Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito
Scripta Materialia, 255, p.116366_1 - 116366_5, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Reduction of grain boundary cohesive energy by hydrogen has been considered as one of the candidate causes of grain boundary fracture in steels and aluminum alloys. Recently, the effects of grain boundary segregation elements have been investigated by first-principles calculations, but there are few studies that quantitatively estimate the grain boundary cohesive energy. In this study, we describe a quantitative evaluation method using first-principles calculation results and show some examples of experimental calculations.
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Materials Transactions, 64(11), p.2553 - 2559, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:76.40(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We attempted to calculate the hydrogen trapping energies on the incoherent interfaces of MgZn precipitates and Mg
precipitates and Mg Si crystallites in aluminum alloys from first-principles calculations. Since the unit cell containing the incoherent interface does not satisfy the periodic boundary condition, resulting in a discontinuity of crystal blocks, the hydrogen trapping energy was calculated in a region far from the discontinuity (vacuum) region. We found considerable trapping energies for hydrogen atoms at the incoherent interfaces consisting of assumed atomistic arrangement. We also conducted preliminary calculations of the reduction in the cohesive energy by hydrogen trapping on the incoherent interfaces of Mg
Si crystallites in aluminum alloys from first-principles calculations. Since the unit cell containing the incoherent interface does not satisfy the periodic boundary condition, resulting in a discontinuity of crystal blocks, the hydrogen trapping energy was calculated in a region far from the discontinuity (vacuum) region. We found considerable trapping energies for hydrogen atoms at the incoherent interfaces consisting of assumed atomistic arrangement. We also conducted preliminary calculations of the reduction in the cohesive energy by hydrogen trapping on the incoherent interfaces of Mg Si in the aluminum matrix.
Si in the aluminum matrix.
 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.80(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito; Ebihara, Kenichi
Materials Transactions, 62(5), p.582 - 589, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:73.99(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Si and Al
Si and Al FeCu
FeCu intermetallic compounds in aluminum alloy; First-principles calculations
intermetallic compounds in aluminum alloy; First-principles calculationsYamaguchi, Masatake; Tsuru, Tomohito; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Materials Transactions, 61(10), p.1907 - 1911, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:69.50(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tsuru, Tomohito; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Ebihara, Kenichi; Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.1998_1 - 1998_8, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:88.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Age-hardening has been one and only process to achieve high strength aluminum alloys since unlike iron and titanium, pure aluminum does not have other solid phases during heat treatment. Highly-concentrated precipitations play therefore dominant role in mechanical properties and hydrogen embrittlement of aluminium alloys. It has been considered that the coherent interface between matrix and precipitation does not contribute to the crack initiation and embrittlement due to its coherency. Here, we discovered the origin of unprecedented quasi-cleavage fracture mode. Hydrogen partitioning at various defect sites is investigated comprehensively combined with experiment, theory and first-principles calculations. We demonstrate that despite low excess free volume, the aluminum-precipitation interface is more preferable trap site than void and grain boundary. The cohesivity of the interface deteriorates significantly with increasing occupancy while hydrogen atoms are trapped stably up to extremely high occupancy equivalent to spontaneous cleavage.
Matsuura, Yuto*; Hayano, Akira; Itakura, Kenichi*; Suzuki, Yukinori*
Applied Soft Computing, 84, p.105737_1 - 105737_9, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:28.37(Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence)LiDAR (laser imaging detection and ranging) has been developed to obtain a high-resolution point cloud data indicating the detailed 3D shapes of an object. To identify discontinuities in a rock mass of a tunnel gallery wall, it is necessary to approximate the rock mass surface with small planes. Normal vectors of the planes are important to identify discontinuities. We developed an algorithm for estimation of planes based on multi-dimensional particle swarm optimization (MD PSO) from point cloud data. Point cloud data were segmented into bounding boxes and grouped into clusters by MD PSO. Planes were estimated using the least squares method for point cloud data in the respective clusters. The newly developed MD PSO algorithm was evaluated using point cloud data obtained from a gallery wall. Evaluation was carried out in comparison with the previous developed variable-box segmentation (VBS) algorithm. The MD PSO-based algorithm showed a 7% higher accuracy than that of the VBS algorithm.
 hydrogen partitioning control
hydrogen partitioning controlToda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Su, H.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito; et al.
Tetsu To Hagane, 105(2), p.240 - 253, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito; Matsuda, Kenji*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Computational Materials Science, 156, p.368 - 375, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:83.47(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The segregation of multiple hydrogen atoms along aluminum (Al) grain boundaries (GBs) and fracture surfaces (FSs) was investigated through first-principles calculations considering the characteristics of GBs. The results indicate that hydrogen segregation is difficult along low-energy GBs. The segregation energy of multiple hydrogen atoms along GBs and FSs and the cohesive energy was obtained for three types of high-energy Al GBs. With increasing hydrogen segregation along the GBs, the cohesive energy of the GB decreases and approaches zero with no decrease in GB segregation energy. The GB cohesive energy decreases in parallel with the volume expansion of the region of low electron density along the GB.
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Tsuru, Tomohito; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Keikinzoku, 68(11), p.588 - 595, 2018/11
no abstracts in English
Ebihara, Kenichi; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Tsuru, Tomohito; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Keikinzoku, 68(11), p.596 - 602, 2018/11
Hydrogen embrittlement (HE) is considered as one cause of stress corrosion cracking. HE is a serious problem in the development of high strength aluminum alloy as with steels. For understanding HE, it is inevitable to know hydrogen trapping states in the alloys and it can be identified using thermal desorption spectrometry of H. In this study, we numerically simulated thermal desorption spectra of hydrogen in aluminum for a cylindrical and a plate specimens and interpreted the desorption peaks included in them on the basis of the trap site concentration and the trap energy. As a result, we found that the peak at the lowest-temperature side can result from grain boundaries and confirmed that the reported interpretation for other peaks is reasonable. We also obtained the result showing the possibility that the trap site concentration of defects changes during heating the specimens. This result may give a suggestion for the interpretation of temperature desorption spectra of steels.
 precipitate in Al-Mg-Zn alloys
precipitate in Al-Mg-Zn alloysTsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Computational Materials Science, 148, p.301 - 306, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:83.65(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high strength 7xxx series Al alloys has been recognized as the critical issues in the practical use of Al alloys. Focusing on the interface between MgZn precipitates and an Al matrix, which is considered as one of the important segregation sites in these alloys, we investigated the stable
precipitates and an Al matrix, which is considered as one of the important segregation sites in these alloys, we investigated the stable  -MgZn
-MgZn -Al interface, and the possible hydrogen trap sites in MgZn
-Al interface, and the possible hydrogen trap sites in MgZn and at the
and at the  -MgZn
-MgZn -Al interface via first-principles calculation. Most of the interstitial sites inside the MgZn
-Al interface via first-principles calculation. Most of the interstitial sites inside the MgZn crystal were not possible trap sites because their energy is relatively higher than that of other trap sites. The trap energy of the most favorable site at the
crystal were not possible trap sites because their energy is relatively higher than that of other trap sites. The trap energy of the most favorable site at the  -MgZn
-MgZn -Al is approximately -0.3 eV/H, which is more stable that of the interstitial site at the grain boundary. The interface between MgZn
-Al is approximately -0.3 eV/H, which is more stable that of the interstitial site at the grain boundary. The interface between MgZn and Al is likely to be a possible trap site in Al alloys.
and Al is likely to be a possible trap site in Al alloys.
Matsukawa, Shun*; Itakura, Kenichi*; Hayano, Akira; Suzuki, Yukinori*
Journal of MMIJ, 133(11), p.256 - 263, 2017/11
LIDAR detects a rock mass surface configurations as a point cloud. DiAna (Discontinuity Analysis) is a Matlab tool which was developed for geo-structural analysis of rock mass discontinuities. DiAna segments a point cloud into bounding boxes to estimate the surface of a rock mass. However, an expert's skills necessary to determine the appropriate size of the bounding boxes for DiAna. We developed the VBS (Variable-Box Segmentation) algorithm to determine the appropriate box size depending on the location of the point cloud and to estimate the surface of a rock mass. The performance of the VBS algorithms was evaluated by comparison with the DiAna algorithm. The results of comparison showed that the VBS algorithm estimated planes more accurately for the reference planes than the DiAna algorithm. Therefore, the VBS algorithm determines appropriate box sizes automatically depending on the location of the point cloud and estimates the surface appropriately.
Hayano, Akira; Itakura, Kenichi*
Journal of MMIJ, 133(4), p.76 - 86, 2017/04
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Proceedings of 2016 International Hydrogen Conference (IHC 2016); Materials Performance in Hydrogen Environments, p.563 - 571, 2017/00
no abstracts in English
Sako, Hiroyuki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Sakaguchi, Takao*; Chujo, Tatsuya*; Esumi, Shinichi*; Gunji, Taku*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hwang, S.; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 956, p.850 - 853, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:65.08(Physics, Nuclear)Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Corrosion Reviews, 33(6), p.547 - 557, 2015/11
A multiscale analysis has been conducted on hydrogen-induced intergranular cracking at ambient temperature in medium strength (840 MPa) Ni-Cr steel with antimony, tin, and phosphorous segregation. Combining first-principles calculations and fracture mechanics experiments, a multiscale relationship between threshold stress intensity factor (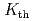 ) and cohesive energy of grain boundary (the ideal work of interfacial separation, 2
) and cohesive energy of grain boundary (the ideal work of interfacial separation, 2
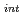 ) was revealed. The
) was revealed. The 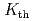 was found to decrease rapidly under a certain threshold of 2
was found to decrease rapidly under a certain threshold of 2
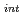 , where the 2
, where the 2
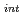 decreases mainly by mobile hydrogen segregation on fracture surfaces. This segregation is considered to arise during formation of the fracture surfaces under thermodynamic equilibrium in slow crack growth. The resulting strong decohesion probably makes it difficult to emit dislocations at microcrack tip region, leading to a large reduction of stress intensity factor. Our analysis based on this mobile hydrogen decohesion demonstrates that the
decreases mainly by mobile hydrogen segregation on fracture surfaces. This segregation is considered to arise during formation of the fracture surfaces under thermodynamic equilibrium in slow crack growth. The resulting strong decohesion probably makes it difficult to emit dislocations at microcrack tip region, leading to a large reduction of stress intensity factor. Our analysis based on this mobile hydrogen decohesion demonstrates that the 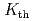 decreases dramatically within a low and narrow range of hydrogen content in iron lattice in high-strength steels.
decreases dramatically within a low and narrow range of hydrogen content in iron lattice in high-strength steels.
Xu, Z.*; Yamachi, Hiroshi*; Sato, Toshinori; Matsui, Hiroya; Itakura, Kenichi*
Doboku Gakkai Rombunshu, F3 (Doboku Johogaku) (Internet), 71(1), p.43 - 55, 2015/10
In the process of underground space development, enormous information is collected in each developing stage, such as investigation, plan, design and construction. It is important to properly feed back these information to design and construction in order to realize rational design and construction of an underground space. And more, these information also become basic data in a plane of structure management. However, it is almost impossible that it is controlled in the individual ability, since collected information quantity is too enormous. For the purpose of intuitively controlling and processing these enormous information, we devised the system for the data management by freely moving in virtual reality space. In this paper, the basic structure of the system constructed by adopting WEB3D and RDBMS, is described, and the practicability is verified.
Hayano, Akira; Matsukawa, Shun*; Xu, Z.*; Itakura, Kenichi*
Proceedings of 8th Asian Rock Mechanics Symposium (ARMS-8) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2014/10
In generally, the geological observation of a gallery wall is performed based on geologists' traditional techniques. However, to reduce the differences in data quality attributable to geologists' individual judgments and experiences, it is necessary to provide a method to acquire objective data that are unaffected by a geologist's subjectivity. It is also necessary to reduce the work volume associated with geological observations of gallery walls. Three-dimensional laser scanning (3DLS) is useful as a means for achieving this goal. In this study, acquisition of geometric data of fractures distributed on the gallery wall has been conducted using 3DLS data while clarifying the geological observation data necessary for modeling of a fractured rock mass. The acquired geometric data of fractures were compared with data acquired by a geologist. Consequently, the fractures were extracted by visible reading of images generated from 3DLS data, then geometric data was generated.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Kaburaki, Hideo; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
"Hagane No Kikaiteki Tokusei Ni Oyobosu Suiso No Koka To Sono Hyoka" Shimpojium Yokoshu (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2014/09
Since hydrogen(H) embrittlement is one factor causing degradation and/or fracture of steel, understanding its mechanism is required. The grain-boundary(GB) decohesion due to segregation of H is considered to cause the delayed fracture of high strength steels and the cold cracking in welding. In the model based on GB decohesion, information of strength of GBs estimated in the atomic scale is used for the estimation of strength or crack propagation in the macroscopic scale. However the modeling between the atomic and the macroscopic scales is not clear. In particular, the validity of the model using the elastic continuum around nano-cracks for stress concentration at the crack tip is not clear. Thus, we examined the difference of the stress distribution around the nano-crack which was estimated by molecular dynamics and by a continuum calculation. As a result, the discrepancy became remarkable at high strain. The stress concentration was not simulated by the elastic continuum model.