Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kumada, Takayuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Oba, Yojiro; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Sekine, Yurina; Micheau, C.; Ueda, Yuki; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sasaki, Miki; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(6), p.1776 - 1783, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:65.66(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The combination of the existing position-sensitive photomultiplier and the 3He main detector with focusing devices, and the newly installed front detectors in SANS-J at JRR-3 covers small-angle neutron scattering signals in the range of the magnitude of the scattering vector Q from 0.002 to 6 nm-1 gaplessly with three standard device layouts. The installation of the front detector and a graphical user interface system largely improved the usability of SANS-J.
 O/H
O/H O vapor generator for contrast-variation neutron scattering
O vapor generator for contrast-variation neutron scatteringArima-Osonoi, Hiroshi*; Takata, Shinichi; Kasai, Satoshi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Miyata, Noboru*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Iwase, Hiroki*; Hiroi, Kosuke; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(6), p.1802 - 1812, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Shibata, Motoki*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Abe, Jun*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroki*; Shibayama, Mitsuhiro*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki; Takata, Shinichi; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; et al.
Polymer Journal, 55(11), p.1165 - 1170, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.7(Polymer Science)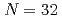 and
and 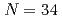 shell gap for Ti and V by the first high-precision multireflection time-of-flight mass measurements at BigRIPS-SLOWRI
shell gap for Ti and V by the first high-precision multireflection time-of-flight mass measurements at BigRIPS-SLOWRIIimura, Shun*; Rosenbusch, M.*; Takamine, Aiko*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Wada, Michiharu*; Chen, S.*; Hou, D. S.*; Xian, W.*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Yan, S.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(1), p.012501_1 - 012501_6, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:94.66(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Iwase, Akihiro*; Fukuda, Kengo*; Saito, Yuichi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Amekura, Hiroshi*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 132(16), p.163902_1 - 163902_10, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Amorphous SiO samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO
samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic
samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic  -Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
-Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
Tsugawa, Kiyoto*; Hayakawa, Sho*; Iwase, Yuki*; Okita, Taira*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Aichi, Masaatsu*
Computational Materials Science, 210, p.111450_1 - 111450_9, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:75.5(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kimata, Tetsuya*; Kakitani, Kenta*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Shimoyama, Iwao; Matsumura, Daiju; Iwase, Akihiro*; Mao, W.*; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Terai, Takayuki*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(3), p.035801_1 - 035801_7, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:71.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Terayama, Satoshi*; Iwase, Yuki*; Hayakawa, Sho*; Okita, Taira*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*
Computational Materials Science, 195, p.110479_1 - 110479_12, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:57.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) He spin filter at a pulsed neutron source
He spin filter at a pulsed neutron sourceOkudaira, Takuya; Ueda, Yuki; Hiroi, Kosuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Takata, Shinichi; Oku, Takayuki; Suzuki, Junichi*; Takahashi, Shingo*; Endo, Hitoshi*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 54(2), p.548 - 556, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:33.1(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Neutron polarization analysis (NPA) for small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) experiments using a pulsed neutron source was successfully achieved by applying a  He spin filter as a spin analyzer for the scattered neutrons. The
He spin filter as a spin analyzer for the scattered neutrons. The  He spin filter covers a sufficient solid angle for performing SANS experiments, and the relaxation time of the
He spin filter covers a sufficient solid angle for performing SANS experiments, and the relaxation time of the  He polarization is sufficient for continuous use over a few days, thus reaching the typical duration required for a complete set of SANS experiments. Although accurate evaluation of the incoherent neutron scattering, which is predominantly attributable to hydrogen atoms in samples, is practically difficult using calculations based on the sample elemental composition, the developed NPA approach with consideration of the influence of multiple neutron scattering enabled reliable decomposition of the SANS intensity distribution into the coherent and incoherent scattering components. To date, NPA has not been well established as a standard technique for SANS experiments at pulsed neutron sources. This work is anticipated to greatly contribute to the accurate determination of the coherent neutron scattering component for scatterers in various types of organic sample systems in SANS experiments at J-PARC.
He polarization is sufficient for continuous use over a few days, thus reaching the typical duration required for a complete set of SANS experiments. Although accurate evaluation of the incoherent neutron scattering, which is predominantly attributable to hydrogen atoms in samples, is practically difficult using calculations based on the sample elemental composition, the developed NPA approach with consideration of the influence of multiple neutron scattering enabled reliable decomposition of the SANS intensity distribution into the coherent and incoherent scattering components. To date, NPA has not been well established as a standard technique for SANS experiments at pulsed neutron sources. This work is anticipated to greatly contribute to the accurate determination of the coherent neutron scattering component for scatterers in various types of organic sample systems in SANS experiments at J-PARC.
 by using Poisson distribution function
by using Poisson distribution functionYamamoto, Yuki*; Ishikawa, Norito; Hori, Fuminobu*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(3), p.26_1 - 26_13, 2020/09
The lattice constant and the magnetic state of CeO are modified by the irradiation with 200 MeV Xe ions. Under the assumption that these modifications are induced in the narrow one-dimensional region (the ion track) along the ion beam path, the dependence of the lattice constant and the saturation magnetization of CeO
are modified by the irradiation with 200 MeV Xe ions. Under the assumption that these modifications are induced in the narrow one-dimensional region (the ion track) along the ion beam path, the dependence of the lattice constant and the saturation magnetization of CeO on the Xe ion fluence can be analyzed by using the Poisson distribution function. The analysis reveals that the lattice constant inside the ion track, which is larger than outside the ion track is not affected by the overlapping of the ion track. The present result implies that the Poisson distribution function is useful for describing the effect of ion track overlapping on the ion irradiation induced ferromagnetic state in CeO
on the Xe ion fluence can be analyzed by using the Poisson distribution function. The analysis reveals that the lattice constant inside the ion track, which is larger than outside the ion track is not affected by the overlapping of the ion track. The present result implies that the Poisson distribution function is useful for describing the effect of ion track overlapping on the ion irradiation induced ferromagnetic state in CeO .
.
Tanaka, Taiki*; Morita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Boll, R. A.*; Brewer, N. T.*; Van Cleve, S.*; Dean, D. J.*; Ishizawa, Satoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(5), p.052502_1 - 052502_6, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:81.08(Physics, Multidisciplinary) = 100 with a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph
= 100 with a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrographIto, Yuta*; Schury, P.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Arai, Fumiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Ishizawa, Satoshi*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kimura, Sota*; Koura, Hiroyuki; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 120(15), p.152501_1 - 152501_6, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:93.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Masses of 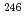 Es,
Es, 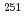 Fm and the transfermium nuclei
Fm and the transfermium nuclei 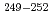 Md, and
Md, and  No, produced by hot- and cold-fusion reactions, in the vicinity of the deformed
No, produced by hot- and cold-fusion reactions, in the vicinity of the deformed 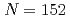 neutron shell closure, have been directly measured using a multi-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph. The masses of
neutron shell closure, have been directly measured using a multi-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph. The masses of 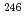 Es and
Es and 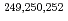 Md were measured for the first time. Using the masses of
Md were measured for the first time. Using the masses of 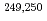 Md as anchor points for
Md as anchor points for  decay chains, the masses of heavier nuclei, up to
decay chains, the masses of heavier nuclei, up to  Bh and
Bh and  Mt, were determined. These new masses were compared with theoretical global mass models and demonstrated to be in good agreement with macroscopic-microscopic models in this region. The empirical shell gap parameter
Mt, were determined. These new masses were compared with theoretical global mass models and demonstrated to be in good agreement with macroscopic-microscopic models in this region. The empirical shell gap parameter 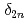 derived from three isotopic masses was updated with the new masses and corroborate the existence of the deformed
derived from three isotopic masses was updated with the new masses and corroborate the existence of the deformed 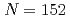 neutron shell closure for Md and Lr.
neutron shell closure for Md and Lr.
Sanami, Toshiya*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Nakamura, Shoji
JAEA-Conf 2017-001, 222 Pages, 2018/01
The 2016 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held at Kobayashi Hall of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, on November 17 and 18, 2016. The symposium was organized by the Nuclear Data Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan in cooperation with Radiation Science Center, High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency and North Kanto Branch of Atomic Energy Society of Japan. In the symposium, there were one tutorial, "Historical Evolution of Accelerators" and four oral sessions, "Overview of the ImPACT Program - Reduction and Resource Recycling of High Level Wastes through Nuclear Transmutation", "Facilities and experiments for nuclear data in Japan", "Nuclear data from measurement to application", and "Progress of neutron nuclear data measurement and research for its basics and application". In addition, recent research progress on experiments, evaluation, benchmark and application was presented in the poster session. Among 65 participants, all presentations and following discussions were very active and fruitful. This report consists of total 31 papers including 10 oral and 21 poster presentations.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kowatari, Munehiko; Nishino, Sho; Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwase, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1188 - 1195, 2017/11
The equivalent doses to the lens of the eye and extremities for radiation workers should be assessed properly to ensure that the dose limits are not exceeded. Recently, the following two issues has pressed demand on more appropriate evaluation of the equivalent doses of the lens of the eye and extremity. One is the new occupational dose limit for the lens of the eye the ICRP recommended. The other is growing demand on handling of highly activated materials in the maintenance works of an accelerator and contaminated materials during the decommissioning works of nuclear facility, which increases the potential exposure risk to the extremities to a wider variety of radio-nuclides. Since the points to be assessed for the exposures to the lens of the eye and the extremities are apart from the trunk, the homogeneity of the radiation fields would be significantly impact on the assessment of these equivalent doses. However, there has been no sufficient and available method to identify the nonhomogeneous situations systematically in terms of the eye lens or extremity monitoring. The goal of this study is to provide the framework to identify the nonhomogeneous exposure situations. In order to fulfil this purpose, newly proposed indices to represent the homogeneity were calculated by Monte Carlo simulation incorporated with mathematical phantom, verifying the benchmark measurements. Important parameters that significantly impact on these indices were also shown from the various trials of calculations of homogeneity indices.
 -ray energy spectra of 80-400 MeV
-ray energy spectra of 80-400 MeV  Li(p,n) reactions under the quasi-monoenergetic neutron field at RCNP, Osaka University
Li(p,n) reactions under the quasi-monoenergetic neutron field at RCNP, Osaka UniversityIwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Nakamura, Takashi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.08019_1 - 08019_3, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)To develop 100-400 MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutron field, we measured neutron and unexpected  -ray energy spectra of the
-ray energy spectra of the  Li(p,n) reaction with 80-389 MeV protons in the 100-m time-of-flight (TOF) tunnel at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP). Neutron energy spectra with energies above 3 MeV were measured by the TOF method and
Li(p,n) reaction with 80-389 MeV protons in the 100-m time-of-flight (TOF) tunnel at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP). Neutron energy spectra with energies above 3 MeV were measured by the TOF method and  energy spectra with energies above 0.1 MeV were measured by the automatic unfolding function of the radiation dose monitor DARWIN. For neutron spectra, the contribution of peak intensity to the total intensity integrated with energies above 3 MeV varied between 0.38 and 0.48. For
energy spectra with energies above 0.1 MeV were measured by the automatic unfolding function of the radiation dose monitor DARWIN. For neutron spectra, the contribution of peak intensity to the total intensity integrated with energies above 3 MeV varied between 0.38 and 0.48. For  -ray spectra, high-energetic
-ray spectra, high-energetic  -rays at around 70 MeV originated from the decay of
-rays at around 70 MeV originated from the decay of 
 were observed over 200 MeV. For the 246-MeV proton incident reaction, the contribution of
were observed over 200 MeV. For the 246-MeV proton incident reaction, the contribution of  -ray dose to neutron dose is negligible because the ratio of
-ray dose to neutron dose is negligible because the ratio of  -ray to neutron is 0.014.
-ray to neutron is 0.014.
Theis, C.*; Carbonez, P.*; Feldbaumer, E.*; Forkel-Wirth, D.*; Jaegerhofer, L.*; Pangallo, M.*; Perrin, D.*; Urscheler, C.*; Roesler, S.*; Vincke, H.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.08018_1 - 08018_5, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)At CERN, gas-filled ionization chambers PTW-34031 (PMI) are commonly used in radiation fields including neutrons, protons and  -rays. A response function for each particle is calculated by the radiation transport code FLUKA. To validate a response function to high energy neutrons, benchmark experiments with quasi mono-energetic neutrons have been carried out at RCNP, Osaka University. For neutron irradiation with energies below 200 MeV, very good agreement was found comparing the FLUKA simulations and the measurements. In addition it was found that at proton energies of 250 and 392 MeV, results calculated with neutron sources underestimate the experimental data due to a non-negligible gamma component originating from the target
-rays. A response function for each particle is calculated by the radiation transport code FLUKA. To validate a response function to high energy neutrons, benchmark experiments with quasi mono-energetic neutrons have been carried out at RCNP, Osaka University. For neutron irradiation with energies below 200 MeV, very good agreement was found comparing the FLUKA simulations and the measurements. In addition it was found that at proton energies of 250 and 392 MeV, results calculated with neutron sources underestimate the experimental data due to a non-negligible gamma component originating from the target  Li(p,n)Be reaction.
Li(p,n)Be reaction.
Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.08016_1 - 08016_3, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron energy spectra behind concrete and iron shields were measured for quasi-monoenergetic neutrons above 200 MeV using a Bonner sphere spectrometer (BSS). Quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were produced by the  Li(p,xn) reaction with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons. The response function of BSS was also measured at neutron energies from 100 MeV to 387 MeV. In data analysis, the measured response function was used and the multiple neutron scattering effect between the BSS and the shielding material was considered. The neutron energy spectra behind the concrete and iron shields were obtained by the unfolding method using the MAXED code. Ambient dose equivalents were obtained as a function of a shield thickness successfully. For the case of the 244 MeV neutron incidence, the multiple neutron scattering effect on the effective dose is large under 50 cm thickness of the concrete shield.
Li(p,xn) reaction with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons. The response function of BSS was also measured at neutron energies from 100 MeV to 387 MeV. In data analysis, the measured response function was used and the multiple neutron scattering effect between the BSS and the shielding material was considered. The neutron energy spectra behind the concrete and iron shields were obtained by the unfolding method using the MAXED code. Ambient dose equivalents were obtained as a function of a shield thickness successfully. For the case of the 244 MeV neutron incidence, the multiple neutron scattering effect on the effective dose is large under 50 cm thickness of the concrete shield.
 and Br
and Br and its effect on corrosion of a low-alloy steel
and its effect on corrosion of a low-alloy steelHata, Kuniki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Kojima, Takao*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Tsukada, Takashi; Iwase, Akihiro*
Proceedings of Symposium on Water Chemistry and Corrosion in Nuclear Power Plants in Asia 2017 (AWC 2017) (USB Flash Drive), p.304 - 314, 2017/09
A model simulation of  radiolysis of mixed solutions of NaCl and NaBr was carried out. The simulation result agreed well with the experimental result, and Br
radiolysis of mixed solutions of NaCl and NaBr was carried out. The simulation result agreed well with the experimental result, and Br played an important role in determining the amounts of products from water radiolysis. The simulation result also showed that, in highly pure NaCl solutions, the steady-state concentration of a radolytic product, H
played an important role in determining the amounts of products from water radiolysis. The simulation result also showed that, in highly pure NaCl solutions, the steady-state concentration of a radolytic product, H O
O , was mainly controlled by three reactions (Cl
, was mainly controlled by three reactions (Cl +
+  OH
OH  ClOH
ClOH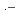 , ClOH
, ClOH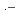
 Cl
Cl +
+  OH, and ClOH
OH, and ClOH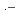 + H
+ H
 Cl
Cl + H
+ H O), which indicated that accurate evaluation of the rate constants of these reactions was very important in improving the radiolysis simulation of solutions containing Cl
O), which indicated that accurate evaluation of the rate constants of these reactions was very important in improving the radiolysis simulation of solutions containing Cl . An immersion test using a low-alloy steel, SQV2A, in the mixed solutions was also carried out under irradiation. The corrosion rate increased or decreased depending on the pH or the concentrations of the halide ions in a similar way to the change in concentration of H
. An immersion test using a low-alloy steel, SQV2A, in the mixed solutions was also carried out under irradiation. The corrosion rate increased or decreased depending on the pH or the concentrations of the halide ions in a similar way to the change in concentration of H O
O produced from water radiolysis, which is affected by the presence of Cl
produced from water radiolysis, which is affected by the presence of Cl and Br
and Br . However, at high pH values (
. However, at high pH values ( 12), the corrosion rate was almost zero even though the concentration of H
12), the corrosion rate was almost zero even though the concentration of H O
O was high. This could be attributed to enhancement of the passivity of test specimens at higher pH values.
was high. This could be attributed to enhancement of the passivity of test specimens at higher pH values.
 Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds
Ta intermetallic compoundsKojima, Hiroshi*; Kaneno, Yasuyuki*; Ochi, Masaaki*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Saito, Yuichi*; Ishikawa, Norito; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Iwase, Akihiro*
Materials Transactions, 58(5), p.739 - 748, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Bulk samples of Ni Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds were irradiated with 16 MeV Au, 4.5 MeV Ni, 4.5 MeV Al, 200 MeV Xe and 1.0 MeV He ions, and the change in near-surface lattice structure was investigated by means of the grazing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXD)and EXAFS. The Ni
Ta intermetallic compounds were irradiated with 16 MeV Au, 4.5 MeV Ni, 4.5 MeV Al, 200 MeV Xe and 1.0 MeV He ions, and the change in near-surface lattice structure was investigated by means of the grazing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXD)and EXAFS. The Ni Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta lattice structures transform from the ordered structures (orthorhombic and monoclinic structures for Ni
Ta lattice structures transform from the ordered structures (orthorhombic and monoclinic structures for Ni Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta, respectively) to the amorphous state by the Au, Ni, Al and Xe ion irradiations. Irrespective of such heavy ion species or energies, the lattice structure transformation to the amorphous state almost correlate with the density of energy deposited through elastic collisions.
Ta, respectively) to the amorphous state by the Au, Ni, Al and Xe ion irradiations. Irrespective of such heavy ion species or energies, the lattice structure transformation to the amorphous state almost correlate with the density of energy deposited through elastic collisions.