Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yonehara, Katsuya*; Ishida, Taku*; Nakano, Keita; Abe, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Spina, T.*; Ammigan, K.*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.138 - 143, 2022/03
To predict the operating lifetime of materials in high-energy radiation environments at proton accelerator facilities, Monte Carlo code are used to calculate the number of displacements per atom (dpa). However, there is no experimental data in the energy region above 30 GeV. In this presentation, we introduce our experimental plan for displacement cross sections with 120-GeV protons at Fermilab Test Beam Facility. Experiments will be performed for the US fiscal year 2022. We developed the sample assembly with four wire sample of Al, Cu, Nb and W with 250- m diameter and 4-cm length. The sample assembly will be maintained at around 4 K by using a cryocooler in a vacuum chamber. Then, changes in the electrical resistivity of samples will be obtained under 120-GeV proton irradiation. Recovery of the accumulated defects through isochronal annealing, which is related to the defect concentration in the sample, will also be measured after the cryogenic irradiation.
m diameter and 4-cm length. The sample assembly will be maintained at around 4 K by using a cryocooler in a vacuum chamber. Then, changes in the electrical resistivity of samples will be obtained under 120-GeV proton irradiation. Recovery of the accumulated defects through isochronal annealing, which is related to the defect concentration in the sample, will also be measured after the cryogenic irradiation.
Kawano, Toshihiko*; Cho, Y. S.*; Dimitriou, P.*; Filipescu, D.*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Plujko, V.*; Tao, X.*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Varlamov, V.*; Xu, R.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 163, p.109 - 162, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:83 Percentile:99.69(Physics, Nuclear)Hagiwara, Kaito*; Yano, Takatomi*; Das, P. K.*; Lorenz, S.*; Ou, Iwa*; Sakuda, Makoto*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Harada, Hideo; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(2), p.023D01_1 - 023D01_26, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:87.27(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Talou, P.*; Plompen, A. J.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 148, p.189 - 213, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:98.17(Physics, Nuclear)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides that significantly impact criticality in nuclear facilities -  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Fe,
Fe,  O and
O and  H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Lee, H. S.*; Soha, A.*; Ramberg, E.*; Coleman, R.*; Jensen, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 337, p.68 - 77, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.68(Instruments & Instrumentation)The energy spectra of neutrons were measured by a time-of-flight method for 120 GeV protons on thick graphite, aluminum, copper, and tungsten targets with an NE213 scintillator at the Fermilab Test Beam Facility. Neutron energy spectra were obtained between 25 and 3000 MeV at emission angles of 30, 45, 120, and 150 . The spectra were parameterized as neutron emissions from three moving sources and then compared with theoretical spectra calculated by PHITS and FLUKA codes. The yields of the theoretical spectra were substantially underestimated compared with the yields of measured spectra. The integrated neutron yields from 25 to 3000 MeV calculated with PHITS code were 16-36% of the experimental yields and those calculated with FLUKA code were 26-57% of the experimental yields for all targets and emission angles.
. The spectra were parameterized as neutron emissions from three moving sources and then compared with theoretical spectra calculated by PHITS and FLUKA codes. The yields of the theoretical spectra were substantially underestimated compared with the yields of measured spectra. The integrated neutron yields from 25 to 3000 MeV calculated with PHITS code were 16-36% of the experimental yields and those calculated with FLUKA code were 26-57% of the experimental yields for all targets and emission angles.
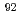 Nb observed in primitive meteorites
Nb observed in primitive meteoritesHayakawa, Takehito; Nakamura, Ko*; Kajino, Toshitaka*; Chiba, Satoshi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Cheoun, M. K.*; Mathews, G. J.*
Astrophysical Journal Letters, 779(1), p.L9_1 - L9_5, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:62.60(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Short-lived radioactivities are used as nuclearcosmochronometers for understanding the free decay time from the last nucleosynthesis episode until the time of solar system formation (SSF). 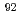 Nb (half-life of 34.7 Myr) is one of a short-lived isotope existed at SSF. However, there is a controversy in that the inferred initial abundance ratios for
Nb (half-life of 34.7 Myr) is one of a short-lived isotope existed at SSF. However, there is a controversy in that the inferred initial abundance ratios for 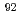 Nb/
Nb/ Nb at the time of SSF cluster around two different values; one is near 10
Nb at the time of SSF cluster around two different values; one is near 10 , while the other is near 10
, while the other is near 10 . Moreover, the astrophysical mechanism for the synthesis of
. Moreover, the astrophysical mechanism for the synthesis of 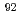 Nb has remained an unsolved problem. Here we argue that conventional nucleosynthesis mechanisms cannot produce
Nb has remained an unsolved problem. Here we argue that conventional nucleosynthesis mechanisms cannot produce 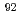 Nb and propose a new mechanism for the nucleosynthesis of this isotopebased upon neutrino induced reactions occurring during core-collapse supernova explosions.
Nb and propose a new mechanism for the nucleosynthesis of this isotopebased upon neutrino induced reactions occurring during core-collapse supernova explosions.
 and 90
and 90 bombarded with 120-GeV protons
bombarded with 120-GeV protonsIwamoto, Yosuke; Sanami, Toshiya*; Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Lee, H. S.*; Soha, A.*; Ramberg, E.*; Coleman, R.*; Jensen, D.*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 3, p.65 - 68, 2012/10
Neutron energy spectra at 15 and 90
and 90 produced from carbon, aluminum, copper and tungsten targets bombarded with 120-GeV protons were measured at Fermilab Test Beam Facility (FTBF) for the validation of simulation codes. The target thicknesses were 60 cm for graphite, 50 cm for aluminum, 20, 40, and 60 cm for copper and 10 cm for tungsten, respectively. The neutron time-of-flight measurements were performed using an NE213 organic liquid scintillator at 5.2 m for 90
produced from carbon, aluminum, copper and tungsten targets bombarded with 120-GeV protons were measured at Fermilab Test Beam Facility (FTBF) for the validation of simulation codes. The target thicknesses were 60 cm for graphite, 50 cm for aluminum, 20, 40, and 60 cm for copper and 10 cm for tungsten, respectively. The neutron time-of-flight measurements were performed using an NE213 organic liquid scintillator at 5.2 m for 90 and 8.0 m for 15
and 8.0 m for 15 measuring from the center of the target to the surface of the detector. The raw signals (waveforms) obtained from photomultiplier tubes were recorded using the 10 bit digitizer (Agilent-acqiris DC282) with 0.5 ns sampling and 500 ns duration. To compare the experimental results, Monte Carlo calculations with the PHITS, MARS and FLUKA codes were performed. It was found that these calculated results underestimate the experimental results in the whole energy range.
measuring from the center of the target to the surface of the detector. The raw signals (waveforms) obtained from photomultiplier tubes were recorded using the 10 bit digitizer (Agilent-acqiris DC282) with 0.5 ns sampling and 500 ns duration. To compare the experimental results, Monte Carlo calculations with the PHITS, MARS and FLUKA codes were performed. It was found that these calculated results underestimate the experimental results in the whole energy range.
Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Arakawa, Hiroyuki*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; Vaziri, K.*; Nakamura, Takashi*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.52 - 56, 2011/02
In pbar target station, the pulsed proton beam with the power of around 75 kW and the time structure of 1.6  s pulse width and 2.2 s cycle time bombards the pbar production target and produces high instantaneous intensity neutron (burst neutron) fields. The duration of the burst neutrons, which is less than
s pulse width and 2.2 s cycle time bombards the pbar production target and produces high instantaneous intensity neutron (burst neutron) fields. The duration of the burst neutrons, which is less than  s, is very severe condition to measure neutron spectra with a conventional Bonner sphere technique with pulse readout electronics because of signal pile-up problem. In this study, we have developed a current readout Bonner sphere technique to measure neutron spectra in a burst neutron field. We have measured the neutron spectra on the pbar target and graphite dump. The neutron spectra obtained with the present technique show generally good agreements with the calculation results using MARS code except difference of the thermal neutron flux due to the geometrical problem.
s, is very severe condition to measure neutron spectra with a conventional Bonner sphere technique with pulse readout electronics because of signal pile-up problem. In this study, we have developed a current readout Bonner sphere technique to measure neutron spectra in a burst neutron field. We have measured the neutron spectra on the pbar target and graphite dump. The neutron spectra obtained with the present technique show generally good agreements with the calculation results using MARS code except difference of the thermal neutron flux due to the geometrical problem.
Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Lee, H.-S.*; Leveling, A.*; Vaziri, K.*; Boehnlein, D.*; Mokhov, N.*; Sakamoto, Yukio; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.44 - 47, 2011/02
Muons become important particle for radiation safety design of high energy and intense accelerator since muons penetrate a thick shielding wall. In this study, the dose rate distributions around high intensity muon beam were measured at the muon alcoves and the bypass tunnel of Neutrinos at the Main Injector (NuMI) facility in Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab). The dosimeters of Luxel budges (OSL, CR39) and TLD budges (UD813PQ) were placed in the second, third and forth alcoves to measure muons, photons, and, thermal and fast neutrons. Neutrons and photons were measured in the bypass tunnel using a Bonner sphere and an ionization chamber. The spatial distribution of muons is calculated using MARS code. The results of dosimeters show same spatial distribution including attenuation along the beam line in comparison with the calculation results.
Sihver, L.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Gustafsson, K.*; Mancusi, D.*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Niita, Koji*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Norihiro
Advances in Space Research, 45(7), p.892 - 899, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:80.67(Engineering, Aerospace)We will first present the current status of the General-Purpose Particle and Heavy-Ion Transport code System (PHITS). In particular, we will describe benchmarking of calculated cross sections against measurements; we will introduce a relativistically covariant version of JQMD, called R-JQMD, that features an improved ground-state initialization algorithm, and we will show heavy-ion charge-changing cross sections simulated with R-JQMD and compare them to experimental data and to results predicted by the JQMD model.
Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Masukawa, Fumihiro; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 168(2), p.482 - 486, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experimental studies of shielding and radiation effects have been started using 120-GeV proton synchrotron at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL) under collaboration between FNAL and Japan. The first campaign of the experiment was carried out at the Pbar target station and Numi experimental station at FNAL, using antiproton and neutrino production targets irradiated by 120-GeV protons. The generated secondary particles passing through steel, concrete and rock were measured by activation methods as well as by other detectors such as scintillator with a veto counter, phoswich detector and a Bonner ball counter on trial. Preliminary experimental results are presented.
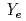 conditions
conditionsIwamoto, Nobuyuki; Umeda, Hideyuki*; Nomoto, Kenichi*; Tominaga, Nozomu*; Thielemann, F. K.*; Hix, W. R.*
AIP Conference Proceedings 847, p.409 - 411, 2006/07
The observations of metal-poor stars with metallicity [Fe/H] 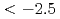 have been extensively performed. The abundance patterns of these stars are well explained by supernova models with extensive material mixing and fallback onto the compact remnant. Nevertheless important deficiencies of odd elements (especially Sc and K) are present in most investigations. Recent simulations of core collapse supernovae showed that innermost ejecta undergo large amounts of neutrino flux and neutrino interactions with materials in these ejecta change electron fraction to
have been extensively performed. The abundance patterns of these stars are well explained by supernova models with extensive material mixing and fallback onto the compact remnant. Nevertheless important deficiencies of odd elements (especially Sc and K) are present in most investigations. Recent simulations of core collapse supernovae showed that innermost ejecta undergo large amounts of neutrino flux and neutrino interactions with materials in these ejecta change electron fraction to 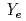
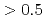 . Nucleosynthesis in the proton-rich environments allows Sc and Zn (which are less produced in normal supernova models) to be enriched. Therefore, it is interesting to investigate the influence of a large variation of
. Nucleosynthesis in the proton-rich environments allows Sc and Zn (which are less produced in normal supernova models) to be enriched. Therefore, it is interesting to investigate the influence of a large variation of 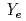 on explosive nucleosynthesis. We calculate nucleosynthesis with
on explosive nucleosynthesis. We calculate nucleosynthesis with 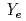 ranging from 0.48 to 0.58 in complete and incomplete Si burning layers in Pop III supernovae. We discuss the production of some important nuclei and compare the abundance patterns with those in observed extremely metal-poor stars.
ranging from 0.48 to 0.58 in complete and incomplete Si burning layers in Pop III supernovae. We discuss the production of some important nuclei and compare the abundance patterns with those in observed extremely metal-poor stars.
 +H
+H (v=0-14)
(v=0-14) H+H
H+H at low collision energies
at low collision energiesIchihara, Akira; Iwamoto, Osamu; Janev, R. K.*
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 33(21), p.4747 - 4758, 2000/11
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:90.22(Optics)no abstracts in English
 F+
F+ Tb reaction
Tb reactionIkezoe, Hiroshi; Nagame, Yuichiro; ; Sugiyama, Yasuharu; Tomita, Yoshiaki; Ideno, K.; Hamada, S.; ; Iwamoto, Akira;
Physical Review C, 49(2), p.968 - 976, 1994/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:79.67(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Shikazono, Naomoto; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sugiyama, Yasuharu; Tomita, Yoshiaki; Ideno, K.; ; B.J.Qi*; H.J.Kim*; Iwamoto, Akira; et al.
Physical Review C, 46(5), p.1922 - 1933, 1992/11
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:89.12(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Shikazono, Naomoto; Nagame, Yuichiro; Otsuki, Tsutomu*; Sugiyama, Yasuharu; Tomita, Yoshiaki; Ideno, K.; Kanno, Ikuo; H.J.Kim*; B.J.Qi*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 538, p.299C - 306C, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
 H and
H and  He emissions in
He emissions in  O +
O +  Au reaction
Au reactionIkezoe, Hiroshi; Shikazono, Naomoto; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sugiyama, Yasuharu; Tomita, Yoshiaki; Ideno, K.; Iwamoto, Akira; Otsuki, Tsutomu*
Physical Review C, 42(4), p.1187 - 1190, 1990/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:61.45(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 He multiplicity in the
He multiplicity in the  F +
F +  Au reaction
Au reactionIkezoe, Hiroshi; Shikazono, Naomoto; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sugiyama, Yasuharu; Tomita, Yoshiaki; Ideno, K.; Iwamoto, Akira;
Physical Review C, 42(1), p.342 - 353, 1990/07
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:85.82(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
; ; ; Minato, Kazuo; ; ; ; Iwamoto, K.; Ikawa, Katsuichi
JAERI-M 86-092, 286 Pages, 1986/07
no abstracts in English
; ; ; Iwamoto, K.
JAERI-M 86-046, 17 Pages, 1986/03
no abstracts in English