Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shinohara, Yuya*; Iwashita, Takuya*; Nakanishi, Masahiro*; Osti, N. C.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nirei, Masami; Dmowski, W.*; Egami, Takeshi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 128(6), p.1544 - 1549, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)Lobzenko, I.; Tsuru, Tomohito; Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Iwashita, Takuya*
Materials Research Express (Internet), 10(8), p.085201_1 - 085201_12, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Unlike alloys with a crystal lattice, metallic glasses (MG) do not possess distinctive defects but demonstrate a highly heterogeneous response to mechanical deformation, even in near-elastic regimes. The difficulties in describing such non-uniform behavior hamper the prediction of the mechanical properties of MGs. We apply first-principles calculations of atomic stress in CuZr MG to reveal its response to shear strain. That approach allows one to probe such parameters as displacement vector, charge transfer, or change in chemical bonds on the lowest atomic level. We find correlations between the mentioned parameters and show the importance of atomic von Mises stress in the comprehensive description of the mechanical state of a glassy system.
Ogura, Koichi; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kado, Masataka; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Hayashi, Yukio; et al.
Journal of the Vacuum Society of Japan, 52(10), p.570 - 574, 2009/10
For accurate control of relativistic laser-plasma interaction under the repetitive operation, we have to measure and control the laser irradiation conditions such as laser parameters, the target shooting accuracy and so on as well as measuring proton parameter on each laser shot. The displacement of the laser shooting position on a tape target, that are used in the high energy proton generation using an ultra-short Ti:sapphire laser system, is measured by observing an X-ray image from laser plasma with an X-ray pinhole camera for each laser shot. The displacement of the shooting position on the target is about 20micron and the accuracy of the target positioning is within 20micron which is small enough for present laser focusing optics with an F number of 3.6 (f=179mm). The technique contributes to accurate control of a repetitive laser driven proton accelerators.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Bulanov, S. V.; Bolton, P. R.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 37(6), p.449 - 454, 2009/06
The acceleration of protons driven by a high-intensity laser is comprehensively investigated via control of the target density by using ASE just before the time of the main-laser interaction. Two cases were investigated for which the ASE intensity differed by three orders of magnitude: In the low contrast case the beam centre for higher energy protons is shifted closer to the laser-propagation direction of 45 , while the center of lower-energy beam remains near the target normal direction. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the characteristic proton acceleration is due to the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
, while the center of lower-energy beam remains near the target normal direction. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the characteristic proton acceleration is due to the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ma, J.*; Sagisaka, Akito; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1872 - 1877, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:28.39(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A dependence of cut-off proton kinetic energy on laser prepulse duration has been observed. ASE pedestal duration is controlled by a fast electro-optic pulse slicer where the risetime is estimated to be 130 ps. We demonstrate a new correlated spectral technique for determining this risetime using a stretched, frequency chirped pulse.
Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Daido, Hiroyuki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Li, Z.*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 46(9A), p.5853 - 5858, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:54.91(Physics, Applied)A laser-driven proton beam with a maximum energy of a few MeV is stably obtained using an ultra-short and high-intensity Titanium Sapphire laser. At the same time, keV X-ray is also generated at almost the same place where protons are emitted. Here, we show the successful demonstration of simultaneous proton and X-ray projection images of a test sample placed close to the source with a resolution of  10
10 m, which is determined from the source sizes. Although the experimental configuration is very simple, the simultaneity is better than a few hundreds of ps. A CR-39 track detector and imaging plate, which are placed as close as possible to the CR-39, are used as detectors of protons and X-ray. The technique is applicable to the precise observation of microstructures.
m, which is determined from the source sizes. Although the experimental configuration is very simple, the simultaneity is better than a few hundreds of ps. A CR-39 track detector and imaging plate, which are placed as close as possible to the CR-39, are used as detectors of protons and X-ray. The technique is applicable to the precise observation of microstructures.
Sagisaka, Akito; Daido, Hiroyuki; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Yogo, Akifumi; Kado, Masataka; Fukumi, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 51(1), p.442 - 446, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.85(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The recent progress of the laser driven accelerators which include high power laser driven electrons and ions are reviewed. The studies at JAEA Kansai are mainly described. Based on the recent progres, the various aspects of the applications are also reviewed.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Nakamura, Shu*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 14(4), p.043104_1 - 043104_6, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:88.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Fast protons are observed by a newly-developed 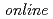 time-of-flight spectrometer, which provides
time-of-flight spectrometer, which provides 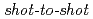 proton-energy distributions immediately after the irradiation of a laser pulse having an intensity of
proton-energy distributions immediately after the irradiation of a laser pulse having an intensity of 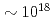 W/cm
W/cm onto a 5-
onto a 5- m-thick copper foil. The maximum proton energy is found to increase when the intensity of a fs-prepulse arriving 9 ns before the main pulse increases from 10
m-thick copper foil. The maximum proton energy is found to increase when the intensity of a fs-prepulse arriving 9 ns before the main pulse increases from 10 to 10
to 10 W/cm
W/cm . Interferometric measurement indicates that the preformed-plasma expansion at the front surface is smaller than 15
. Interferometric measurement indicates that the preformed-plasma expansion at the front surface is smaller than 15  m, which corresponds to the spatial resolution of the diagnostics. This sharp gradient of the plasma makes a beneficial effect on increasing the absorption efficiency of the main-pulse energy, resulting in the increase in the proton energy. This is supported by the result that the X-ray intensity from the laser plasma clearly increases with the prepulse intensity.
m, which corresponds to the spatial resolution of the diagnostics. This sharp gradient of the plasma makes a beneficial effect on increasing the absorption efficiency of the main-pulse energy, resulting in the increase in the proton energy. This is supported by the result that the X-ray intensity from the laser plasma clearly increases with the prepulse intensity.
Daido, Hiroyuki; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Mori, Michiaki; Ma, J.-L.; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Proceedings of 7th Pacific Rim Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO-PR 2007) (CD-ROM), p.77 - 79, 2007/00
We are developing a proton accelerator using an intense lasers with a focused intensity of  10
10 W/cm
W/cm . To monitor proton energy spectra as well as plasma parameters at each laser shot, we are using real time detectors. The proton energy of MeV is stably obtained for applications.
. To monitor proton energy spectra as well as plasma parameters at each laser shot, we are using real time detectors. The proton energy of MeV is stably obtained for applications.
Yogo, Akifumi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Kado, Masataka; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
Applied Physics B, 83(4), p.487 - 489, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:41.92(Optics)We present experimental results on protons accelerated up to 950 keV from a 3- m thick tantalum foil with a 133-nm thick polystyrene layer on its rear surface, irradiated with a laser pulse having the duration of 70 fs and the intensity of
m thick tantalum foil with a 133-nm thick polystyrene layer on its rear surface, irradiated with a laser pulse having the duration of 70 fs and the intensity of 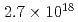 W/cm
W/cm . The energy distribution of fast protons was measured simultaneously with that of the hot-electrons from the rear surface. The proton yield from the polystyrene-coated target is about 10 times as high as that from the uncoated metal target. This enhancement of the proton yield is roughly proportional to the increase of hydrogen atoms given by the 133-nm thick polystyrene layer, assuming a contaminant layer of
. The energy distribution of fast protons was measured simultaneously with that of the hot-electrons from the rear surface. The proton yield from the polystyrene-coated target is about 10 times as high as that from the uncoated metal target. This enhancement of the proton yield is roughly proportional to the increase of hydrogen atoms given by the 133-nm thick polystyrene layer, assuming a contaminant layer of  10-nm thickness is on the metal surface without coating. This result shows that the polystyrene layer contributes to the yield enhancement.
10-nm thickness is on the metal surface without coating. This result shows that the polystyrene layer contributes to the yield enhancement.
Sagisaka, Akito; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Takai, Mamiko; Yogo, Akifumi; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
Proceedings of RCNP-JAEA Workshop on Nuclear Photon Science "Hadron-nuclear physics probed by photon", p.195 - 200, 2006/00
High energy ions, electrons, and X-ray are generated from ultrashort pulse high-intensity laser-matter interactions. High-energy protons are observed with a thin-foil target irradiated with a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser at the peak intensity of  2.7
2.7 10
10 W/cm
W/cm . The maximum proton energy is
. The maximum proton energy is  900 keV.
900 keV.
Sagisaka, Akito; Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Takai, Mamiko; Orimo, Satoshi; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ogura, Koichi; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Orimo, Satoshi; Nakamura, Shu*; Sagisaka, Akito; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kado, Masataka; Mori, Michiaki; Hayashi, Yukio; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Takai, Mamiko; Mori, Michiaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Daido, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Shu*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Mori, Michiaki; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Nakai, Yoshiki; et al.
no journal, ,
We report the result on a novel online analysis of fast ions generated in an ultraintense laser-foil interaction. Fast protons are observed by a time-of-flight (TOF) detector, which is precisely calibrated using proton beams from an ion accelerator as to its detection efficiency depending on the proton energy. The TOF detector provides shot-to-shot energy distributions of protons immediately after the irradiation of a high-intensity laser pulse of 10 W/cm
W/cm . Definite correlations are found between the prepulse intensity and the high energy cutoff of protons as well as the conversion efficiency of the laser energy into the proton energy, governing the stability of the repetitive proton generation.
. Definite correlations are found between the prepulse intensity and the high energy cutoff of protons as well as the conversion efficiency of the laser energy into the proton energy, governing the stability of the repetitive proton generation.
Orimo, Satoshi; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kondo, Shuji; Yamamoto, Yoichi*; Shimomura, Takuya*; Tanoue, Manabu*; et al.
no journal, ,
We are investigating an intense fs-laser driven MeV proton source using a thin foil, and its applications. Simultaneous imaging of a sample with a proton and an X-ray beams has been demonstrated by a ultra-short pulse higt intensity Ti:Sapphire laser systems at JAEA and GIST. For generating a short-pulse proton beams and X-rays, an intense laser pulse irradiates a tape targets. The p-polarized laser pulse with 50 mm diameter is focused onto the cupper tape target at 45 degree incident angle with focal length of 238 mm (F/4.8), giving an intensity on target of 3-9 10
10 W/cm10
W/cm10 . The cupper and polyimide tape was 5, 7.5 micron in thickness and 20 mm in width. The target system supplies a fresh surface to the focus spot at every shot. We obtained simultaneously the projection image of a Ni mesh pattern having a periodically structured pattern by the proton detected CR39 and X-rays detected on imaging plate.
. The cupper and polyimide tape was 5, 7.5 micron in thickness and 20 mm in width. The target system supplies a fresh surface to the focus spot at every shot. We obtained simultaneously the projection image of a Ni mesh pattern having a periodically structured pattern by the proton detected CR39 and X-rays detected on imaging plate.
Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Nakamura, Shu*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Noda, Akira*; Nemoto, Koshichi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sagisaka, Akito; Daido, Hiroyuki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ma, J.-L.; Mori, Michiaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Takai, Mamiko; Oishi, Yuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yogo, Akifumi; Mori, Michiaki; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Kondo, Shuji; Nakai, Yoshiki; Akutsu, Atsushi; Yamamoto, Yoichi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Nakamura, Shu*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Noda, Akira*; Oishi, Yuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English