Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
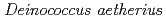 sp. nov., isolated from the stratosphere
sp. nov., isolated from the stratosphereYang, Y.*; Ito, Takashi*; Yokobori, Shinichi*; Shimada, Haruo*; Itahashi, Shiho*; Sato, Katsuya; Oba, Hirofumi*; Narumi, Issei; Yamagishi, Akihiko*
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 60, p.776 - 779, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:50.16(Microbiology)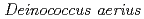 sp. nov., isolated from the high atmosphere
sp. nov., isolated from the high atmosphereYang, Y.*; Ito, Takashi*; Yokobori, Shinichi*; Itahashi, Shiho*; Shimada, Haruo*; Sato, Katsuya; Oba, Hirofumi; Narumi, Issei; Yamagishi, Akihiko*
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 59, p.1862 - 1866, 2009/00
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:54.86(Microbiology)An orange pigmented, non-motile, coccoid bacterial strain, TR0125, was isolated from dust samples collected in the high atmosphere above Japan. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that it was within the radiation of  species. Major peptidoglycan amino acids were D-glutamic acid, glycine, D-alanine, L-alanine and ornithine. Predominant fatty acids were 17:0 iso, iso 17:1
species. Major peptidoglycan amino acids were D-glutamic acid, glycine, D-alanine, L-alanine and ornithine. Predominant fatty acids were 17:0 iso, iso 17:1  9c and 15:0 iso. Strong resistance to desiccation, UV-C and
9c and 15:0 iso. Strong resistance to desiccation, UV-C and  -radiation, high DNA G+C content also supported the affiliation of strain TR0125
-radiation, high DNA G+C content also supported the affiliation of strain TR0125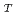 to the genus
to the genus  . TR0125
. TR0125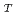 had a highest similarity value (95.7 %) of the 16S rRNA gene sequence to the type strain of the species
had a highest similarity value (95.7 %) of the 16S rRNA gene sequence to the type strain of the species 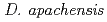 , and phylogenetic analysis shows that it was further separated from
, and phylogenetic analysis shows that it was further separated from 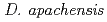 than from
than from  , indicating that strain TR0125
, indicating that strain TR0125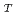 was not a member of these two
was not a member of these two  species. Besides, there were phenotypic differences between strain TR0125
species. Besides, there were phenotypic differences between strain TR0125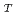 and type strains of the two species. Therefore, we propose a new species of the genus
and type strains of the two species. Therefore, we propose a new species of the genus  ,
, 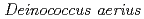 sp. nov. (type strain, TR0125
sp. nov. (type strain, TR0125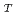 = JCM 11750
= JCM 11750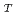 = DSM 21212
= DSM 21212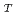 ), to accommodate this isolate.
), to accommodate this isolate.
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Yang, Y.*; Sugino, Tomohiro*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Itahashi, Shiho*; Fujisaki, Kenta*; Fushimi, Hidehiko*; Hasegawa, Sunao*; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiro*; et al.
no journal, ,