Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Murase, Kiyoka*; Kataoka, Ryuho*; Nishiyama, Takanori*; Nishimura, Koji*; Hashimoto, Taishi*; Tanaka, Yoshimasa*; Kadokura, Akira*; Tomikawa, Yoshihiro*; Tsutsumi, Masaki*; Ogawa, Yasunobu*; et al.
Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate (Internet), 12, p.18_1 - 18_16, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.72(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We identified two energetic electron precipitation (EEP) events during the growth phase of moderate substorms and estimated the mesospheric ionization rate for an EEP event for which the most comprehensive dataset from ground-based and space-born instruments was available. The mesospheric ionization signature reached below 70 km altitude and continued for ~15 min until the substorm onset, as observed by the PANSY radar and imaging riometer at Syowa Station in the Antarctic region. We also used energetic electron flux observed by the Arase and POES 15 satellites as the input for the air-shower simulation code PHITS to quantitatively estimate the mesospheric ionization rate. Combining the cutting-edge observations and simulations, we shed new light on the space weather impact of the EEP events during geomagnetically quiet times, which is important to understand the possible link between the space environment and climate.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Hata, Kuniki; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 556, p.153203_1 - 153203_10, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Solute clusters (SCs) formed in pressurized water reactor surveillance test specimens neutron-irradiated to a fluence of 1  10
10 n/cm
n/cm were analyzed via atom probe tomography to understand the effect of silicon on solute clustering and irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel steels. In high-Cu bearing materials, Cu atoms were aggregated at the center of cluster surrounded by the Ni, Mn, and Si atoms like a core-shell structure. In low-Cu bearing materials, Ni, Mn, and Si atoms formed cluster and these solutes were not comprised core-shell structure in SCs. While the number of Cu atoms in clusters was decreased with decreasing nominal Cu content, the number of Si atoms had clearly increased. The cluster radius (
were analyzed via atom probe tomography to understand the effect of silicon on solute clustering and irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel steels. In high-Cu bearing materials, Cu atoms were aggregated at the center of cluster surrounded by the Ni, Mn, and Si atoms like a core-shell structure. In low-Cu bearing materials, Ni, Mn, and Si atoms formed cluster and these solutes were not comprised core-shell structure in SCs. While the number of Cu atoms in clusters was decreased with decreasing nominal Cu content, the number of Si atoms had clearly increased. The cluster radius ( ) and number density (
) and number density (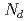 ) decreased and increased, respectively, with increasing nominal Si content. The shift in the reference temperature for nil-ductility transition (
) decreased and increased, respectively, with increasing nominal Si content. The shift in the reference temperature for nil-ductility transition ( RT
RT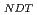 ) showed a good correlation with the square root of volume fraction (
) showed a good correlation with the square root of volume fraction (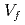 ) multiplied by r (
) multiplied by r (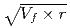 ). This suggested that the dislocation cutting through the particles mechanism dominates the precipitation hardening responsible for irradiation embrittlement. The negative relation between the nominal Si content and
). This suggested that the dislocation cutting through the particles mechanism dominates the precipitation hardening responsible for irradiation embrittlement. The negative relation between the nominal Si content and  RT
RT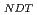 indicated that increasing of nominal Si content reduces the degree of embrittlement.
indicated that increasing of nominal Si content reduces the degree of embrittlement.
Suzudo, Tomoaki; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Caro, A.*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 540, p.152306_1 - 152306_10, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:75.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Spinodal decomposition in thermally aged Fe-Cr alloys leads to significant hardening, which is the direct cause of the so-called 475C-embrittlement. To illustrate how spinodal decomposition induces hardening by atomistic interactions, we conducted a series of numerical simulations as well as reference experiments. The numerical results indicated that the hardness scales linearly with the short-range order (SRO) parameter, while the experimental result reproduced this relationship within statistical error. Both seemingly suggest that neighboring Cr-Cr atomic pairs essentially cause hardening, because SRO is by definition uniquely dependent on the appearance probability of such pairs. A further numerical investigation supported this notion, as it suggests that the dominant cause of hardening is the pinning effect of dislocations passing over such Cr-Cr pairs.
Kataoka, Ryuho*; Nishiyama, Takanori*; Tanaka, Yoshimasa*; Kadokura, Akira*; Uchida, Herbert Akihito*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Ejiri, Mitsumu*; Tomikawa, Yoshihiro*; Tsutsumi, Masaki*; Sato, Kaoru*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 71(1), p.9_1 - 9_10, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:40.25(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Transient ionization of the mesosphere was detected at around 65 km altitude during the isolated auroral expansion occurred at 2221-2226 UT on June 30, 2017. A general-purpose Monte Carlo particle transport code PHITS suggested that significant ionization is possible in the middle atmosphere due to auroral X-rays from the auroral electrons of  10 keV.
10 keV.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwata, Keiko; Tobita, Toru; Otsu, Takuyo; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Hanawa, Satoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
JAEA-Research 2017-018, 122 Pages, 2018/03
Warm pre-stress (WPS) effect is a phenomenon that after applying a load at a high temperature fracture does not occur in unloading during cooling, and then the fracture toughness in reloading at a lower temperature increases effectively. Engineering evaluation models to predict an apparent fracture toughness in reloading are established using experimental data with linear elasticity. However, there is a lack of data on the WPS effect for the effects of specimen size and surface crack in elastic-plastic regime. In this study, fracture toughness tests were performed after applying load-temperature histories which simulate pressurized thermal shock transients to confirm the WPS effect. The experimental results of an apparent fracture toughness tend to be lower than the predictive results using the engineering evaluation models in the case of a high degree of plastic deformation in preloading. Considering the plastic component of preloading can refine the engineering evaluation models.
Matsuki, Takuya; Masui, Kenji; Sekine, Megumi; Tanigawa, Masafumi; Yasuda, Takeshi; Tsutagi, Koichi; Ishiyama, Koichi; Nishida, Naoki; Horigome, Kazushi; Mukai, Yasunobu; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has proposed in its long-term research and development (R&D) plan, development of a real-time measurement technology to monitor and verify nuclear material movement continuously as part of an advanced approach to effectively and efficiently conduct safeguards for reprocessing facilities. Since the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) has solutions containing both Pu and fission products (FP), a new detector development project to monitor Pu with FP is being carried out from 2015 to 2017. This project is mainly conducted in the High Active Liquid Waste Storage (HALWS) in the TRP. For the first step of this project, as the confirmation of composition of high active liquid waste (HALW) to evaluate neutron/ -ray emitted from solution in the selected HALW tank which has the most amount of Pu in HALW tanks at the TRP, we took HALW sample and conducted
-ray emitted from solution in the selected HALW tank which has the most amount of Pu in HALW tanks at the TRP, we took HALW sample and conducted  -ray spectrum measurement for HALW. As a study of detector setting location, to survey the available neutron/
-ray spectrum measurement for HALW. As a study of detector setting location, to survey the available neutron/ -ray (i.e. intensity) at the outside surface of the cell where HALW tank is located, we implemented continuous measurement by neutron/
-ray (i.e. intensity) at the outside surface of the cell where HALW tank is located, we implemented continuous measurement by neutron/ -ray detector. In this paper, we report three
-ray detector. In this paper, we report three  -ray peaks related with
-ray peaks related with  Pu and
Pu and  Pu measured in the composition research of HALW, which is needed to identify Pu amount by the new detector that we are developing and the result of radiation measurement on the surface of the cell.
Pu measured in the composition research of HALW, which is needed to identify Pu amount by the new detector that we are developing and the result of radiation measurement on the surface of the cell.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Kakubo, Yuta*; Matsukawa, Yoshitaka*; Nozawa, Yasuko*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Katsuyama, Jinya; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Onizawa, Kunio; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 452(1-3), p.235 - 240, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:95.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Microstructures and hardness of stainless steel weld overlay cladding of reactor pressure vessels subjected to the thermal aging at 400  C for 100-10,000 h were investigated using atom probe tomography and nanoindentation technique. The Cr concentration fluctuation in the
C for 100-10,000 h were investigated using atom probe tomography and nanoindentation technique. The Cr concentration fluctuation in the  -ferrite phase caused by spinodal decomposition rapidly progressed by the 100 h aging while NiSiMn clusters increased in number density at 2,000 h and coarsened at 10,000 h. The hardness of the
-ferrite phase caused by spinodal decomposition rapidly progressed by the 100 h aging while NiSiMn clusters increased in number density at 2,000 h and coarsened at 10,000 h. The hardness of the  -ferrite phase also rapidly increased at the short aging time. The Cr concentration fluctuation and the hardness were in good correlation with the degree of the Cr concentration fluctuation rather than the formation of the NiSiMn clusters. These results strongly suggested that the dominant factor of the hardening of the
-ferrite phase also rapidly increased at the short aging time. The Cr concentration fluctuation and the hardness were in good correlation with the degree of the Cr concentration fluctuation rather than the formation of the NiSiMn clusters. These results strongly suggested that the dominant factor of the hardening of the  -ferrite phase by the thermal aging was Cr spinodal decomposition.
-ferrite phase by the thermal aging was Cr spinodal decomposition.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Kakubo, Yuta*; Matsukawa, Yoshitaka*; Nozawa, Yasuko*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Katsuyama, Jinya; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 449(1-3), p.273 - 276, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:81.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Microstructural changes and hardness of stainless steel weld overlay cladding of reactor pressure vessels subjected to the neutron irradiation with a dose of 7.2  10
10 n cm
n cm (E
(E  1 MeV) and a flux of 1.1
1 MeV) and a flux of 1.1  10
10 n cm
n cm s
s at 290
at 290 C were investigated by atom probe tomography and with nanoindentation technique. In order to isolate the effect of the irradiation, we compared the results of the measurements of the irradiated sample with that of the aged one at 300
C were investigated by atom probe tomography and with nanoindentation technique. In order to isolate the effect of the irradiation, we compared the results of the measurements of the irradiated sample with that of the aged one at 300 C for the time equivalent to the irradiation. The Cr concentration fluctuation was enhanced in the
C for the time equivalent to the irradiation. The Cr concentration fluctuation was enhanced in the  -ferrite phase of the irradiated sample. In addition, the enhancement of the concentration fluctuation of Si, which was not observed in the aged sample, was observed. The hardening at the
-ferrite phase of the irradiated sample. In addition, the enhancement of the concentration fluctuation of Si, which was not observed in the aged sample, was observed. The hardening at the  -ferrite phase was occurred by both the irradiation and the aging. However, the former was more than that expected from the Cr concentration fluctuation, which suggested that the Si concentration fluctuation and irradiation-induced defects were possible origins of the additional hardening.
-ferrite phase was occurred by both the irradiation and the aging. However, the former was more than that expected from the Cr concentration fluctuation, which suggested that the Si concentration fluctuation and irradiation-induced defects were possible origins of the additional hardening.
Sonoda, Tetsu*; Wada, Michiharu*; Tomita, Hideki*; Sakamoto, Chika*; Takatsuka, Takaaki*; Furukawa, Takeshi*; Iimura, Hideki; Ito, Yuta*; Kubo, Toshiyuki*; Matsuo, Yukari*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 295, p.1 - 10, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:83.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Kameda, Jun*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 415(2), p.198 - 204, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:92.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Microstructural changes by thermal aging in stainless steel weld overlay cladding of nuclear reactor pressure vessels were investigated using atom probe tomography. The cladding material was composed of about 90% austenite phase and 10%  -ferrite phase and thermally aged at 400
-ferrite phase and thermally aged at 400 C for 10,000 h. In the ferrite phase, the thermal aging increased a fluctuation of Cr concentration due to spinodal decomposition and caused the precipitation of G phase with chemical composition of Ni:Si:Mn = 16:7:6. Moreover, significant hardening of the ferrite phase was induced by the thermal aging. On the other hand, the thermal aging did not affect on the microstructures and the hardness in the austenite phase, which indicates the microstructural changes were responsible for the hardening in the ferrite phase. The analyses of the magnitude of the spinodal decomposition and the hardness implied that the spinodal decomposition was the main cause of the hardening.
C for 10,000 h. In the ferrite phase, the thermal aging increased a fluctuation of Cr concentration due to spinodal decomposition and caused the precipitation of G phase with chemical composition of Ni:Si:Mn = 16:7:6. Moreover, significant hardening of the ferrite phase was induced by the thermal aging. On the other hand, the thermal aging did not affect on the microstructures and the hardness in the austenite phase, which indicates the microstructural changes were responsible for the hardening in the ferrite phase. The analyses of the magnitude of the spinodal decomposition and the hardness implied that the spinodal decomposition was the main cause of the hardening.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Kuramoto, Akira*; Kameda, Jun*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Hasegawa, Masayuki*; Okubo, Tadakatsu*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 402(2-3), p.93 - 101, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:96.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This study reports the effects of the composition and dose on microstructure evolution and hardening in high- and low-impurity A533B-1 steels neutron-irradiated in a wide range from 0.32 to 9.9  10
10 n cm
n cm (E
(E  1 MeV) under a constant high flux at JMTR. The early hardening was found to be caused by mainly matrix defects. The gradual hardening after middle stage of irradiation was found to be caused by the formation of Cu rich clusters (CRCs) and Mn-Ni-Si rich clusters (MNSCs), respectively, in the high- and low-impurity steels. By applying a RB model, it was found that the dislocation-pinning strength of the CRCs and MNSCs is almost the same. Moreover, the high-impurity steel subjected to the highest dose revealed the formation of MNSCs.
1 MeV) under a constant high flux at JMTR. The early hardening was found to be caused by mainly matrix defects. The gradual hardening after middle stage of irradiation was found to be caused by the formation of Cu rich clusters (CRCs) and Mn-Ni-Si rich clusters (MNSCs), respectively, in the high- and low-impurity steels. By applying a RB model, it was found that the dislocation-pinning strength of the CRCs and MNSCs is almost the same. Moreover, the high-impurity steel subjected to the highest dose revealed the formation of MNSCs.
Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Strasser, P.*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Koda, Akihiro*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Nakahara, Kazutaka*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Kobayashi, Yasuo*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 225, p.012036_1 - 012036_7, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:92.71(Physics, Applied)Strasser, P.*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Kobayashi, Yasuo*; Nakahara, Kazutaka*; Kato, Mineo*; Takeshita, Soshi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 225, p.012050_1 - 012050_8, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:95.21(Physics, Applied)Kagohara, Kyoko; Ishiyama, Tatsuya*; Imaizumi, Toshifumi*; Miyauchi, Takahiro*; Sato, Hiroshi*; Matsuta, Nobuhisa*; Miwa, Atsushi*; Ikawa, Takeshi*
Tectonophysics, 470(3-4), p.319 - 328, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.49(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Seismic reflection profiles across coseismic fault scarps of the A.D. 1896 Rikuu earthquake along the eastern margin of the Yokote basin fault zone (EYBFZ), correlated with borehole stratigraphy and geologic mapping, provide insights into its detailed structural evolution. In spite of along-strike variations of thrust geometries both at ground surface and at shallow depth, the EYBFZ has commonly formed as forward breaking imbricate thrust systems. Spatial variations in the long-term uplift rates estimated from cross-section balancing are consistent with mountain topography, in contrast to their weak coupling with the magnitudes of short-term uplift rates and coseismic uplift during the A.D. 1896 earthquake. This suggests that mechanical decoupling of Miocene mudstone that formed frontal emergent thrust faults may have enhanced the slip at shallowest structural levels at shorter timescales.
Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Strasser, P.*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Koda, Akihiro*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Nakahara, Kazutaka*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Kato, Mineo*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(5-7), p.957 - 961, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:47.84(Physics, Condensed Matter)The muon science facility (MUSE) is one of the experimental areas of the J-PARC. The MUSE facility is located in the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF), which is a building integrated to include both neutron and muon science programs. Construction of the MLF building was started at the beginning of 2004, and was recently completed at the end of the 2006 fiscal year. We have been working on the installation of the beamline components, expecting the first muon beam in the autumn of 2008.
Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide; Anderegg, J. W.*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Hasegawa, Masayuki*; Kameda, Jun*
Acta Materialia, 56(16), p.4510 - 4521, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:92.13(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effects of intergranular P segregation and hardening on the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) in several neutron-irradiated reactor pressure vessel steels with different bulk contents of P and Cu have been investigated using a scanning Auger microbe, a local electrode atom probe and positron annihilation spectroscopy. Increasing the neutron fluence at 563 K promotes intergranular P segregation. The content of P more significantly affects irradiation hardening than that of Cu due to distinct formation of P-rich precipitates arising from the stabilization of vacancies. Analyzing the correlations between the P segregation, hardening, fraction of intergranular fracture and DBTT, it is found neutron irradiation mitigates an embrittling effect of segregated P, and therefore the hardening more strongly affects the DBTT shift than the P segregation.
 Li(
Li( , n)
, n) B reaction
B reactionIshiyama, Hironobu*; Hashimoto, Takashi; Ishikawa, Tomoko*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Das, S. K.*; Miyatake, Hiroari; Mizoi, Yutaka*; Fukuda, Tomokazu*; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Fuchi, Yoshihide*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 640(3), p.82 - 85, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:84.97(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The excitation function of the  Li(
Li( ,n)
,n) B reaction was measured while identifying the final state event by event in the region of E
B reaction was measured while identifying the final state event by event in the region of E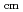 = 0.7 - 2.6 MeV using a highly efficient detector system and a low-energy
= 0.7 - 2.6 MeV using a highly efficient detector system and a low-energy  Li beam. The results are much improved both in statistics and precisions, and show smaller cross sections than those of previous measurements by a factor of more than 2 in the low-energy region of E
Li beam. The results are much improved both in statistics and precisions, and show smaller cross sections than those of previous measurements by a factor of more than 2 in the low-energy region of E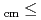 1.5 MeV. A resonance-like structure is found at around E
1.5 MeV. A resonance-like structure is found at around E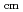 = 0.85 MeV.
= 0.85 MeV.
 Li(
Li( ,n)
,n) B reaction for astrophysical interest
B reaction for astrophysical interestDas, S. K.*; Fukuda, Tomokazu*; Mizoi, Yutaka*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Yoshikawa, Nobuharu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 847, p.374 - 376, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
 SR study of magnetic order in La
SR study of magnetic order in La Ba
Ba CuO
CuO under high pressure
under high pressureSato, Koki*; Goko, Tatsuro*; Takeshita, Satoshi*; Hayashi, Yuko*; Arai, Juichiro*; Higemoto, Wataru; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Nagamine, Kanetada*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 374-375, p.40 - 43, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:22.76(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have performed muon spin relaxation and resistivity measurements under high pressure in La Ba
Ba CuO
CuO with x=0.125 and 0.135. With increasing pressure, the superconducting critical temperature increases for both samples. Even by applying pressure, static magnetic order still exists. This result indicates the LTT structure is not always necessary for stabilizing the static magnetic order. However, the magnetic volume fraction estimated is reduced by applying pressure. The reduction of the magnetic volume fraction for x=0.125 is less than that for x=0.135. This means hole concentration is one of the important factors for the appearance of the static magnetic order.
with x=0.125 and 0.135. With increasing pressure, the superconducting critical temperature increases for both samples. Even by applying pressure, static magnetic order still exists. This result indicates the LTT structure is not always necessary for stabilizing the static magnetic order. However, the magnetic volume fraction estimated is reduced by applying pressure. The reduction of the magnetic volume fraction for x=0.125 is less than that for x=0.135. This means hole concentration is one of the important factors for the appearance of the static magnetic order.