Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Masuki, Yuma*; Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Naito, Sayuri*; Murakami, Takuma*; Umemura, Ayako*; Fujita, Natsuko; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Minami, Masayo*; Niwa, Masakazu; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 485, p.136843_1 - 136843_10, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)Lacustrine deposits have 30-fold higher As abundance than the average crustal deposit. Arsenic is mostly concentrated as discrete horizons deposited in spring and autumn. As-rich layers contain FeAsS, AsS, and As S
S but As-rich hotspots mostly contain FeAsS. As accumulation to sediment is controlled by redox potential with organic matter.
but As-rich hotspots mostly contain FeAsS. As accumulation to sediment is controlled by redox potential with organic matter.
Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Umemura, Ayako*; Naito, Sayuri*; Masuki, Yuma*; Itayama, Yui*; Niwa, Masakazu; Shirono, Shinichi*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Kawakami, Shinichi*
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 210, p.106817_1 - 106817_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:19.24(Spectroscopy)X-ray fluorescence (XRF) scanning of lacustrine sediments has been used to extend the approach to a wider range of elemental records in both ages and timescales of variations in past environments and climates. However, one of severe problems with effects of the XRF intensity by grain size and mineralogical composition known as "heterogeneity effects" have been pointed out. This study investigated the heterogeneity effect of Fe intensities on X-ray beam using several binary powder mixtures and lacustrine sediment cores.
Oikawa, Kenichi; Harjo, S.; Pham, A. H.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Morito, Shigekazu*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oba, Takuya*; Ito, Masakazu*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011062_1 - 011062_6, 2021/03
Oikawa, Kenichi; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Omae, Kazuma*; Pham, A.*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Harjo, S.; et al.
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.207 - 213, 2020/02
Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Takano, Masao*; Sano, Naomi; Tani, Yukinori*; Ochiai, Shinya*; Naito, Sayuri*; Murakami, Takuma*; Niwa, Masakazu; Kawakami, Shinichi*
Sedimentology, 66(6), p.2490 - 2510, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:51.05(Geology)Micro-X-ray fluorescence (XRF) scanning spectroscopy of marine and lake sedimentary sequences can provide detailed paleoenvironmental records available through element intensities proxy data. However, problems for effects of interstitial pore water on the micro-XRF intensities have been pointed out so far because of direct measurement on the split wet sediment surfaces. In this study, new methods for the XRF corrections were developed by being considered with the micro-X-ray scanning spectroscopy.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Onoe, Hironori; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Takeda, Masaki; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-014, 274 Pages, 2016/08
We synthesized the research results from the Mizunami/Horonobe Underground Research Laboratories (URLs) and geo-stability projects in the second midterm research phase. This report can be used as a technical basis for the Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan/Regulator at each decision point from siting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase).
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Higashi, Yasuo*; Sugawara, Hirotaka*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Kurokawa, Shinichi*
Proceedings of 7th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '16) (Internet), p.906 - 909, 2016/06
An accelerator based boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) facility is being planned at Okinawa institute of science and technology (OIST). The proton accelerator consists of a radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac and a drift tube linac (DTL). The required beam power is 60 kW. The present beam energy and current are 10 MeV and 30 mA, respectively. The pulse length is 3.3 ms and the repetition rate is 60 Hz, therefore, the duty factor is 20%. In this paper, present design of this compact, medium current, high duty proton linac is presented.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Higashi, Yasuo*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Kurokawa, Shinichi*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.948 - 950, 2015/09
An accelerator based boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) facility is being planned at Okinawa institute of science and technology (OIST). The proton accelerator consists of a radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac and a drift tube linac (DTL). The reqired beam power is 60 kW. The present beam energy and current are 10 MeV and 30 mA, respectively. The pulse length is 3.3 ms and the repetition rate is 60 Hz, therefore, the duty factor is 20%. In this paper, present designof this compact, midium current, high duty proton linac is presented.
Saito, Shinzo; Okamoto, Koji*; Kataoka, Isao*; Sugiyama, Kenichiro*; Muramatsu, Ken*; Ichimiya, Masakazu*; Kondo, Satoru; Yonomoto, Taisuke
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2015/05
Matsuda, Norihiro; Mikami, Satoshi; Shimoura, Susumu*; Takahashi, Junko*; Nakano, Masakazu; Shimada, Kiyotaka*; Uno, Kiichiro; Hagiwara, Shigetomo; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 139, p.427 - 434, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:108 Percentile:93.69(Environmental Sciences) Ba
Ba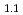 Ga
Ga Mg
Mg O
O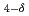
Hamao, Naoki*; Kitamura, Naoto*; Ito, Takanori*; Igawa, Naoki; Idemoto, Yasushi*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Kaku, Masanori*; Kubodera, Masakazu*
Solid State Ionics, 253, p.123 - 129, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.25(Chemistry, Physical)La Ba
Ba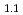 Ga
Ga Mg
Mg O
O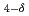 which is one of the candidates for solid electrolyte of solid oxide fuel cell was synthesized by means of a conventional solid-state reaction, and investigated by conductivity measurements, the Rietveld and maximum entropy method analyses using neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffraction data. Conductivity measurements indicated that simultaneous Ba and Mg substitutions for LaBaGaO
which is one of the candidates for solid electrolyte of solid oxide fuel cell was synthesized by means of a conventional solid-state reaction, and investigated by conductivity measurements, the Rietveld and maximum entropy method analyses using neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffraction data. Conductivity measurements indicated that simultaneous Ba and Mg substitutions for LaBaGaO were effective way to improve the protonic conductivity. From the Rietveld and maximum entropy method analyses, it was confirmed that La
were effective way to improve the protonic conductivity. From the Rietveld and maximum entropy method analyses, it was confirmed that La Ba
Ba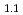 Ga
Ga Mg
Mg O
O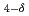 kept the same crystal structure as LaBaGaO
kept the same crystal structure as LaBaGaO even at elevated temperature, i.e. 1000 K, and that protons existed around the O3 site and formed hydrogen bonds. It is also found that oxygens in LaBaGaO
even at elevated temperature, i.e. 1000 K, and that protons existed around the O3 site and formed hydrogen bonds. It is also found that oxygens in LaBaGaO -based samples formed Ga-O
-based samples formed Ga-O tetrahedra, and the bonding strength was varied by the partial substitutions.
tetrahedra, and the bonding strength was varied by the partial substitutions.
 reflector and proton beam window
reflector and proton beam windowTeshigawara, Makoto; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Wakui, Takashi; Meigo, Shinichiro; Seki, Masakazu; Harada, Masahide; Ito, Manabu; Suzuki, Toru; Ikezaki, Kiyomi; Maekawa, Fujio; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2012-024, 303 Pages, 2012/07
3 GeV Protons with 1 MW beam power are irradiated to mercury target of spallation neutron source in Materials and Life science Facility (MLF), which is one of facilities of J-PARC. Irradiated components, such as target container, moderator, reflector and proton beam window, are needed to replace periodically due to irradiation damage of high energy protons and neutrons. These used components are replaced remotely because of highly activated. Maintenance scenario was settled so as to handle these components. Required remote handling machines were designed and installed in hot cell and other room of the MLF. We performed remote handling tests by using actual components to confirm the design. We report results, such as replacement procedure, trouble and its solution, etc., for moderator, reflector and proton beam window in order to provide the handling of actual used components.
Oka, Toshitaka; Oshima, Akihiro*; Motohashi, Ryota*; Seto, Naoto*; Watanabe, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Ryoji*; Saito, Koki*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Washio, Masakazu*; et al.
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 80(2), p.278 - 280, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:51.22(Chemistry, Physical)The chemical structures of various ion-beam irradiated isotactic-polypropylene samples were studied. Results of micro-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy suggest not only the linear energy transfer, but also the fluence is effective in local transformation of the isotactic-polypropylene.
Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Saito, Yoshio*; Baba, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 25th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2010) (CD-ROM), p.521 - 523, 2010/09
The fabrication of a new RFQ has been started as a backup machine for the J-PARC linac. The RFQ cavity is divided by three unit tanks in the longitudinal direction. The unit tank consists of two major vanes and two minor vanes, those are brazed together. A one-step vacuum brazing of a unit tank was adopted to unite these four vanes together with the flanges and ports. At the first tank brazing, the vacuum leak has been occurred due to the non-uniform temperature rise during the heating. Repair of this leakage and the results of the improved brazing of the second tank are reported.
Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*; Saito, Yoshio*; Baba, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 25th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2010) (CD-ROM), p.518 - 520, 2010/09
The fabrication of a new RFQ has been started in the J-PARC linac. The RFQ cavity is divided by three unit tanks in the longitudinal direction. The unit tank consists of two major vanes and two minor vanes, those will be brazed together. To reduce the costs and periods to develop the special formed bite for the modulation machining, a numerical controlled machining using a conventional ball-end-mill was adopted for the vane modulation cutting instead of the wheel shape cutter. The dimension accuracy was confirmed by cutting test pieces. Moreover, the obtained surface seems smooth enough for the operation. Results of the ball-end-mill machining for the vanes are described.
Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Saito, Yoshio*; Baba, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.783 - 785, 2010/05
The J-PARC RFQ (length 3.1 m, 4-vane type, 324 MHz) accelerates a negative hydrogen beam from 0.05 MeV to 3 MeV toward the following DTL. The stability of the operating RFQ decreased for a few months at the end of 2008, then, we started a preparation of a new RFQ as a backup machine in the case of RFQ problem. The beam dynamics design of the new RFQ is the same as the current cavity for a quick resumption of operation, however, the engineering and RF designs are changed to improve stability. The processes of the vane machining and the surface treatments have been carefully considered to reduce the discharge problem. The vacuum brazing technique has been chosen for vane jointing. The design of the new RFQ and the fabrication progress is descried in this proceeding.
Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kobayashi, Tetsuya; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Hori, Yoichiro*; Kubota, Chikashi*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.621 - 623, 2010/05
The J-PARC RFQ accelerates a negative hydrogen beam from 50 keV to 3 MeV. Beam commissioning of the J-PARC linac started in November 2006 and the linac has delivered beams to the 3 GeV synchrotron since September 2007. Trip rates of the RFQ, however, unexpectedly increased in September 2008. We tried to recover by tender conditioning, improvement of vacuum properties, etc. User operations for the Material and Life Experimental Facilities were successfully carried out at 20 kW in June 2009, and the beam power was increased to 120 kW in November. The high power operation at 300 kW for one hour was also demonstrated. Status and improvement of the J-PARC RFQ are presented.
Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Saito, Yoshio*; Baba, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 6th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (CD-ROM), p.1047 - 1049, 2010/03
The beam commissioning of J-PARC linac has been started since November 2006. After the scheduled shutdown in summer 2007, the beam is successfully delivered from the linac to the RCS. Since then, a stable beam provision was emphasized. However, the trip in the RFQ was increased at the end of Sept. 2008, then, the stability of the beam operation decreased. To improve this situation, we started to prepare a new RFQ cavity as a backup machine. The basic concept of the engineering design is the simplicity and the effective vacuum pumping aiming at the stable operation. A 3m long cavity is divided into 3 modules longitudinally. A numerical control machining with ball-end mill is chosen for a vane machining. Four vanes are vacuum brazed each other after machining. Each modules are aligned on the platform using a linear motion guide. A basic design of the key components on machining and brazing are described in this proceeding.
Hasegawa, Kazuo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kobayashi, Tetsuya; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 6th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (CD-ROM), p.693 - 695, 2010/03
The J-PARC RFQ (length 3.1m, 4-vane type, 324 MHz) accelerates a beam from the ion source to the DTL. The beam test of the linac was started in November 2006 and 181 MeV beam was successfully accelerated in January 2007. Since then, the linac has been delivered beams for commissioning of the linac itself, downstream accelerators and facilities. Trip rates of the RFQ, however, suddenly increased in Autumn 2008, and we are suffering from this issue for user run operation. We tried to recover by tender conditioning, modification of RF control, improvement of vacuum and so on. We manage to have beam operation. In this report, we describe the status of the RFQ.
Kurosawa, Hideki; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Shimada, Koji; Niwa, Masakazu; Kosaka, Hideki*; Saito, Satoshi*; Ninomiya, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2009-043, 144 Pages, 2010/01
Research on the influence of fault activity on deep geological environments contributes to the reliability of geological disposal systems for HLW. In this study, preliminary test shows that measured value within 1 hour after measurement start is supposed to include hydrogen gas generated by rock fracturing during the drilling of sampling holes and that stored in surrounding disturbed rocks, though the monitoring from a hand-drilled hole is effective for a rapid measurement. We investigated the concentration of hydrogen gas emitted from the Yamasaki fault zone, in southeast Japan. In our survey, the points where high concentrations of hydrogen gas emission was detected were unevenly distributed along the active fault, and in the southeast portion of the study area where small earthquakes frequently occurred.