Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Tongu, Hiromu*; Hayano, Hitoshi*; Geng, R. L.*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 19(9), p.P09037_1 - P09037_15, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 34(5), p.4904504_1 - 4904504_4, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A permanent magnet can be used to generate an axisymmetric uniform magnetic field over a long distance. To satisfy Ampere's law, which states that the line-integral value of the magnetic field is zero, a magnetic field region of opposite polarity appears somewhere along the axis while maintaining uniformity in a certain range along the axis. Using this configuration, a magnetic field generator for a Faraday rotation device for laser light was fabricated. This device has a large bore of 30 mm in diameter to handle ultra-high-power lasers and can hold a large crystal disc for Faraday rotation. The irregularity in the central plane is less than 1% within the bore diameter. This configuration can also be applied to long axisymmetric beam transport magnets. This technique can be extended to control the gradient of the magnetic field distributions, such as the focusing field of a klystron.
Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Terunuma, Nobuhiro*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 34(5), p.4004005_1 - 4004005_5, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We are developing a correction magnet for charged particle beams using permanent magnets. By rotating the rod of the permanent magnet that generates the magnetic field, the magnetic field can be changed to bipolarity. To verify the principle of this bi-polarity change, a prototype was built, and its performance was evaluated. The performance evaluation of the prototype machine revealed that the inhomogeneity of the remanent magnetization of the permanent magnet has a significant effect on the multipole component. To suppress this effect, a compensating magnet with additional anisotropic intermediate poles is being considered.
Takeuchi, Yusuke*; Tojo, Junji*; Yamanaka, T.*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; et al.
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.562 - 564, 2022/10
A muon linac is under development for future muon g-2/EDM experiments at J-PARC. The linac provides a 212 MeV muon beam to an MRI-type compact storage ring. After the initial acceleration using the electrostatic field created by mesh and cylindrical electrodes, the muons are accelerated using four types of radio-frequency accelerators. To validate the linac design as a whole, end-to-end simulations were performed using General Particle Tracer. In addition, error studies were performed to investigate the effects on beam and spin dynamics of various errors in the accelerator components and input beam distribution. This paper describes the results of the end-to-end simulations and error studies.
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 32(6), p.4006705_1 - 4006705_5, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.88(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Space charge compensation technique using multipole magnetic field components has been proposed to transport high intensity beam in the J-PARC linac. In order to realize this compensation technique, a compact size permanent hybrid multi-pole magnet would be suitable. A magnet system for the simultaneous production of quadrupole and adjustable octupole components using permanent magnet materials and have manufactured a first model of the magnet systems.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Otani, Masashi*; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; et al.
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.636 - 641, 2022/09
The muon linac project for the precise measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic and electric dipole moments, which is currently one of the hottest issues of the elementary particle physics, is in progress at J-PARC. The muons from the J-PARC muon facility are once cooled to room temperature, then accelerated up to 212 MeV with a normalized emittance of 1.5  mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Kondo, Akihiro*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 32(6), p.4007304_1 - 4007304_4, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)High-field magnets are often demanded advanced scientific studies. Although a hybrid coil design comprising Nb-Ti, Nb Sn, and HTS (High-Temperature Superconductors) are potential candidates for such application, the costs of Nb
Sn, and HTS (High-Temperature Superconductors) are potential candidates for such application, the costs of Nb Sn and HTS are expensive compared with Nb-Ti. By generating an additional field of about 1 T by permanent magnets, the required amounts of superconducting material may be reduced. Magnetic properties of some magnetic materials have been studied by other works at temperatures as low as 100 K. The remanent field of conventional NdFeB magnets decreases at 100 K due to spin reorientation. PrFeB magnets consisting of praseodymium (Pr) instead of neodymium (Nd) do not show such degradation and the coercivity of PrFeB at 100 K is 7 T. In this study, the B-H curve, as a primary magnetic property, of a PrFeB magnet sample was measured in the temperature range down to 4 K. As a result, no decrease in magnetization of the praseodymium magnets, and the coercivity was 10 T.
Sn and HTS are expensive compared with Nb-Ti. By generating an additional field of about 1 T by permanent magnets, the required amounts of superconducting material may be reduced. Magnetic properties of some magnetic materials have been studied by other works at temperatures as low as 100 K. The remanent field of conventional NdFeB magnets decreases at 100 K due to spin reorientation. PrFeB magnets consisting of praseodymium (Pr) instead of neodymium (Nd) do not show such degradation and the coercivity of PrFeB at 100 K is 7 T. In this study, the B-H curve, as a primary magnetic property, of a PrFeB magnet sample was measured in the temperature range down to 4 K. As a result, no decrease in magnetization of the praseodymium magnets, and the coercivity was 10 T.
Takeuchi, Yusuke*; Tojo, Junji*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC 22) (Internet), p.1534 - 1537, 2022/06
The muon g-2/EDM experiment is under preparation at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), and the muon linear accelerator for the experiment is being developed. A Disk-and-Washer (DAW) cavity will be used for the medium-velocity part of the accelerator, and muons will be accelerated from 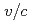 =
=  = 0.3 to 0.7 with the operating frequency of 1.296 GHz. Machining, brazing, and low-power measurements of a prototype cell reflecting the design of the first tank of DAW were performed to identify fabrication problems. Several problems were identified, such as misalignment of washers during brazing, and some measures will be taken in the actual tank fabrication. In this paper, the results of the prototype cell fabrication will be reported.
= 0.3 to 0.7 with the operating frequency of 1.296 GHz. Machining, brazing, and low-power measurements of a prototype cell reflecting the design of the first tank of DAW were performed to identify fabrication problems. Several problems were identified, such as misalignment of washers during brazing, and some measures will be taken in the actual tank fabrication. In this paper, the results of the prototype cell fabrication will be reported.
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Tongu, Hiromu*; Hayano, Hitoshi*; Geng, R. L.*
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2021) (Internet), p.323 - 325, 2022/05
In order to evaluate the performance of a superconducting cavity, we are developing a mapping system to measure the distribution of cavity temperature, field emission X-rays, and trapped magnetic flux with high positional resolution. In order to construct a system with high positional resolution, a large number of sensors are required. However, as the number of sensors increases, so does the amount of wiring, which increases the complexity of the wiring in the cryogenic apparatus, and also increases the heat transfer through the wiring, which disturb efficient operation of cavity tests. We are developing an efficient mapping system with a multiplexer that scans the readout signal on the same circuit as the sensor in the cryogenic dewar where the cavity test is conducted. In this presentation, we report the outline and test results of the mapping system under development
Otani, Masashi*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Naito, Fujio*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Iinuma, Hiromi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012097_1 - 012097_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:78.48(Physics, Particles & Fields)A disk and washer (DAW) coupled cavity linac (CCL) has been developed for a middle velocity part in a muon linac to measure muon anomalous magnetic moment and search for electric dipole moment. I will accelerate muons from 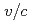 =
=  = 0.3 to 0.7 at an operational frequency of 1.3GHz. In this poster, the cavity design, beam dynamics design, and the cold-model measurements will be presented.
= 0.3 to 0.7 at an operational frequency of 1.3GHz. In this poster, the cavity design, beam dynamics design, and the cold-model measurements will be presented.
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Mitsuhiro*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012054_1 - 012054_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:94.59(Physics, Particles & Fields)An inter-digital H-mode drift-tube linac (IH-DTL) is developed in a muon linac at the J-PARC E34 experiment. IH-DTL will accelerate muons from 0.34 MeV to 4.5 MeV at a drive frequency of 324 MHz. Since IH-DTL adopts an APF method, with which the beam is focused in the transverse direction using the rf field only, the proper beam matching of the phase-space distribution is required before the injection into the IH-DTL. Thus, an IH-DTL prototype was fabricated to evaluate the performance of the cavity and beam transmission. As a preparation of the high-power test, tuners and coupler are designed and fabricated. In this paper, the development of the tuner and the coupler and the result of the low-power measurement will be presented.
Abe, Masashi*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Terunuma, Nobuhiro*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Yako, Tomoki*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.700 - 702, 2019/10
Application of permanent magnets to the damping ring of International Linear Collider (ILC) is investigated. Replacing electromagnets with permanent magnets can reduce not only electricity for exciting the coils and maintenance cost of power supplies but also leakage accidents of cooling water. Bending magnets and correction magnets are used in damping ring, but we tried to calculate magnetic field distributions in a correction magnets using permanent magnets with 3D magnetic field code CST studio. The orbit correction magnet requires that the polarity and the intensity of the generated magnetic field be variable in order to correct the beam orbit error. In this research, adjustment of the generated magnetic field was made possible by mounting the rotation mechanism on the permanent magnet in the magnetic circuit in the correction magnet. In addition, in order to suppress deterioration of beam quality due to an incorrect multipole magnetic field, optimization of the shape of the magnetic circuit was performed, and a magnet design that could be installed on a accelerator was established.
Yako, Tomoki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Abe, Masashi*; Kurihara, Toshikazu*; Fukuda, Masafumi*; Sato, Masaharu*; Sugimura, Takashi*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Takamiya, Koichi*; Iinuma, Yuto*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1003 - 1005, 2019/10
Permanent magnets are used as materials for beam optics elements, but it is known that radiation demagnetization occurs in neodymium magnets and samarium cobalt magnets. However, there is not enough information on the radiation demagnetization of ferrite magnets which is weak in strength but inexpensive. In order to verify the suitability of the ferrite magnet as a beam optics element, radiation demagnetization experiments by neutron irradiation of the ferrite magnet were carried out at the Kyoto University Research Reactor (KUR). In the experiment, neutron fluence up to 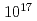 cm
cm was irradiated, and no significant demagnetization was detected on the fluence.
was irradiated, and no significant demagnetization was detected on the fluence.
Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Hayano, Hitoshi*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.32 - 35, 2019/10
Research and development of gradient enhancement of superconducting RF accelerating cavity is carried out by accelerator research institute in the world, but defects on the cavity surface limit accelerating electric field. Therefore, development of "Inside inspection system for superconducting accelerated cavity" that optically visualizes the state of the inner surface of the superconducting cavity has been carried out, and results have been achieved. In this research, we apply image processing technology that has developed remarkably in recent years to the internal inspection system, and advanced the defect recognition method. Extraction of depth information and image synthesis were performed from images obtained with different focal positions with the camera for internal surface inspection. Also, by performing pattern recognition processing on the images, automatic detection of defects has become possible. By integrating these techniques into the cavity inner surface inspection system, it becomes possible to shorten the scan time for defect search and acquire the defect shape.
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Sue, Yuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.404 - 407, 2019/07
An inter-digital H-mode drift-tube linac (IH-DTL) is developed in a muon linac at the J-PARC E34 experiment. IH-DTL will accelerate muons from 0.34 MeV to 4.5 MeV at a drive frequency of 324 MHz. Since IH-DTL adopts an APF method, with which the beam is focused in the transverse direction using the rf field only, the proper beam matching of the phase-space distribution is required before the injection into the IH-DTL. Thus, an IH-DTL prototype was fabricated to evaluate the performance of the cavity and beam transmission. As a preparation of the high-power test, tuners and coupler are designed and fabricated. In the low power measurement, we decided the loop structure with witch the VSWR = 1.01 and field distortion of within 7%. In this paper, the development of the tuner and the coupler and the result of the low-power measurement will be presented.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:156 Percentile:99.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Mitsuhiro*; Kitamura, Ryo*; et al.
Proceedings of 29th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2018) (Internet), p.180 - 183, 2019/01
We have developed an Interdigital H-mode (IH) Drift-Tube Linac (DTL) design with an alternative phase focusing (APF) scheme for a muon linac, in order to measure the anomalous magnetic moment and electric dipole moment (EDM) of muons at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The IH-DTL accelerates muons from beta 0.08 to 0.28 at an operational frequency of 324 MHz. The output beam emittances are calculated as 0.315  and 0.195
and 0.195  mm mrad in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, which satisfies the experimental requirement.
mm mrad in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, which satisfies the experimental requirement.
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Sue, Yuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.904 - 908, 2018/10
We have developed an Interdigital H-mode (IH) Drift-Tube Linac (DTL) design with an Alternative Phase Focusing (APF) scheme for a muon linac, in order to measure the anomalous magnetic moment and Electric Dipole Moment (EDM) of muons at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The IH-DTL accelerates muons from beta 0.08 to 0.28 at an operational frequency of 324 MHz. The output beam emittances are calculated as 0.315  and 0.195
and 0.195  mm mrad in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, which satisfies the experimental requirement.
mm mrad in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, which satisfies the experimental requirement.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Otani, Masashi*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Mitsuhiro*; Kitamura, Ryo*; et al.
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.5041 - 5046, 2018/06
J-PARC is developing the reacceleration system of the ultra slow (30 meV) muon (USM) obtained by two-photon laser resonant ionization of muonium atoms. The muon beam thus obtained has low emittance, meeting the requirement for the g-2/EDM experiment. J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment (g-2) with a precision of 0.1 ppm and search for EDM with a sensitivity to 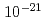 e cm. The USM's are accelerated to 212 MeV by using a muon dedicated linac to be a ultra cold muon beam. The muon LINAC consists of an RFQ, a inter-digital H-mode DTL, disk and washer coupled cell structures, and disk loaded structures. Proof of the slow muon acceleration scheme is an essential step to realize the world first muon linac. In October 2017, we have succeeded to accelerate slow negative muoniums generated using a simpler muonium source to 89 keV. In this talk, present design of the muon linac and the result of the world first muon acceleration experiment are reported.
e cm. The USM's are accelerated to 212 MeV by using a muon dedicated linac to be a ultra cold muon beam. The muon LINAC consists of an RFQ, a inter-digital H-mode DTL, disk and washer coupled cell structures, and disk loaded structures. Proof of the slow muon acceleration scheme is an essential step to realize the world first muon linac. In October 2017, we have succeeded to accelerate slow negative muoniums generated using a simpler muonium source to 89 keV. In this talk, present design of the muon linac and the result of the world first muon acceleration experiment are reported.
Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshida, Mitsuhiro*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hayashizaki, Noriyosu*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; et al.
Proceedings of 28th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2016) (Internet), p.1037 - 1041, 2017/05
We are developing a linac dedicated to the muon acceleration. It enables us to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment with an accuracy of 0.1 ppm and search for electric dipole moment with a sensitivity of 10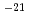 cm to explore beyond Standard Model of elementary particle physics. As a first step for demonstration of the muon acceleration, we are developing the source of slow muon with which RFQ acceleration is conducted. This paper describes status of these developments.
cm to explore beyond Standard Model of elementary particle physics. As a first step for demonstration of the muon acceleration, we are developing the source of slow muon with which RFQ acceleration is conducted. This paper describes status of these developments.