Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Yuki*; Ishiwata, Tobimaru*; Horiuchi, Misato*; Nishiki, Yuto*; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Otake, Tsubasa*; Kawakita, Ryohei; Takayama, Yusuke; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Sato, Tsutomu*
Shigen, Sozai Koenshu (Internet), 11(1), 7 Pages, 2024/03
no abstracts in English
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:97.1(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Takahashi, Hidefumi*; Aono, Kai*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Nomoto, Takuya*; Sakano, Masato*; Ishizaka, Kyoko*; Arita, Ryotaro*; Ishiwata, Shintaro*
Physical Review B, 102(17), p.174425_1 - 174425_6, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.47(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The competing magnetic ground states of the itinerant magnet EuCuSb, which has a hexagonal layered structure, were studied via magnetization, resistivity, and neutron-diffraction measurements on single-crystal samples. EuCuSb has a three-dimensional semimetallic band structure as confirmed by band calculation and angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy, consistent with the nearly isotropic metallic conductivity in the paramagnetic state. However, below the antiferromagnetic transition temperature of 
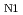 (8.5 K), the resistivity, especially along the hexagonal axis, increases significantly. This implies the emergence of anisotropic magnetic ordering coupled to the conducting electrons. Neutron-diffraction measurements show that the Eu spins, which order ferromagnetically within each layer, are collinearly modulated (up-up-down-down) along the hexagonal axis below
(8.5 K), the resistivity, especially along the hexagonal axis, increases significantly. This implies the emergence of anisotropic magnetic ordering coupled to the conducting electrons. Neutron-diffraction measurements show that the Eu spins, which order ferromagnetically within each layer, are collinearly modulated (up-up-down-down) along the hexagonal axis below 
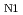 , followed by the partial emergence of helical spin modulation below
, followed by the partial emergence of helical spin modulation below 
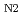 (6 K). Based on the observation of anomalous magnetoresistance with hysteretic behavior, we discuss the competing nature of the ground state inherent in a frustrated Heisenberg-like spin system with a centrosymmetric structure.
(6 K). Based on the observation of anomalous magnetoresistance with hysteretic behavior, we discuss the competing nature of the ground state inherent in a frustrated Heisenberg-like spin system with a centrosymmetric structure.
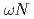 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:44.35(Physics, Nuclear)Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:262 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Matsuoka, Moe*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Osawa, Takahito; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Abe, Masanao*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Arai, Takehiko*; Komatsu, Mutsumi*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 69(1), p.120_1 - 120_12, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:21.58(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)We have conducted ground-based performance evaluation tests of the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) onboard Hayabusa2 spacecraft and established a method for evaluating its measured reflectance spectra. Reflectance spectra of nine powdered carbonaceous chondrite samples were measured by both NIRS3 and a FT-IR spectrometer. Since raw data obtained by NIRS3 had considerable spectral distortion caused by systematic offsets in sensitivity of individual pixels, we have established two methods for correcting the NIRS3 data by comparing them with the corresponding FT-IR data. In order to characterize the absorption bands in NIRS3 spectra, the depth of each band component D is defined for each wavelength
is defined for each wavelength  (
( m). Reflectance spectra of asteroid Ryugu, the target asteroid of Hayabusa2, to be recorded by the NIRS3 are expected to reveal the characteristics of the surface materials by using the evaluation technique.
m). Reflectance spectra of asteroid Ryugu, the target asteroid of Hayabusa2, to be recorded by the NIRS3 are expected to reveal the characteristics of the surface materials by using the evaluation technique.
Iwata, Takahiro*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Arai, Takehiko*; Arai, Tomoko*; Hirata, Naru*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Honda, Chikatoshi*; Imae, Naoya*; et al.
Space Science Reviews, 208(1-4), p.317 - 337, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:71.62(Astronomy & Astrophysics)NIRS3: The Near Infrared Spectrometer is installed on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft to observe the target C-type asteroid 162173 Ryugu at near infrared wavelengths of 1.8 to 3.2 micrometer. It aims to obtain reflectance spectra in order to detect absorption bands of hydrated and hydroxide minerals in the 3 micrometer-band. We adopted a linear-image sensor with indium arsenide (InAs) photo diodes and a cooling system with a passive radiator to achieve an optics temperature of 188 K, which enables to retaining sufficient sensitivity and noise level in the 3 micrometer wavelength region. We conducted ground performance tests for the NIRS3 flight model (FM) to confirm its baseline specifications. The results imply that the properties such as the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conform to scientific requirements to determine the degree of aqueous alteration, such as CM or CI chondrite, and the stage of thermal metamorphism on the asteroid surface.
Iwata, Keiji*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Suzuki, Kanki*; Shobu, Takahisa; Orihara, Hideto*; Sakai, Yusuke*; Akita, Koichi; Oya, Shinichi*; Ishiyama, Kazushi*
Journal of Applied Physics, 117(17), p.17A910_1 - 17A910_4, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.86(Physics, Applied)Internal stress distribution for generating closure domains occurring in laser-irradiated Fe-3%Si(110) steels was investigated using high-energy X-ray analysis and domain theory based on the variational principle. The measured triaxial stresses inside the specimen were compressive and the stress in the rolling direction became more dominant than stresses in the other directions. The calculations based on the variational principle of magnetic energy for closure domains showed that the measured triaxial stresses made the closure domains more stable than the basic domain without closure domains. The experimental and calculation results reveal that the laser-introduced internal stresses result in the occurrence of the closure domains.
Taguchi, Yasujiro*; Sakai, Hideaki*; Okuyama, Daisuke*; Ishiwata, Shintaro*; Fujioka, Jun*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Hashizume, Daisuke*; Kagawa, Fumitaka*; Takahashi, Yoichiro*; Shimano, Ryo*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 407(11), p.1685 - 1688, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.87(Physics, Condensed Matter) -type hexaferrites with a room-temperature conical state and magnetically controllable spin helicity
-type hexaferrites with a room-temperature conical state and magnetically controllable spin helicityTokunaga, Yusuke*; Kaneko, Yoshio*; Okuyama, Daisuke*; Ishiwata, Shintaro*; Arima, Takahisa*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Taguchi, Yasujiro*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
Physical Review Letters, 105(25), p.257201_1 - 257201_4, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:269 Percentile:98.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sakai, Yusuke*; Akita, Koichi*; Oya, Shinichi*; Sueyoshi, Kazuyuki*; Shobu, Takahisa; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Suzuki, Kanki*; Iwata, Keiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Ishiwata, Shintaro*; Okuyama, Daisuke*; Nishi, Masakazu*; Tokunaga, Yusuke*; Arima, Takahisa*; Taguchi, Yasujiro*; Tokura, Yoshiki*
no journal, ,
Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi; Iwata, Yusuke*; Tomota, Yo*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) is produced by water radiolysis. To study effects of H
) is produced by water radiolysis. To study effects of H O
O environments on SCC behavior of stainless steel, crack growth test was conducted in high temperature water containing H
environments on SCC behavior of stainless steel, crack growth test was conducted in high temperature water containing H O
O . Two types of 0.25T-compact tension (CT) specimens were prepared from thermally sensitized type 304 stainless steel. After fatigue pre-crack length of 4.4-4.8 mm introduction, the pre-crack was shortened to 1.1-1.7 mm. For the CT specimens with long pre-crack length, intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed near side grooves. For the CT specimens with shortened pre-crack length, IGSCC area spread to the central region. SCC grew linearly in H
. Two types of 0.25T-compact tension (CT) specimens were prepared from thermally sensitized type 304 stainless steel. After fatigue pre-crack length of 4.4-4.8 mm introduction, the pre-crack was shortened to 1.1-1.7 mm. For the CT specimens with long pre-crack length, intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed near side grooves. For the CT specimens with shortened pre-crack length, IGSCC area spread to the central region. SCC grew linearly in H O
O environments although SCC growth in O
environments although SCC growth in O environments branched off. As outer oxide layer on the pre-crack, Fe
environments branched off. As outer oxide layer on the pre-crack, Fe O
O was observed in O
was observed in O environments. In H
environments. In H O
O environments, it changed from Fe
environments, it changed from Fe O
O toward the crack tip to Fe
toward the crack tip to Fe O
O .
.
Harazono, Yoshinobu*; Futakuchi, Yusuke*; Yoshikawa, Kota*; Iwata, Hiroki*; Ueyama, Masahito*; Nagano, Hirohiko; Sakabe, Ayaka*; Kosugi, Yoshiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yogo, Akifumi*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Iwamoto, Akihumi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Golovin, D.*; Mori, Takato*; Lan, Z.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Horiuchi, Misato*; Saito, Masaki*; Ishiwata, Tobimaru*; Nishiki, Yuto*; Sato, Tsutomu*; Takayama, Yusuke; Mitsui, Seiichiro
no journal, ,
In geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes, the use of swelling clay is intrinsic as a buffer around waste packages. In order to achieve long-term safety, longevity of montmorillonite, a major constituent of bentonite buffer, under disposal related conditions is important. One of the alteration processes of concern is cementation of clay layers due to precipitation of secondary minerals such as silica. In this study, we examined natural bentonite ores that could serve as natural analogues for the cementation process, especially focusing on microstructure of consolidated bentonite. Bentonite ores were collected from the Tsukinuno Mine in Yamagata Prefecture, Japan. This bentonite is thought to have been formed by the diagenesis of volcanic ash. A dry polishing technique was used to form a smooth surface that well shows the original microstructure of bentonite ores, allowing petrographic discussion as in the observation of non-clayey rocks. Besides coarse quartz (probably pyroclastic origin), fine silica with grain sizes ranging from a few microns to submicron is widely observed in bentonite ores. The distribution of fine silica is characterized by discrete grains or short chains or small clusters in the fine-grained montmorillonite matrix, suggesting that they formed in closed system diagenesis and a low mobility of silica in clay matrix. Thin foils including fine silica and montmorillonite were extracted from polished sections using a focused ion beam apparatus and observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). TEM observations demonstrated a microstructure where montmorillonite edge is directly bonded to the fine silica particles. The microstructure as seen in this study, is interpreted to be formed by the authigenic silica precipitation during diagenesis, not by a physical mixture. The silica coating of montmorillonite edge could prevent water access to its interlayer space and free swelling, which leads to a decrease in swelling pressure.
Takir, D.*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; et al.
no journal, ,
JAXA spacecraft and sample return mission Hayabusa2 has arrived at the near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, which is classified a primitive carbonaceous object. Here we report recent results of near-infrared spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. The observations provide direct measurements of the surface composition of Ryugu and context for the returned samples. NIRS3 has detected a weak and narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micrometer across entire observed surface. This absorption feature is attributed to the presence of OH-bearing minerals. The NIRS3 observations also revealed that Ryugu is the darkest object to be observed up-close by a visiting spacecraft. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are consistent with thermally-and/or shock-metamorphosed, and/or carbon-rich space-weathered primitive and hydrated carbonaceous chondrites.
Ishiwata, Tobimaru*; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Otake, Tsubasa*; Sato, Tsutomu*; Kawakita, Ryohei; Takayama, Yusuke; Mitsui, Seiichiro
no journal, ,
It is known that the cementation of bentontie may cause the reduction of swelling pressure. However, fundamental mechanism of this reducing swelling pressure has not been well understood. To understand the mechanism, it is essential to identify the cementitious materials and observe the changes in microstructure associated with cementation. In this study, the microstructural observation and swelling tests were conducted on several bentonite ores collected from Tsukinuno Mine in Yamagata Prefecture, Japan, as natural analog of cementation, and the relationship between petrographic texture and swelling pressure was discussed. Thin sections of bentonite ores were prepared by dry polishing technique to observe flat surfaces in micro scales. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) demonstrated the widespread distribution of authigenic, a few micron silica in the matrix of montmorillonite. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed that the micro silica minerals (commonly quartz and less commonly amorphous silica) adhered to the edge of montmorillonite grains. These observations suggest that the adherence of these cementitious materials to montmorillonite prevents water access to the interlayer of montmorillonite and swelling, resulting in a decrease in swelling pressure. While these microstructures were observed commonly in all samples collected from several bentonite beds, the relative abundance of montmorillonite and micro silica minerals varied among different beds. It is possible that the swelling pressure in the cemented bentonite is affected by the relative abundance of montmorillonite and cementitious materials.