Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Torii, Hiroyuki*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; Kanda, Sotaro*; Kawagoe, Kiyotomo*; Kawall, D.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kurosawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Physical Review A, 104(2), p.L020801_1 - L020801_6, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:82.75(Optics)Iwasaki, Yuma*; Sawada, Ryoto*; Stanev, V.*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; Omori, Yasutomo*; Someya, Hiroko*; Takeuchi, Ichiro*; Saito, Eiji; Yorozu, Shinichi*
npj Computational Materials (Internet), 5, p.103_1 - 103_6, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:88.26(Chemistry, Physical)Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:156 Percentile:99.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Iwasaki, Yuma*; Takeuchi, Ichiro*; Stanev, V.*; Gilad Kusne, A.*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; Ihara, Kazuki*; Sawada, Ryoto*; Terashima, Koichi*; Someya, Hiroko*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9, p.2751_1 - 2751_7, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:83 Percentile:93.83(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:98.57(Quantum Science & Technology)Ueno, Yasuhiro*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 238(1), p.14_1 - 14_6, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:87.91(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Strasser, P.*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 237(1), p.124_1 - 124_9, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:89.49(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Kirihara, Akihiro*; Kondo, Koichi*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Ihara, Kazuki*; Iwasaki, Yuma*; Someya, Hiroko*; Matsuba, Asuka*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Saito, Eiji; Yamamoto, Naoharu*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.23114_1 - 23114_7, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:65 Percentile:89.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Heat-flow sensing is expected to be an important technological component of smart thermal management in the future. Conventionally, the thermoelectric (TE) conversion technique, which is based on the Seebeck effect, has been used to measure a heat flow by converting the flow into electric voltage. However, for ubiquitous heat-flow visualization, thin and flexible sensors with extremely low thermal resistance are highly desired. Recently, another type of TE effect, the longitudinal spin Seebeck effect (LSSE), has aroused great interest because the LSSE potentially offers favourable features for TE applications such as simple thin-film device structures. Here we demonstrate an LSSE-based flexible TE sheet that is especially suitable for a heat-flow sensing application. This TE sheet contained a Ni Zn
Zn Fe
Fe O
O film which was formed on a flexible plastic sheet using a spray-coating method known as ferrite plating. The experimental results suggest that the ferrite-plated film, which has a columnar crystal structure aligned perpendicular to the film plane, functions as a unique one-dimensional spin- current conductor suitable for bendable LSSE-based sensors. This newly developed thin TE sheet may be attached to differently shaped heat sources without obstructing an innate heat flux, paving the way to versatile heat-flow measurements and management.
film which was formed on a flexible plastic sheet using a spray-coating method known as ferrite plating. The experimental results suggest that the ferrite-plated film, which has a columnar crystal structure aligned perpendicular to the film plane, functions as a unique one-dimensional spin- current conductor suitable for bendable LSSE-based sensors. This newly developed thin TE sheet may be attached to differently shaped heat sources without obstructing an innate heat flux, paving the way to versatile heat-flow measurements and management.
Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Kato, Atsushi; Nabeshima, Kunihiko; Otaka, Masahiko; Uzawa, Masayuki*; Ikari, Risako*; Iwasaki, Mikinori*
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2015/05
Design study and evaluation for SDC and safety SDG on the BOP of the demonstration JSFR including fuel handling system, power supply system, component cooling water system, building arrangement are reported. For the fuel handling system, enhancement of storage cooling system has been investigated adding diversified cooling systems. For the power supply, existing emergency power supply system has been reinforced and alternative emergency power supply system is added. For the component cooling system and air conditioning, requirements and relation between safety grade components are investigated. Additionally for the component cooling system, design impact when adding decay heat removal system by sea water has been investigated. For reactor building, over view of evaluation on the external events and design policy for distributed arrangement is reported. Those design study and evaluation provides background information of SDC and SDG.
Sato, Isamu; Miwa, Shuhei; Tanaka, Kosuke; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Hirosawa, Takashi; Iwasaki, Maho; Onishi, Takashi; Osaka, Masahiko; Takai, Toshihide; Amaya, Masaki; et al.
Proceedings of 2014 Water Reactor Fuel Performance Meeting/ Top Fuel / LWR Fuel Performance Meeting (WRFPM 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2014/09
A new research program on severe accidents is lunched for the evaluation of FP release and transport behavior in BWR system. The purpose of the program is to improve the FP release and transport model using experimental database about FP chemistry focusing on Cs and I chemistry. In this program, effects of B including in control rod materials, B C for the Cs and I chemistry are paid attention. The experimental database used for the improvement will consist of results to obtain with newly-prepared test device under atmosphere with broad-ranging oxygen and/or steam partial pressure simulated those in BWR. The state of preparation for these experimental studies and analyses is introduced. In addition, the preliminary test was moved into action to show B chemical effect on Cs and I transport under one of the processes, which is deposited Cs compounds and B vapor and aerosol interaction. In this experiment, a "B stripping effect" to deposited CsI was observed.
C for the Cs and I chemistry are paid attention. The experimental database used for the improvement will consist of results to obtain with newly-prepared test device under atmosphere with broad-ranging oxygen and/or steam partial pressure simulated those in BWR. The state of preparation for these experimental studies and analyses is introduced. In addition, the preliminary test was moved into action to show B chemical effect on Cs and I transport under one of the processes, which is deposited Cs compounds and B vapor and aerosol interaction. In this experiment, a "B stripping effect" to deposited CsI was observed.
Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Strasser, P.*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Beveridge, J. L.*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Fukuchi, Koichi*; Sato, Nobuhiko*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 374-375, p.484 - 487, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:31.27(Physics, Condensed Matter)The construction of the Materials and Life Science building was started in the beginning of the fiscal year of 2004. After commissioning of the accelerator and beam transport sections in 2008, muon beams will be available for users in 2009. In this letter, the latest construction status of the J-PARC Muon Science Facility is reported.
Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Strasser, P.*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Beveridge, J. L.*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Sato, Nobuhiko*; Fukuchi, Koichi*; et al.
Nuclear Physics B; Proceedings Supplements, 149, p.393 - 395, 2005/12
The J-PARC muon science experimental area is planned to be located in the integrated building of the facility for materials and life science study. One muon target will be installed upstream of the neutron target. The main feature of the facility is introduced.
Do, V. K.; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo; Kuno, Takehiko; Miura, Katsue; Iwasaki, Maho; Sato, Soichi
no journal, ,
Technical support for environmental restoration of Fukushima and decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) are the most important mission of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In this presentation, we outline Okuma Analysis and Research Center and our mission on technical development for analyzing rubble and wastes from the decommissioning of 1F. Novel analytical methods are being developed at the center for determining difficult-to-measure nuclides. In addition, some analytical techniques based on liquid electrode plasma optical emission spectrometry, a novel optically spectroscopic method, for measuring elemental composition of highly active liquid wastes is reported.
Aoki, Kenji; Shimizu, Kazuyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Takeuchi, Kenji; Hiyama, Hisao; Iwasaki, Shogo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwasaki, Maho; Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko; Amaya, Masaki; Koyama, Shinichi; Seki, Takayuki*; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Ishigamori, Toshio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nanamura, Takuya; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Sakuma, Fuminori*; Yamaga, Takumi*; Iwasaki, Masahiko*
no journal, ,
Bound states caused by attractive 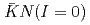 interaction, such as
interaction, such as 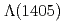 and kaonic nuclei, are interesting systems with strangeness. Many experimental attempts have tried to establish an existence of the lightest kaonic nuclei, "
and kaonic nuclei, are interesting systems with strangeness. Many experimental attempts have tried to establish an existence of the lightest kaonic nuclei, "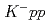 ". However, no clear conclusion was reached. Recently, J-PARC E15 collaboration searched for "
". However, no clear conclusion was reached. Recently, J-PARC E15 collaboration searched for "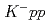 ", using the in-flight
", using the in-flight 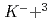 He reaction with an exclusive analysis of the
He reaction with an exclusive analysis of the 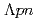 final state. By reconstructing not only the
final state. By reconstructing not only the 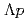 invariant-mass but also momentum transfer to the
invariant-mass but also momentum transfer to the 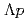 system, they definitely showed event concentration interpreted as "
system, they definitely showed event concentration interpreted as "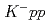 " bound state. Moreover, small spatial size of "
" bound state. Moreover, small spatial size of "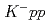 " is implied. In order to expand this successful experimental method to heavier kaonic nuclei, such as
" is implied. In order to expand this successful experimental method to heavier kaonic nuclei, such as 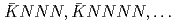 , and detailed study for fundamental properties of the
, and detailed study for fundamental properties of the 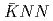 state, we are developing a new magnetic spectrometer. Because an exclusive analysis requires detections of decay particles from the kaonic nuclei as many as possible, the new spectrometer will have larger solid angle of 93%. To realize it, superconducting solenoid magnet and some detectors, a cylindrical drift chamber and charged particle/neutron counters, are 3-4 meters long. Detection efficiencies for neutron would be improved at least 1.7 times better than current spectrometer. In this presentation, I will talk about designs and development status of the new large acceptance spectrometer.
state, we are developing a new magnetic spectrometer. Because an exclusive analysis requires detections of decay particles from the kaonic nuclei as many as possible, the new spectrometer will have larger solid angle of 93%. To realize it, superconducting solenoid magnet and some detectors, a cylindrical drift chamber and charged particle/neutron counters, are 3-4 meters long. Detection efficiencies for neutron would be improved at least 1.7 times better than current spectrometer. In this presentation, I will talk about designs and development status of the new large acceptance spectrometer.