Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
浜田 信行*; 岩川 眞由美*; 今留 香織*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 楚良 桜*; Ni, M.*; 今井 高志*; 小林 泰彦
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(Suppl.A), P. A118, 2009/05
There is significant evidence for radiation-induced bystander effects; however, little information exists on the bystander effect of energetic heavy ions. Here we compared heavy-ion response of irradiated and bystander fibroblasts in confluent cultures. Bystander cells manifested a more transient apoptotic response and delayed p53 phosphorylation than irradiated cells did. More than half of the genes whose expression changed in bystander cells was downregulated, and most of the genes upregulated in irradiated cells were downregulated in bystander cells. The data highlight the distinct response of irradiated and bystander cells.
浜田 信行*; 岩川 眞由美*; 今井 高志*; 小林 泰彦
放射線科学, 51(8), p.31 - 41, 2008/08
重粒子線治療の際、巨視的にみれば、標的のがん病巣以外に存在する生体内のすべての細胞を、バイスタンダー細胞と考えることができる。バイスタンダー効果に関連して、右肺のがんを光子放射線で照射した場合に、左肺のがんも縮小するというような遠達効果という現象も報告されている。薬剤によって誘発されるバイスタンダー効果が臨床応用されているように、重粒子線誘発バイスタンダー効果もがん治療に利用することはできないであろうか。光子放射線の照射によって誘発されるバイスタンダー効果の程度については、100名以上のヒトに由来する組織を用いた実験から個人差、そして、マウス個体を用いた実験から性差が報告されている。動物個体を用いた重粒子線誘発バイスタンダー効果の報告はこれまでにないが、生体における意義、すなわち、治療への寄与の程度や宇宙飛行士へのリスクを推定するために必要である。
岩川 眞由美*; 浜田 信行*; 今留 香織*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 小林 泰彦; 今井 高志*
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 642(1-2), p.57 - 67, 2008/07
被引用回数:36 パーセンタイル:66.57(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)We performed microarray analysis of irradiated and bystander fibroblasts in confluent cultures. To see the effects in bystander cells, each of 1, 5 and 25 sites was targeted with 10 particles of carbon ions using microbeams, where particles traversed 0.00026, 0.0013 and 0.0066% of cells, respectively. To see the effects in irradiated cells, cultures were exposed to 10% survival dose (D), 0.1D and 0.01D of corresponding broadbeams. Irrespective of the target numbers (1, 5 or 25 sites) and the time (2 or 6 h postirradiation), similar expression changes were observed in bystander cells. Among 874 probes that showed more than 1.5-fold changes in bystander cells, 25% were upregulated and the remainder downregulated. These included genes related to cell communication, stress response and cell cycle. Pathway analysis revealed serial bystander activation of G protein/PI-3 kinase pathways. Instead, genes related to cell cycle or death and cell communication were upregulated in irradiated cells, but not in bystander cells. Our results indicate different expression profiles in irradiated and bystander cells, and imply that intercellular signaling between irradiated and bystander cells activate intracellular signaling, leading to the transcriptional stress response in bystander cells.
浜田 信行*; 岩川 眞由美*; 金杉 勇一*; 今留 香織*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 高倉 かほる*; 今井 高志*; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
本研究では、高密度培養したヒト正常線維芽細胞に誘発される重粒子線のバイスタンダー効果を解析した。まず、マイクロビームで0.0003%の細胞に照射してバイスタンダー細胞の応答を調べるとともに、ブロードビームを照射した照射細胞の応答も調べた。バイスタンダー細胞では、アポトーシスが一過性に誘発され、p53が遅延的にリン酸化された。バイスタンダー細胞で変動した遺伝子の半数以上は発現が減少していた。また、照射細胞で発現が増加した遺伝子の大半はバイスタンダー細胞では減少していた。照射細胞ではp21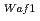 経路とNF-kB経路、バイスタンダー細胞ではGタンパク質/PI-3キナーゼ経路の活性化が示唆された。このことから、バイスタンダー細胞は照射細胞と異なる応答を示すことがわかった。さらに、照射細胞ではインターロイキン遺伝子の発現が増加したが、バイスタンダー細胞ではその受容体遺伝子が増加していたことから、照射細胞からバイスタンダー細胞への細胞間情報伝達の可能性が示唆された。次に、X線又は重粒子線を照射した細胞の培養上清を処理したバイスタンダー細胞に誘発される染色体異常を調べた。全体的な異常の頻度は同程度であったが、異常の型が異なっていた。このことから、バイスタンダー効果は線質によらず誘発されるが、その機序は線質によって異なる可能性が示唆された。
経路とNF-kB経路、バイスタンダー細胞ではGタンパク質/PI-3キナーゼ経路の活性化が示唆された。このことから、バイスタンダー細胞は照射細胞と異なる応答を示すことがわかった。さらに、照射細胞ではインターロイキン遺伝子の発現が増加したが、バイスタンダー細胞ではその受容体遺伝子が増加していたことから、照射細胞からバイスタンダー細胞への細胞間情報伝達の可能性が示唆された。次に、X線又は重粒子線を照射した細胞の培養上清を処理したバイスタンダー細胞に誘発される染色体異常を調べた。全体的な異常の頻度は同程度であったが、異常の型が異なっていた。このことから、バイスタンダー効果は線質によらず誘発されるが、その機序は線質によって異なる可能性が示唆された。
浜田 信行*; 岩川 眞由美*; 今留 香織*; 金杉 勇一*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 高倉 かほる*; 今井 高志*; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
本研究では、高密度培養したヒト正常線維芽細胞に誘発される重粒子線のバイスタンダー効果を解析した。まず、マイクロビームで0.0003%の細胞に照射してバイスタンダー細胞の応答を調べるとともに、ブロードビームを照射した照射細胞の応答も調べた。バイスタンダー細胞では、アポトーシスが一過性に誘発され、p53が遅延的にリン酸化された。バイスタンダー細胞で変動した遺伝子の半数以上は発現が減少していた。また、照射細胞で発現が増加した遺伝子の大半はバイスタンダー細胞では減少していた。照射細胞ではp21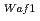 経路とNF-kB経路、バイスタンダー細胞ではGタンパク質/PI-3キナーゼ経路の活性化が示唆された。このことから、バイスタンダー細胞は照射細胞と異なる応答を示すことがわかった。さらに、照射細胞ではインターロイキン遺伝子の発現が増加したが、バイスタンダー細胞ではその受容体遺伝子が増加していたことから、照射細胞からバイスタンダー細胞への細胞間情報伝達の可能性が示唆された。次に、X線又は重粒子線を照射した細胞の培養上清を処理したバイスタンダー細胞に誘発される染色体異常を調べた。全体的な異常の頻度は同程度であったが、異常の型が異なっていた。このことから、バイスタンダー効果は線質によらず誘発されるが、その機序は線質によって異なる可能性が示唆された。
経路とNF-kB経路、バイスタンダー細胞ではGタンパク質/PI-3キナーゼ経路の活性化が示唆された。このことから、バイスタンダー細胞は照射細胞と異なる応答を示すことがわかった。さらに、照射細胞ではインターロイキン遺伝子の発現が増加したが、バイスタンダー細胞ではその受容体遺伝子が増加していたことから、照射細胞からバイスタンダー細胞への細胞間情報伝達の可能性が示唆された。次に、X線又は重粒子線を照射した細胞の培養上清を処理したバイスタンダー細胞に誘発される染色体異常を調べた。全体的な異常の頻度は同程度であったが、異常の型が異なっていた。このことから、バイスタンダー効果は線質によらず誘発されるが、その機序は線質によって異なる可能性が示唆された。
浜田 信行*; Ni, M.; 岩川 眞由美*; 今留 香織*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 楚良 桜*; 今井 高志*; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
Considering that less irradiated cells should coexist with more bystander cells in a population exposed to a lower dose of heavy ions, a clarification of the effects arising not only in irradiated cells but in their bystander cells would be crucial to comprehend the mechanism of action of heavy ions. Herein we have investigated heavy ion-induced bystander response in a situation whereby 0.0003% of cells in a confluent human fibroblast population were targeted using precise microbeams. Conventional broadfield irradiation was conducted in parallel to see the effects in irradiated cells. Intriguingly, bystander cells manifested a more transient apoptotic response and delayed p53 phosphorylation, compared with irradiated cells. Taken together, nearly three quarters of the genes whose expression changed in bystander cells were downregulated, and most of the genes upregulated in irradiated cells were downregulated in bystander cells. These findings highlight the distinct response of irradiated and bystander cells. Furthermore, interleukin genes were upregulated in irradiated cells whereas its receptor gene was upregulated in bystander cells, suggestive of the signal transmission from irradiated to bystander cells. Collectively, these induced bystander responses might be a defensive mechanism that would avert or minimize further expansion of aberrant cells.
浜田 信行*; Ni, M.; 金杉 勇一*; 岩川 眞由美*; 今留 香織*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 楚良 桜*; 今井 高志*; 高倉 かほる*; et al.
no journal, ,
Here we have investigated heavy ion-induced bystander response in confluent human fibroblast cultures. First, precise microbeams were employed to target 0.0003% of cells. Conventional broadfield irradiation was carried out in parallel to see the effects in irradiated cells. Intriguingly, bystander cells manifested a more transient apoptotic response and delayed p53 phosphorylation, compared with irradiated cells. Taken together, nearly three quarters of the genes whose expression changed in bystander cells were downregulated, and most of the genes upregulated in irradiated cells were downregulated in bystander cells. These findings highlight the distinct response of irradiated and bystander cells. Furthermore, interleukin genes were upregulated in irradiated cells whereas its receptor gene was upregulated in bystander cells, suggestive of the signal transmission from irradiated to bystander cells. Second, chromosome aberrations were analyzed in cells treated with conditioned medium from X- or heavy ion-irradiated cells. We found the difference in the types of aberrations, but very little in the total aberration yields, indicating that bystander responses occur independently of radiation types but are induced through different mechanisms. Collectively, these induced bystander responses could be a defensive mechanism that would avert or minimize further expansion of aberrant cells.