Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kaira, Kyoichi*; Sunose, Yutaka*; Ohshima, Yasuhiro; Ishioka, Noriko; Arakawa, Kazuhisa*; Ogawa, Tetsushi*; Sunaga, Noriaki*; Shimizu, Kimihiro*; Tominaga, Hideyuki*; Oriuchi, Noboru*; et al.
BMC Cancer, 13, p.482_1 - 482_12, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:83 Percentile:89.67(Oncology)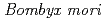 , induces the somatic mutation
, induces the somatic mutationFurusawa, Toshiharu*; Fukamoto, Kana*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Eiko*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Suzuki, Hiromi*; Ishioka, Noriaki*; Wada, Seiichi*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(4), p.371 - 375, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:33.33(Biology)Using heavy-ion microbeam, we report target irradiation of selected compartments within the diapause-terminated egg and its mutational consequences in the silkworm, 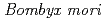 . On one hand, carbon-ion exposure of embryo to 0.5 - 6 Gy increased the somatic mutation frequency, suggesting targeted radiation effects. On the other, such increases were not observed when yolk was targeted, suggesting a lack of nontargeted bystander effect.
. On one hand, carbon-ion exposure of embryo to 0.5 - 6 Gy increased the somatic mutation frequency, suggesting targeted radiation effects. On the other, such increases were not observed when yolk was targeted, suggesting a lack of nontargeted bystander effect.
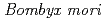
Furusawa, Toshiharu*; Suzuki, Eiko*; Nagaoka, Shunji*; Suzuki, Hiromi*; Ishioka, Noriaki*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 115, 2008/03
Using heavy ion microbeam, we investigated the somatic mutation arising on the larvae in embyro and yolk in the egg of silkworm, 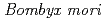 . The incidence of the somatic mutation was 12%, and the same level of mutation following the microbeam irradiation at the center of the egg. However, the microbeam irradiation to the abdomen of the silkworm larvae induced the increase of somatic mutation, 63% (3 Gy) and 80% (6 Gy).
. The incidence of the somatic mutation was 12%, and the same level of mutation following the microbeam irradiation at the center of the egg. However, the microbeam irradiation to the abdomen of the silkworm larvae induced the increase of somatic mutation, 63% (3 Gy) and 80% (6 Gy).
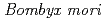 , egg by the incidence of somatic mutation appearing in the larvae
, egg by the incidence of somatic mutation appearing in the larvaeFurusawa, Toshiharu*; Suzuki, Eiko*; Nagaoka, Shunji*; Suzuki, Hiromi*; Ishioka, Noriaki*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko; et al.
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 118, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
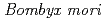 , hatched from diapause eggs
, hatched from diapause eggsFurusawa, Toshiharu*; Suzuki, Eiko*; Nagaoka, Shunji*; Suzuki, Hiromi*; Ishioka, Noriaki*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English