.
37.5 nM/day with and without Fe(III) amendment. Suspended particulates were not visible in the 249-m sample on the filter, while they were abundant and contained amorphous Fe(III) and Fe(III)-bearing phyllosilicates in the 214-m sample. This supports the in-situ activity of Fe(III)-dependent AOM in the deep subsurface borehole.
Ino, Kohei*; Hernsdorf, A. W.*; Konno, Yuta*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Yanagawa, Katsunori*; Kato, Shingo*; Sunamura, Michinari*; Hirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Ito, Kazumasa*; et al.
ISME Journal, 12(1), p.31 - 47, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:89.82(Ecology)In this study, we found the dominance ofanaerobic methane-oxidizing archaea in groundwater enriched in sulfate and methane from a 300-m deep underground borehole in granitic rock.
Suzuki, Yohei*; Mukai, Hiroki*; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Yokoyama, Takatomi*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Mizuno, Takashi
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.22701_1 - 22701_6, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:44.87(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The stimulation of bacterial activities that convert hexavalent uranium to tetravalent uranium appears to be feasible for cost-effective remediation of contaminated aquifers. However, U(VI) reduction typically results in the precipitation of U(IV) particles less than 5 nanometers in diameter. Here we show that U(IV) nanoparticles of coffinite formed in fracture-filling calcium carbonate in a granitic aquifer. As the microbiologically induced precipitation of calcium carbonate in aquifer systems worldwide is extremely common, we anticipate simultaneous stimulation of microbial activities for precipitation reactions of calcium carbonate and U(IV) nanoparticles, which leads to long-term sequestration of uranium and other radionuclides in contaminated aquifers and deep geological repositories.
Fukuda, Akari*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Ioka, Seiichiro*; Amano, Yuki; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Suzuki, Yohei*; Mizuno, Takashi
Microbial Ecology, 60(1), p.214 - 225, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:65.40(Ecology)To better understand the geochemical and microbiological relationships, we characterized granitic groundwater collected from a 1,148 to 1,169 -m deep borehole interval at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory site, Japan, in 2005 and 2008. Geochemical analyses of the groundwater samples indicated that major electron acceptors, such as NO
 and SO
and SO
 , were not abundant, while dissolved organic carbon (not including organic acids), CH
, were not abundant, while dissolved organic carbon (not including organic acids), CH and H
and H were moderately rich. The most common phylotypes were both related to
were moderately rich. The most common phylotypes were both related to  spp., the cultivated members of which can utilize minor electron donors, such as aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Geomicrobiological results suggest that deep granitic groundwater has been stably colonized by
spp., the cultivated members of which can utilize minor electron donors, such as aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Geomicrobiological results suggest that deep granitic groundwater has been stably colonized by 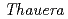 spp. probably owing to the limitation of O
spp. probably owing to the limitation of O , NO
, NO
 and organic acids.
and organic acids.
Nishimura, Hiroki*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Fukuda, Akari*; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Suzuki, Yohei*
no journal, ,
The family Methanoperedenaceae archaea mediate anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM). We newly developed a high-pressure laboratory incubation system and investigated groundwater from 214- and 249-m deep boreholes at Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan, where the high and low abundances of Methanoperedenaceae archaea have been revealed, respectively. We incubated the samples amended with or without amorphous Fe(III) and  C-labelled methane at an in-situ pressure of 1.6 MPa. After three to seven-day incubation, AOM activities were not detected from the 249-m sample but from the 214-m sample. The AOM rates were 93.7
C-labelled methane at an in-situ pressure of 1.6 MPa. After three to seven-day incubation, AOM activities were not detected from the 249-m sample but from the 214-m sample. The AOM rates were 93.7 40.6 and 27.7
40.6 and 27.7 37.5 nM/day with and without Fe(III) amendment. Suspended particulates were not visible in the 249-m sample on the filter, while they were abundant and contained amorphous Fe(III) and Fe(III)-bearing phyllosilicates in the 214-m sample. This supports the in-situ activity of Fe(III)-dependent AOM in the deep subsurface borehole.
37.5 nM/day with and without Fe(III) amendment. Suspended particulates were not visible in the 249-m sample on the filter, while they were abundant and contained amorphous Fe(III) and Fe(III)-bearing phyllosilicates in the 214-m sample. This supports the in-situ activity of Fe(III)-dependent AOM in the deep subsurface borehole.
Fukuda, Akari*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Ito, Kazumasa*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Suzuki, Yohei*; Mizuno, Takashi
no journal, ,
JAEA and AIST have been conducting collaborative work on hydrochemical study at MIU construction site. The aim of this collaborative study is to establish the methodology for investigation, analysis and evaluation of colloid/organics/microbes study. This paper reports the biogeochemical study. As the result, it is suggested that groundwater taken from deeper part (1150m depth) is relatively oxidized.
Suzuki, Yohei*; Fukuda, Akari*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Mizuno, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishimura, Hiroki*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Fukuda, Akari*; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Suzuki, Yohei*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English