Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yabe, Takanori; Murakami, Makio; Shiota, Yuki; Isobe, Yuta; Shiohama, Yasutaka; Hamano, Tomoharu; Takagi, Tsuyohiko; Nagaoki, Yoshihiro
JAEA-Technology 2022-002, 66 Pages, 2022/07
In the first stage of "Monju" decommissioning project, "Fuel Unloading Operations" have been carrying out. The operations consists of two processes. The first process is "Fuel Treatment and Storage" is that the fuel assemblies unloaded from the Ex-Vessel fuel Storage Tank are canned after sodium cleaning, and then transferred to the storage pool. The second process is "Fuel Unloading" that the fuel assemblies in the reactor core are replaced with dummy fuel assemblies and stored in the Ex-Vessel fuel Storage Tank. "Fuel Treatment and Storage" and "Fuel Unloading" are performed alternately until 370 fuel assemblies in the core and 160 fuel assemblies in the Ex-Vessel fuel Storage Tank are all transferred to the storage pool. In fiscal 2018, as "Fuel Treatment and Storage", 86 fuel assemblies were transferred to the storage pool. As "Fuel Unloading", 76 dummy fuel assemblies were stored in the Ex-Vessel fuel Storage Tank. In fiscal 2019, as "Fuel Unloading", 60 fuel assemblies and 40 blanket fuel assemblies were unloaded from the core. These assemblies were stored in the Ex-Vessel fuel Storage Tank, and dummy fuel assemblies were loaded into the core instead. During these operations, a total of 38 cases of alarming or equipment malfunctions classified into 24 types occurred. However, no significant events that menaces to safety have occurred. The operations were continued safely by removing the direct factors for the malfunctions in the equipment operation and performance.
Shiota, Yuki; Yabe, Takanori; Murakami, Makio; Isobe, Yuta; Sato, Masami; Hamano, Tomoharu; Takagi, Tsuyohiko; Nagaoki, Yoshihiro
JAEA-Technology 2022-001, 117 Pages, 2022/07
In the first stage of Monju decommissioning project, fuel unload work began to be carried out. There are two tasks in this work. One is fuel treatment and storage work that gets rid of sodium on the fuel assemblies unloaded from Ex-Vessel fuel Storage Tank (EVST) and carries it in the storage pool, and the other is fuel unloading that the fuel assemblies in the reactor core is replaced with dummy fuels and stored in EVST. Fuel treatment and storage work and fuel unloading work are performed alternately, and 370 bodies in the core and 160 pieces in EVST are all carried to the storage pool. 86 fuel assemblies was carried to the storage pool in fuel treatment and storage work in 2018 and 76 dummy fuels were stored in EVST for fuel unloading work. During the work, 86 types and 232 alarms / malfunctions occurred, but there was no impact on safety. There was one equipment's failure at gripper's claw open / close clutch of ex-vessel fuel transfer machine B, but it was repaired and restarted. Also it was eliminated the cause of problem or concession that the equipment failure due to the sticking of the sodium compound and continuous use of the equipment. Some problems related to system control occurred, but the work was done after checking the safety. With estimation of various troubles, reduction of frequency of trouble occurrence and minimization of impacts on schedule performed.
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.7(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,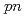 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
Kanto, Yasuhiro*; Onizawa, Kunio; Machida, Hideo*; Isobe, Yoshihiro*; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 87(1), p.11 - 16, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:62.15(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)JAEA had sponsored research committees on probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) organized by the Japan Welding Engineering Society (JWES) for more than a decade. This work still continues with the same members in JWES. The purpose of the continuous activity is to provide probabilistic approaches in several fields of integrity problems of nuclear power plant. This paper shows some of the newest results of the JWES research committee. First topic is evaluation of the new JSME code case with rules of fitness-for-service from the view of PFM, including reactor pressure vessel subject to pressurized thermal shock loading, piping with a crack of the allowable size and effect of sizing accuracy for piping integrity. Another is development of new PFM techniques including reliability assessment of piping with domestic SCC data and maintenance optimization of LWRs based on risk and economic models. The last topic is the international round robin program just starting from 2008.
Kanto, Yasuhiro*; Onizawa, Kunio; Machida, Hideo*; Isobe, Yoshihiro*; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
Proceedings of 7th International Conference on the Integrity of Nuclear Components, p.219 - 228, 2008/07
This paper describes a review of recent Japanese activities on probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analyses. JAEA had sponsored research committees on PFM organized by the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers and the Japan Welding Engineering Society (JWES) for more than a decade. This work still continues with the same members in JWES. The purpose of the continuous activity is to provide probabilistic approaches in several fields of integrity of reactor components. This paper summarizes some of the latest results of this activity. First topic is evaluation of the JSME rules on Fittness-For-Service from the view of PFM, including reactor pressure vessel with a crack of the allowable size, and effect of sizing accuracy in inspection. The next one is development of new PFM techniques including piping reliability assessment on domestic SCC data and maintenance optimization based on risk and economic models. The last is the international round robin program just starting from 2008.
Narita, Osamu; Iwata, Noboru; Isobe, Yoshihiro; Seki, Masakazu; Kadosaka, Hidetake; Ninomiya, Kazushige; Sato, Osamu
JAEA-Technology 2006-037, 102 Pages, 2006/06
We edited and published the Environmental Report according to the law on Promotion of the Environmental Concerning Activity by means of the Publish of Environmental Concerning Data. The report included the environmental concerning activity at the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) and the Japan Nuclear Fuel Cycle Development Institute (JNC) in the first half year of 2005. This report is the first one which is regulated and obligated by the law. We have made much effort for gathering the data and gained a lot of experience on editing the report. We hope this paper is useful not only for the back data of our environmental report, but also for the organization which is planning to publish the similar environmental report.
Yomogida, Takumi; Yamada, Shinya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; Sato, Toshiki*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Toyama, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Noda, Hirofumi*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Biotite is known as a host phase that retains uranium (U) in uranium deposits at Ningyo-Toge and Tono, and it is expected that the distribution of U in biotite will provide insight into the concentration and long-term immobilization of U. However, biotite contains rubidium (Rb), which interferes with X-ray fluorescence analysis, making it difficult to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite by measurement using a conventional solid state detector (SSD). In this study, we developed a method to use a transition edge sensor (TES) as a detector in microbeam X-ray fluorescence analysis, which enables us to detect X-ray fluorescence with an energy resolution of about 20 eV and to obtain a Rb K line at 13.373 keV and a U L
line at 13.373 keV and a U L line at 13.612 keV can be completely separated. Therefore,the developed method enables us to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite.
line at 13.612 keV can be completely separated. Therefore,the developed method enables us to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite.
Yomogida, Takumi; Yamada, Shinya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; Sato, Toshiki*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Toyama, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Noda, Hirofumi*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The reduction of uranium on biotite was studied to obtain insight into the immobilization of uranium in the environment. The chemical species of uranium in biotite were studied using a superconducting transition edge sensor and an X-ray emission spectrometer to remove interference from rubidium in biotite. As a result, the speciation of uranium in biotite collected from former uranium deposits was possible. The XANES spectra of the biotite indicated that the uranium in the biotite was partially reduced.