Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Imaizumi, Yuya; Kamiyama, Kenji; Matsuba, Kenichi; Isozaki, Mikio; Suzuki, Toru; Emura, Yuki
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2017/04
In order to simulate the typical accident conditions of the fuel relocation phase in SFRs, the molten alloy of low melting point was discharged into a shallow water pool. The distance between the nozzle exit and the bottom plate was set to a value which was indicated to be insufficient to fragment. As the experimental result, the melt jet reached the bottom plate, and dispersed in all directions along the plate, together with the progress of fragmentation. In addition, the melt temperature on the bottom plate decreased rapidly along the radius direction. These results suggest that the fragmentation which would accompany this rapid cooling would be enhanced by the plate. This enhancement would be caused by the extension of the melt-water interface when the melt was dispersed forcibly by the plate. The solidified debris remained after the discharge showed remarkable fragmentation which was assumed to be caused by the formations of small vapor bubbles in the interface.
Takatsu, Hideyuki; Enoeda, Mikio; Suzuki, Satoshi; Hirose, Takanori; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Takahashi, Koji
Proceedings of International Conference on Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP '11), p.35 - 40, 2011/04
ITER is a mega-science fusion project, under an international collaboration of seven Members, to construct, operate, exploit and decommission a tokamak-type experimental reactor at Cadarache site with a mission to demonstrate the scientific and technological feasibility. The ITER Project started technical activities in 2007 and is now in a serious construction phase. Domestic Agencies of the seven member countries are in the process of manufacturing long lead-time components. Some of the ITER components apply HIP technology in manufacturing processes in view of a number of potential advantages. In this paper, examples and status of application of HIP technology by the Domestic Agency of Japan are overviewed.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi*; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Uto, Hiroyasu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nishitani, Takeo; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-019, 194 Pages, 2010/08
This report describes the results of the conceptual design study of the SlimCS fusion DEMO reactor aiming at demonstrating fusion power production in a plant scale and allowing to assess the economic prospects of a fusion power plant. The design study has focused on a compact and low aspect ratio tokamak reactor concept with a reduced-sized central solenoid, which is novel compared with previous tokamak reactor concept such as SSTR (Steady State Tokamak Reactor). The reactor has the main parameters of a major radius of 5.5 m, aspect ratio of 2.6, elongation of 2.0, normalized beta of 4.3, fusion out put of 2.95 GW and average neutron wall load of 3 MW/m . This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
. This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
 -ray emitting nuclides (Joint research)
-ray emitting nuclides (Joint research)Ishimori, Kenichiro; Oki, Keiichi; Takaizumi, Hirohide; Kameo, Yutaka; Oki, Yoshiyuki*; Nakashima, Mikio
JAEA-Technology 2007-065, 20 Pages, 2008/01
In order to prepare a reference material which is used for radiochemical analysis of solidified products made from non-metallic miscellaneous low level radioactive solid wastes by melting in Nuclear Science Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, the preparation method of the reference material was investigated. Under the optimum melting conditions obtained in this report, the reference material containing  Np,
Np,  Am and
Am and  Cm as
Cm as  -ray emitting nuclides was successfully prepared. From radiochemical analysis of the reference material, the radioactive concentration of respective nuclides was determined to be 0.188
-ray emitting nuclides was successfully prepared. From radiochemical analysis of the reference material, the radioactive concentration of respective nuclides was determined to be 0.188 0.001 Bq/g for
0.001 Bq/g for  Np, 0.368
Np, 0.368 0.004 Bq/g for
0.004 Bq/g for  Am, 0.402
Am, 0.402 0.010 Bq/g for
0.010 Bq/g for  Cm.
Cm.
Nishitani, Takeo; Yamauchi, Michinori; Izumi, Mikio*; Hayakawa, Atsuro*; Ebisawa, Katsuyuki*; Kondoh, Takashi; Kusama, Yoshinori
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(5-14), p.1192 - 1197, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Sakurai, Shinji; Hayashi, Takao; Shibama, Yusuke; Isono, Takaaki; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.892 - 899, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:86.49(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The concept for a compact DEMO reactor named "SlimCS" is presented. Distinctive features of the concept is low aspect ratio ( = 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low-
= 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low- , i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
, i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
Aoyama, Yoshio; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Yamaguchi, Hiromi; Sano, Akira*; Naito, Susumu*; Sumida, Akio*; Izumi, Mikio*; Maekawa, Tatsuyuki*; Sato, Mitsuyoshi*; Nambu, Kenichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-15) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2007/04
no abstracts in English
Naito, Susumu*; Hirata, Yosuke*; Izumi, Mikio*; Sano, Akira*; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Aoyama, Yoshio; Yamaguchi, Hiromi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44(2), p.121 - 128, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)A reinforced ion current prediction model in the alpha radioactivity measurement using ionized air transportation was presented. Although our previous model explained a qualitative trend of the measured ion current values, their absolute values were considerably overestimated. In order to explain them quantitatively, the model was reinforced in consideration of columnar recombination. It was found that our new model explains the considerable ion loss in the initial stage of ion diffusion and narrows the gap between the predicted and measured ion current values. This model also indicated a prospective suppression of ion loss due to columnar recombination by spraying a high-speed air flow on the contaminated surface. This suppression was experimentally investigated and confirmed. In conclusion, the theoretical relationship between alpha radioactivity and ion current was clarified quantitatively in laminar flow and turbulent pipe flow.
 -ray generated ion clusters in air
-ray generated ion clusters in airTong, L.*; Nambu, Kenichi*; Hirata, Yosuke*; Izumi, Mikio*; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Yamaguchi, Hiromi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 45(10B), p.8217 - 8220, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)A particle model is developed using the test-particle Monte Carlo method to study the transport properties of alpha-ray generated ion clusters in a flow of air. The simulated transport properties provide a theoretical basis for designing the alpha radioactivity measurement system. An accurate ion-molecule collision model is proposed to simulate the collisions between ion and air molecule. The recombination between positive and negative ions is simulated using Nanu and Denpoh method [J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 67(1998) 1288]. The calculations are performed from low gas pressures of 0.001 and 0.01 atm to high gas pressures of 0.1 and 1 atm in a circular pipe. The simulation presents such a steady state ion transport that the generation of ions reaches a quasi-equilibrium with the loss of ions, absorbed by a measuring sensor and lost on the pipe wall.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Sakurai, Shinji; Hayashi, Takao; Shibama, Yusuke; Isono, Takaaki; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2006/10
no abstracts in English

Belik, A. A.*; Iikubo, Satoshi; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; Shamoto, Shinichi; Niitaka, Seiji*; Azuma, Masaki*; Shimakawa, Yuichi*; Takano, Mikio*; Izumi, Fujio*; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 18(3), p.798 - 803, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:292 Percentile:98.59(Chemistry, Physical)The crystal and magnetic structures of polycrystalline BiCoO have been determined by the Rietveldmethod from neutron diffraction data measured at temperatures from 5 to 520 K. BiCoO
have been determined by the Rietveldmethod from neutron diffraction data measured at temperatures from 5 to 520 K. BiCoO (space groupP4mm; Z=1; a=3.72937(7)
(space groupP4mm; Z=1; a=3.72937(7)  and c=4.72382(15)
and c=4.72382(15)  at room temperature; tetragonality c/a=1.267) is isotypic with BaTiO
at room temperature; tetragonality c/a=1.267) is isotypic with BaTiO and PbTiO
and PbTiO in the whole temperature range. BiCoO
in the whole temperature range. BiCoO is an insulator with a Neeltemperature of 470 K. A possible model for antiferromagnetic order is proposed with a propagationvector of k=(1/2, 1/2, 0). In this model, magnetic moments of Co
is an insulator with a Neeltemperature of 470 K. A possible model for antiferromagnetic order is proposed with a propagationvector of k=(1/2, 1/2, 0). In this model, magnetic moments of Co ions are parallel to the c directionand align antiferromagnetically in the ab plane. The antiferromagnetic ab layers stack ferromagneticallyalong the c axis, forming a C-type antiferromagnetic structure. Refined magnetic moments at 5 and 300K are 3.24(2)
ions are parallel to the c directionand align antiferromagnetically in the ab plane. The antiferromagnetic ab layers stack ferromagneticallyalong the c axis, forming a C-type antiferromagnetic structure. Refined magnetic moments at 5 and 300K are 3.24(2)
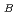 and 2.93(2)
and 2.93(2)
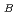 , respectively. The structure refinements revealed no deviation fromstoichiometry in BiCoO
, respectively. The structure refinements revealed no deviation fromstoichiometry in BiCoO . BiCoO
. BiCoO decomposed in air above 720 K to give Co
decomposed in air above 720 K to give Co O
O and sillenite-like Bi
and sillenite-like Bi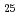 CoO
CoO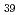 .
.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Sato, Masayasu; Isono, Takaaki; Sakurai, Shinji; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; Suzuki, Satoshi; Ando, Masami; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1151 - 1158, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:125 Percentile:98.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Naito, Susumu*; Sano, Akira*; Izumi, Mikio*; Noda, Etsuo*; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Sato, Mitsuyoshi*; Suto, Osamu; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Kondo, Shinichi*; Iinuma, Koichi*; et al.
Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, 2005 IEEE, Vol.1, p.495 - 499, 2005/10
An alpha radioactivity monitor (alpha-clearance monitor) is being developed to measure alpha radioactivity of uranium contaminated waste with large and complex surfaces. It uses an alpha radioactivity measurement method by collecting the air ionized by alpha particles using an air stream and by measuring its ion current. One of the major problems of the alpha-clearance monitor is the background ion current mainly by radon in atmosphere ( 700 fA), which is much larger than ion current of an alpha particle (several fA). It strongly influences on the detection limit of alpha radioactivity. In order to improve the detection limit, we developed a method to monitor the radon concentration inside the monitor without the additional radon detector. In addition, the influencing factors on the detection limit: ion mobility and ion recombination coefficient were measured and evaluated on various environmental conditions (temperature, humidity and aerosol density).
700 fA), which is much larger than ion current of an alpha particle (several fA). It strongly influences on the detection limit of alpha radioactivity. In order to improve the detection limit, we developed a method to monitor the radon concentration inside the monitor without the additional radon detector. In addition, the influencing factors on the detection limit: ion mobility and ion recombination coefficient were measured and evaluated on various environmental conditions (temperature, humidity and aerosol density).
Nishitani, Takeo; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Izumi, Mikio*; Kusama, Yoshinori
JAERI-Tech 2005-047, 34 Pages, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
Seki, Masahiro; Hishinuma, Akimichi; Kurihara, Kenichi; Akiba, Masato; Abe, Tetsuya; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Ohira, Shigeru; Okumura, Yoshikazu; et al.
Kaku Yugoro Kogaku Gairon; Mirai Enerugi Eno Chosen, 246 Pages, 2001/09
no abstracts in English
Takatsu, Hideyuki; Mori, Seiji*; Yoshida, Hiroshi; Hashimoto, T.*; Kurasawa, Toshimasa; Koizumi, Koichi; Enoeda, Mikio; Sato, Satoshi; Kuroda, Toshimasa*; ; et al.
Fusion Technology 1992, p.1504 - 1508, 1993/00
no abstracts in English
Emura, Yuki; Matsuba, Kenichi; Isozaki, Mikio; Imaizumi, Yuya; Kamiyama, Kenji
no journal, ,
A series of simulation tests discharging a molten alloy with low-melting point into a shallow water pool is being conducted in order to investigate fuel-coolant interaction and sedimentation behavior of molten core materials on the structure of core inlet coolant plenum in the core disruptive accident of sodium-cooled fast reactors. The present study shows effects of the initial temperature of the molten alloy, the confined coolant volume, etc. on the test results.
Aoyama, Yoshio; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Yamaguchi, Hiromi; Izumi, Mikio*; Naito, Susumu*; Yamamoto, Shuji*; Sano, Akira*; Nambu, Kenichi*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Oda, Akinori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray spectrometry
-ray spectrometryHaraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Kimura, Atsushi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Toh, Yosuke; Nakashima, Mikio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Imaizumi, Yuya; Kamiyama, Kenji; Matsuba, Kenichi; Isozaki, Mikio; Suzuki, Toru; Emura, Yuki
no journal, ,
For the study of the fuel-coolant interaction and deposition behavior of the molten core material on the in-vessel structure in the relocation phase of the core disruptive accident in SFR, several experiments discharging low-melting-point alloy into a shallow water pool were conducted. The experimental results and the mechanism discussion are reported.