Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Sugihara, Kenta*; Hirano, Yukinori*; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi*; Saito, Shigeru; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Technology 2024-026, 123 Pages, 2025/03
Based on the design of the ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) at the J-PARC Transmutation Experimental Facility, a conceptual study was conducted on the J-PARC proton beam irradiation facility. This research was carried out based on the recommendations of the Nuclear Transmutation Technology Evaluation Task Force of the MEXT. The recommendations state that it is desirable to consider facility specifications that can make the most of the benefits of using the existing J-PARC proton accelerator while also solving the engineering issues of the ADS. We considered facilities that could respond to a variety of needs while reducing the facilities that were not needed in the TEF-T design. In order to clarify these diverse needs, we investigated the usage status of representative accelerator facilities around the world. As a result, it became clear that the main purposes of these facilities were (1) Material irradiation, (2) Soft error testing of semiconductor devices using spallation neutrons, (3) Production of RI for medical use, and (4) Proton beam use, and we investigated the facilities necessary for these purposes. In considering the facility concept, we assumed a user community in 2022 and reflected user opinions in the facility design. This report summarizes the results of the conceptual study of the proton irradiation facility, various needs and responses to them, the roadmap for facility construction, and future issues.
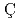 elik, Y.*; Stankovskiy, A.*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Van den Eynde, G.*
elik, Y.*; Stankovskiy, A.*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Van den Eynde, G.*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 212, p.111048_1 - 111048_12, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Iwamoto, Hiroki; Niikura, Megumi*; Mizuno, Rurie*
Physical Review C, 111(3), p.034614_1 - 034614_13, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)A negative muon in the 1 orbital can be captured by a nucleus, leading to subsequent nuclear dacay processes. The accurate prediction of total nuclear capture rates, which could be crucial in fields such as geochemistry, nuclear astrophysics, and semiconductor device developement, remains challenging with curren physics models. This study aims to develop a comprehensive machine learning (ML) model to estimate the total nuclear capture rate of a negative muon, integrating physical information and experimental data within a Bayesian framework. The study employs an ML model based on Gaussian process regression, using experimental data with evaluated uncertainties as training data. The model incoporates the Goulard-Primakoff formula as prior information and applies a transfer learning approach to improve estimations, particularly in data-sparse regions. The developed ML model is shown to outperform theoretical physics models in both accuracy and comprehensiveness, with key experiments identified to further refine the model performance. The estimates generated in this study will be incorporated into muon nuclear data applied accross a variety of research fields.
orbital can be captured by a nucleus, leading to subsequent nuclear dacay processes. The accurate prediction of total nuclear capture rates, which could be crucial in fields such as geochemistry, nuclear astrophysics, and semiconductor device developement, remains challenging with curren physics models. This study aims to develop a comprehensive machine learning (ML) model to estimate the total nuclear capture rate of a negative muon, integrating physical information and experimental data within a Bayesian framework. The study employs an ML model based on Gaussian process regression, using experimental data with evaluated uncertainties as training data. The model incoporates the Goulard-Primakoff formula as prior information and applies a transfer learning approach to improve estimations, particularly in data-sparse regions. The developed ML model is shown to outperform theoretical physics models in both accuracy and comprehensiveness, with key experiments identified to further refine the model performance. The estimates generated in this study will be incorporated into muon nuclear data applied accross a variety of research fields.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yonehara, Katsuya*; Pellemoine, F.*; Liu, Z.*; Lynch, K.*; Yoshida, Makoto*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165543_1 - 165543_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of displacements per atom is widely used as an indicator of irradiation damage to materials in proton accelerator facilities. Experiments have been carried out on protons below 3 GeV to verify the dpa of metallic materials. However, the dpa for high-energy protons above 3 GeV has not been measured. In order to validate the displacement cross sections of metals in the high-energy region, the electrical resistivity changes of aluminium, copper and tungsten wires at a temperature of 8 K were measured using protons with energy of 120 GeV. The results show that the conventional irradiation damage model of PHITS overestimates the experimental data. On the other hand, the calculation results using the athermal recombination correction model were in agreement with the experimental data.
 from 3-GeV protons and
from 3-GeV protons and  Hg with the
Hg with the  Bi(n,xn) reactions
Bi(n,xn) reactionsSugihara, Kenta*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Conf 2024-002, p.162 - 167, 2024/11
A neutron energy spectrum is important for shielding design at an Accelerator-Driven System facility (1.5-GeV p + Lead Bismuth Eutectic). A similar spectrum can be obtained at J-PARC (3-GeV proton +  Hg). To check the validity of the unfolding, the unfolding with the
Hg). To check the validity of the unfolding, the unfolding with the  Bi(n,xn) reactions and the response functions (JENDL/HE-2007 and TALYS) was applied. In our poster, we present the derivation of the spectrum and comparison with the spectrum with a Time-of-Flight technique.
Bi(n,xn) reactions and the response functions (JENDL/HE-2007 and TALYS) was applied. In our poster, we present the derivation of the spectrum and comparison with the spectrum with a Time-of-Flight technique.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Iwamoto, Hiroki
Proceedings of 21st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.32 - 37, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Nishihara, Kenji; Sugawara, Takanori; Fukushima, Masahiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Katano, Ryota; Abe, Takumi
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
A pilot plant for the accelerator-driven system is proposed as a scaled-down version of a lead-bismuth cooled ADS with 800 MW thermal output for transmutation of minor actinides. In this presentation, the design policy of the pilot plant is presented.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Sugihara, Kenta*
Physical Review C, 109(5), p.054610_1 - 054610_12, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)Nuclide production cross sections are crucial in nuclear research, development, space exploration, and astrophysical investigations. Despite their importance, limited experimental data availability restricts the practicality of phenomenological approaches to comprehensive cross-section estimation. To address this, we propose a Gaussian process-based machine learning (ML) model capable of transferring knowledge from elements with abundant data to those with limited or no experimental data. Our ML model not only enables comprehensive cross-section estimations for various elements but also demonstrates predictive capabilities akin to physics models, even in regions with scarce training data.
 Mg,
Mg,  Si,
Si,  Fe,
Fe,  Cu, and
Cu, and  Zn
ZnSugihara, Kenta*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 549, p.165299_1 - 165299_12, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Iwamoto, Hiroki
JAEA-Conf 2023-001, p.40 - 45, 2024/02
no abstracts in English
 Ti and
Ti and  Nb at 0.8 and 3.0 GeV
Nb at 0.8 and 3.0 GeVSugihara, Kenta*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 545, p.165153_1 - 165153_9, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Instruments & Instrumentation) Pb and
Pb and  Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeV
Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeVIwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Sugihara, Kenta*; 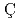 elik, Y.*; et al.
elik, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 544, p.165107_1 - 165107_15, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:71.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The lack of double-differential cross-section (DDX) data for neutron production below the incident proton energy of 200 MeV hinders the validation of spallation models in technical applications, such as research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs). The present study aims to obtain experimental DDX data for ADS spallation target materials in this energy region and identify issues related to the spallation models by comparing them with the analytical predictions. The DDXs for the (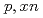 ) reactions of
) reactions of  Pb and
Pb and  Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30
Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30 to 150
to 150 using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01023_1 - 01023_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron, lead, and bismuth have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics. The measured TTNYs and DDXs were compared with calculations by the Monte Carlo transport code PHITS with its default physics model of INCL version 4.6 combined with GEM and those with the JENDL-4.0/HE nuclear data library.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takeshita, Hayato; Maekawa, Fujio
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01033_1 - 01033_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.05001_1 - 05001_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)In high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as Accelerator Driven System (ADS) and the spallation neutron source, it is crucial to evaluate the damage of beam-interception materials and accelerator components, such as a magnet coil. The displacement per atom (dpa) is used as a damage index, which is derived by integrating the particle flux and the displacement cross section based on the NRT model. Although the dpa is employed as the standard, the experimental data of displacement cross section are scarce for a proton in the energy region above 20 MeV. To obtain the data for superconducting materials for high-intensity accelerators and magnets, the displacement cross section of Nb for proton irradiation with a kinetic energy range between 0.4 and 3 GeV was measured. For sustaining damage in the sample, the Nb sample was cooled at a cryogenic temperature ( 8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Sadamatsu, Hiroki*; Araki, Shohei; Nakano, Keita; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01041_1 - 01041_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Intensive fast neutron sources using deuteron accelerators have been proposed for the study of medical RI production, radiation damage for fusion reactor materials, nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste, and so on. Neutron production data from various materials bombarded by deuterons are required for the design of such neutron sources. In the present work, we have conducted a systematic measurement of double-differential neutron production cross sections (DDXs) for a wide atomic number range of targets (Li, Be, C, Al, Cu, Nb, In, Ta, and Au) at an incident energy of 200 MeV in the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP), Osaka University. A deuteron beam accelerated to 200 MeV was transported to the neutron experimental hall and focused on a thin target foil. Emitted neutrons from the target were detected by two different-size EJ301 liquid organic scintillators located at two distances of 7 m and 20 m, respectively. The neutron DDXs were measured at six angles from 0 to 25
to 25 ). The neutron energy was determined by a conventional time-of-flight (TOF) method. The measured DDXs were compared with theoretical model calculations by the DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS) and PHITS. The result indicated that the DEURACS calculation provides better agreement with the measured DDXs than the PHITS calculation.
). The neutron energy was determined by a conventional time-of-flight (TOF) method. The measured DDXs were compared with theoretical model calculations by the DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS) and PHITS. The result indicated that the DEURACS calculation provides better agreement with the measured DDXs than the PHITS calculation.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.435 - 449, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) for Fe, Pb, and Bi targets induced by 107-MeV protons were measured using the fixed-field alternating gradient accelerator at Kyoto University for research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs) and fundamental ADS reactor physics research at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). Note that TTNYs were obtained with the time-of-flight method using a neutron detector system comprising eight neutron detectors; each detector has a small NE213 liquid organic scintillator and photomultiplier tube. The TTNYs obtained were compared with calculation results using Monte Carlo-based spallation models (i.e., INCL4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, JQMD/GEM, and JQMD/SMM/GEM) and the evaluated high-energy nuclear data library, i.e., JENDL-4.0/HE, implemented in the particle and heavy iontransport code system (PHITS). All models, including JENDL-4.0/HE, failed to predict high-energy peaks at a detector angle of 5 . Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of
. Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of  20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Abe, Yutaka*; Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shin*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Yoshida, Tadashi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(1), p.1 - 60, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:213 Percentile:99.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.404 - 409, 2023/01
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2022-001, p.129 - 133, 2022/11
For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors composed of the NE213 liquid organic scintillators and photomultiplier tubes, which were connected to a multi-channel digitizer mounted with a field-programmable gate array (FPGA), for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination applying the gate integration method to the FPGA. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics.