Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Araki, Shohei; Aizawa, Eiju; Murakami, Takahiko; Arakaki, Yu; Tada, Yuta; Kamikawa, Yutaka; Hasegawa, Kenta; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Sumiya, Masato; Seki, Masakazu; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 217, p.111323_1 - 111323_8, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has modified the STACY from a homogeneous system using solution fuel to a heterogeneous system using fuel rods in order to obtain criticality characteristics of fuel debris. The modification of the STACY was completed in December 2023. A series of performance inspections were conducted for the start of experimental operations. A new thermal power calibration is required for the performance inspections in order to operate at less than 200 W, which is the permitted thermal power. However, the thermal power measurement method and calibration data used in the former STACY is no longer available due to the modification of the modified STACY. We measured the thermal power of the STACY using the activation method that was improved to adapt to the measurement condition and calibrated the power meter system. Since the positions where activation foils could be installed were very limited, the thermal power was evaluated using numerical calculations supplemented by experimental data. Neutron flux data at the positions of the activation foil was measured by the activation method. Neutron distribution in the core was calculated by the Monte Carlo code MVP. A response function of the activation foil was calculated using the PHITS. The uncertainty of the thermal power measurement was conservatively estimated to be about 15%. Four operations were conducted for the thermal power measurement. The power meter was calibrated by using three operational data and tested with the one operational data. It was found that the indicated value of the meter adjusted by the STACY before the modification work would tend to overestimate the actual output by about 40%. In addition, the current calibration was able to calibrate the meter to within 3% accuracy.
Kawaguchi, Maho*; Shiba, Shigeki*; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Okawa, Tsuyoshi*; Gunji, Satoshi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
The Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) has been working on an experimental approach for evaluating the criticality of fuel debris produced by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNP) accident since 2014, collaborating with the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). As part of the approach, JAEA has modified the STAtic experiment Critical facilitY (STACY) for critical experiments to evaluate characteriscs of pseudo-fuel debris. As the preliminary analyses, we verified critical characteristics with major nuclear data libraries for the proposed core configuration patterns. The three-dimensional continuous-energy Monte Carlo neutron and photon transport code, SERPENT-V2.2.0 was used with the latest JENDL, JENDL-5. As a result, larger multiplication factors of JENDL-5 across the modified STACY core configuration patterns were evaluated in comparison to the other libraries. And,  H scattering and
H scattering and  U fission sensitivity coefficients of JENDL-5 were different from those of the other libraries. Comparing among analyses with those libraries, the updated S(
U fission sensitivity coefficients of JENDL-5 were different from those of the other libraries. Comparing among analyses with those libraries, the updated S( ,
,  ) of JENDL-5 might affect the result of critical characteristics in the critical analyses for the modified STACY core configuration.
) of JENDL-5 might affect the result of critical characteristics in the critical analyses for the modified STACY core configuration.
Shiba, Shigeki*; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Okawa, Tsuyoshi*; Gunji, Satoshi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
The Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) has tackled the experimental approach for determining the criticality of pseudo-fuel debris plausibly simulating actual fuel debris since 2014, collaborating with the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. To elucidate the characteristics of the pseudo-fuel debris, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency modified the STACY (STAtic experiment Critical facilitY) to conduct critical experiments simulating fuel debris. Thus, we proposed three types of modified STACY core configurations. In critical experiments in the modified STACY core, it is important to judge whether the proposed modified STACY core configurations are representative of molten core-concrete interaction debris or not. In this study, we built pseudo-fuel debris models considering a volume ratio of pseudo-fuel debris to moderation (V /V
/V ) and calculated uncertainty-based similarity values (C
) and calculated uncertainty-based similarity values (C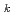 ) between the modified STACY core configurations and pseudo-fuel debris models using Tools for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Methodology Implementation-Indices and Parameters (TSUNAMI-IP) in SCALE 6.2. Consequently, the modified STACY core configuration loading structure rods we proposed completely resulted in high similarity to the pseudo-fuel debris models through V
) between the modified STACY core configurations and pseudo-fuel debris models using Tools for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Methodology Implementation-Indices and Parameters (TSUNAMI-IP) in SCALE 6.2. Consequently, the modified STACY core configuration loading structure rods we proposed completely resulted in high similarity to the pseudo-fuel debris models through V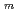 /V
/V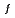 values. The main contributions to C
values. The main contributions to C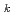 values were
values were  U
U 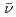 ,
,  U
U  , and
, and  Fe (n,
Fe (n, ), except for the pseudo-fuel debris model, including extremely high concrete components.
), except for the pseudo-fuel debris model, including extremely high concrete components.
 Ac production rate and its uncertainty in the experimental fast reactor Joyo utilizing the total Monte Carlo method
Ac production rate and its uncertainty in the experimental fast reactor Joyo utilizing the total Monte Carlo methodSasaki, Yuto; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Maeda, Shigetaka; Takaki, Naoyuki*
no journal, ,
Ac-225 is attracting attention as an alpha emitting medical radioisotope. Since its demand is expected to increase, domestic production of Ac-225 is required from the viewpoint of medical research and economic security of Japan. To establish the technical bases for the Ac-225 production, JAEA has evaluated the radioactivity can be produced in the experimental fast reactor Joyo and designed the concept that upgrades the existing facilities for transporting the irradiated target from Joyo to a neighboring PIE facility rapidly. This study has revealed that Joyo can sufficiently produce Ac-225 as a raw material for pharmaceuticals.
Araki, Shohei; Arakaki, Yu; Maekawa, Tomoyuki; Murakami, Takahiko; Hasegawa, Kenta; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Tada, Yuta; Kamikawa, Yutaka; Sumiya, Masato; Seki, Masakazu; et al.
no journal, ,
In the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, fuel debris was formed by fuel melting and mixing with in-core structures. Although the detailed properties of the fuel debris are still unknown, it is thought to contain materials such as iron and concrete. Then, in order to understand the criticality characteristics of fuel debris, JAEA is conducting a comprehensive numerical analysis assuming the composition of fuel debris containing concrete and iron. However, integral experimental data including these materials are scarce, and the validation of the analytical results has not been fully investigated. Thus, JAEA modified the criticality facility STACY in order to obtain experimental data that will contribute to the validation. This report describes the outline and status of the modified-STACY, and the plan is also presented.
Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Araki, Shohei; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Gunji, Satoshi; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Shiba, Shigeki*
no journal, ,
To develop technologies for criticality safety management during the fuel debris retrieval at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, JAEA modified the Static Experiment Critical Facility (STACY) from a solution fuel system to a light-water moderated heterogeneous system for critical experiments to study the criticality characteristics of fuel debris. The STACY achieved first criticality in April 2024 and was configured five different cores patterns with different grid intervals, critical water level, and number of fuel rods for first criticality and performance tests. In this presentation, criticality data of the above five patterns of cores and the results of analysis using MVP2 will be reported.
Araki, Shohei; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Arakaki, Yu; Kamikawa, Yutaka; Hasegawa, Kenta; Tada, Yuta; Sumiya, Masato; Seki, Masakazu; Aizawa, Eiju; Ishii, Junichi; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to understand the criticality characteristics of the fuel debris generated by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, it is essential to obtain critical experiment data that includes reactor structural materials such as iron and concrete that are considered to be contained in the fuel debris. To gather such critical experiment data, JAEA had conducted a major modification of the critical assembly STACY, and the modified STACY achieved first criticality in March 2024. In this presentation, we will discuss the experiments conducted in the modified STACY, with a particular focus on iron, which is considered to have a significant impact on criticality safety due to its strong neutron absorption effect.
Takaki, Naoyuki*; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Sasaki, Yuto*; Maeda, Shigetaka
no journal, ,
We compared the production characteristics of Tc-99m and Ac-225 in the fast experimental reactor "Joyo" and commercial PWR, summarized the characteristics of each, and showed the possibility of domestic production of medical RI using domestic infrastructure.
Iwahashi, Daiki*; Sasaki, Yuto*; Maeda, Shigetaka; Takaki, Naoyuki*
no journal, ,
Ac-225 is attracting attention as a radioisotope for targeted  -therapy (TAT) used for the treatment of prostate cancer and the like. Therefore, we investigated a method of loading Ra-226 into the fast reactor Joyo and producing Ac-225 by transmutation. Ac-225 production can be expected by the (n,2n) reaction using fast neutrons in the center of the core and the (3n,
-therapy (TAT) used for the treatment of prostate cancer and the like. Therefore, we investigated a method of loading Ra-226 into the fast reactor Joyo and producing Ac-225 by transmutation. Ac-225 production can be expected by the (n,2n) reaction using fast neutrons in the center of the core and the (3n,
 ) reaction using thermalized neutrons in the reflector region.
) reaction using thermalized neutrons in the reflector region.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Aizawa, Eiju; Ishii, Junichi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Shiba, Shigeki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Yuto*; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Maeda, Shigetaka; Takaki, Naoyuki*
no journal, ,
Mo-99 (half-life: 66 hours) / Tc-99m (half-life: 6 hours), which is the most sought after RI for diagnosis, is 100% dependent on imports. Therefore, domestic production is expected due to the instability of supply due to the deterioration of overseas manufacturing reactors and transportation troubles caused by natural disasters, and discussions are becoming active in the RI expert subcommittee. In this study, we investigated a method for efficiently producing Mo-99 by the neutron capture reaction of Mo-98 utilizing the neutron deceleration field around the core of the high-speed experimental reactor "Joyo". Specifically, a parameter survey was conducted on the core configuration, target loading position, deceleration aggregate material and its filling ratio, etc., and the most efficient core configuration was clarified.
Takaki, Naoyuki*; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Sasaki, Yuto*; Maeda, Shigetaka
no journal, ,
The production technology of medical radioisotopes (RI) using existing nuclear fission reactors has been studied to improve/achieve their domestic preparedness in Japan. The target nuclides currently considered in our project are Mo/Tc which is the most commonly used ones in medical diagnosis and Ac-225 which is recently known as effective alpha emitting nuclide for targeted alpha-particle therapy. Existing fission reactors, PWRs and Joyo, have potentials to work as excellent facilities for medical isotope production, as by-products of heat/electricity generation without consuming electricity and need for new plant construction.