Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwata, Keiko; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Ha, Yoosung; Shimodaira, Masaki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Honda, Mitsunori; Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.143 - 152, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:33.4(Instruments & Instrumentation)Iwata, Keiko; Hata, Kuniki; Tobita, Toru; Hirota, Takatoshi*; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2021/07
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwata, Keiko; Tobita, Toru; Otsu, Takuyo; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Hanawa, Satoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
JAEA-Research 2017-018, 122 Pages, 2018/03
Warm pre-stress (WPS) effect is a phenomenon that after applying a load at a high temperature fracture does not occur in unloading during cooling, and then the fracture toughness in reloading at a lower temperature increases effectively. Engineering evaluation models to predict an apparent fracture toughness in reloading are established using experimental data with linear elasticity. However, there is a lack of data on the WPS effect for the effects of specimen size and surface crack in elastic-plastic regime. In this study, fracture toughness tests were performed after applying load-temperature histories which simulate pressurized thermal shock transients to confirm the WPS effect. The experimental results of an apparent fracture toughness tend to be lower than the predictive results using the engineering evaluation models in the case of a high degree of plastic deformation in preloading. Considering the plastic component of preloading can refine the engineering evaluation models.
Iwata, Keiko; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Ha, Yoosung; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hanawa, Satoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Photon Factory Activity Report 2017, 2 Pages, 2018/00
no abstracts in English
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Kasahara, Shigeki*; Iwata, Keiko; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 307, p.411 - 417, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)To investigate influential parameters for irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, we attempt to analyze statistically existing data on the crack growth rate (CGR) in irradiated austenitic stainless steels (SSs) in boiling water reactor (BWR) environments using the Bayesian nonparametric (BNP) method. From the probability distribution of CGR and some input parameters, such as yield stress of irradiated material (
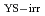 ), stress intensity factor (
), stress intensity factor ( ), electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP), and fast neutron fluence, the mean CGR is estimated and compared with the measured CGR. The analytical results show good reproducibility of the measured CGR. The results also indicate the possible neutron fluence effects on CGR in high CGR region (i.e., high neutron fluence condition) by radiation-induced segregation (RIS), localized deformation, and/or other mechanisms than radiation hardening.
), electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP), and fast neutron fluence, the mean CGR is estimated and compared with the measured CGR. The analytical results show good reproducibility of the measured CGR. The results also indicate the possible neutron fluence effects on CGR in high CGR region (i.e., high neutron fluence condition) by radiation-induced segregation (RIS), localized deformation, and/or other mechanisms than radiation hardening.
Iwata, Keiko; Tobita, Toru; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2016/07
The effect of warm pre-stressing (WPS) on fracture toughness was evaluated for a reactor pressure vessel steel. Various types of thermomechanical loadings were applied to 1T-CT specimens. The results were compared with predictions from several analytical WPS engineering models. The specimen size effect was subsequently investigated under the load-unload-cool-fracture transient condition using 1T-, 0.4T-, and 0.16T-CT specimens. Analyses of the plastic zone distribution and residual stress were conducted to identify the difference in the WPS effect among the specimens.
Iwata, Hajime*; Sakamaki, Keiko*; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Onuki, Toshihiko; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
The aim of this study is to understand the fate of plutonium derived from atomic bomb, which has been preserved in the bottom sediment for 60 years, based on the investigation of the speciation and size distribution of plutonium. Approximately 60 % of plutonium is present as bound to organic matters and 30 % is present as insoluble species such as Pu oxides. Our results also suggest that the fast transformation of plutonium to the species bound to the organic matter for the period of 60 years, evidencing the important role of the natural organic matters on the plutonium speciation in the environment.
Sakamaki, Keiko; Iwata, Hajime*; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Hajime*; Kawamoto, Yuji*; Sakamaki, Keiko; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Onuki, Toshihiko; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Keiko; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Shimoyama, Iwao; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Iwase, Akihiro*; Kojima, Hiroshi*; Mayumi, Ren*
no journal, ,
Microstructure analysis on reactor pressure vessel steel was conducted by using X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) method, where local atomic structures and coordination number around selected atoms are obtained. In our presentation, microstructural changes of thermally aged or electron-irradiated samples will be discussed.
Iwata, Keiko; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Ha, Yoosung; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Kojima, Hiroshi*; Mayumi, Ren*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
no journal, ,
Microstructure analysis for thermally aged stainless overlay cladding was conducted by using X-ray absorption. X-ray absorption fine structure analysis was adapted, which was possible to obtain the average information of a material and to identify the bond length and chemical state by the selected atoms. In this study, changes of coordination number and bond length around the Mn atom were recognized.
Ha, Yoosung; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Iwata, Keiko; Tobita, Toru; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishiyama, Yutaka
no journal, ,
The microstructure of heat affected zone (HAZ) in stainless over-ray clad is predicted by finite element method (FEM). From the results of FEM analysis, the coarse grain area and fine grain area could obtain from HAZ and base metal also obtained in 1/4 thickness part for the irradiation experiment. After ion irradiation, the irradiation hardening of HAZ has higher tendency than that of base metal. In addition, the change of hardening is observed in fine grain area.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Tobita, Toru; Iwata, Keiko; Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishiyama, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ha, Yoosung; Iwata, Keiko; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hanawa, Satoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ha, Yoosung; Iwata, Keiko; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Honda, Mitsunori; Hanawa, Satoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ha, Yoosung; Iwata, Keiko; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Hanawa, Satoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Keiko; Ha, Yoosung; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Shimodaira, Masaki; Honda, Mitsunori; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimodaira, Masaki; Hata, Kuniki; Iwata, Keiko; Ha, Yoosung; Kasahara, Shigeki; Katsuyama, Jinya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Keiko; Ha, Yoosung; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Shimodaira, Masaki; Katsuyama, Jinya; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Honda, Mitsunori; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
no journal, ,
In this study, we performed that extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis for ion- and neutron-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steel to investigate microstructural changes of solute atom clusters induced by irradiation. To verify changes of EXAFS spectra recognized in ion-irradiated samples, we constructed lattice structure models with defects induced by irradiation and calculated theoretical EXAFS spectra for these models. Comparison between measured spectra and EXAFS simulations suggests that tensile-type interstitials or vacancy defects could be located around Cu and Ni atoms. Although the improvement for decreasing of noise in measured spectra at Cu K-edge, we will indicate that microstructure around Cu atoms may change from bcc structure due to irradiation.