Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Jeon, H.*; Hou, Y.*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Aze, Takahiro*; Miyairi, Yosuke*; Yokoyama, Yusuke*; Ogawa, Hiroshi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 527, p.1 - 6, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The measurement the radiocarbon of dissolved organic matter (DO C) in seawater can provide information about a timescale of the dynamics of dissolved organic matter as well as about its sources in the ocean. Due to the low DOC concentration in seawater, in spite of the development of accelerator mass spectrometry, a relatively large volume of seawater (
C) in seawater can provide information about a timescale of the dynamics of dissolved organic matter as well as about its sources in the ocean. Due to the low DOC concentration in seawater, in spite of the development of accelerator mass spectrometry, a relatively large volume of seawater ( 1 L) is required for that analysis. In addition, complicated processing such as UV irradiation that emits high heat is required. In this study, we have developed a safer and easier method to analyze DO
1 L) is required for that analysis. In addition, complicated processing such as UV irradiation that emits high heat is required. In this study, we have developed a safer and easier method to analyze DO C in seawater than the conventional method. A particularly significant change was the adoption of a low-pressure mercury lamp in the decomposition system, which enabled direct decomposition of organic matter at lower temperatures. We also propose a method to quantitatively evaluate the accuracy of this system by analyzing simulated seawater consists of a soluble reference material of organic matter and sodium chloride. This method is expected to be applied not only to carbon isotope ratio analysis but also to analysis of trace elements and isotopes of various dissolved organic substances.
C in seawater than the conventional method. A particularly significant change was the adoption of a low-pressure mercury lamp in the decomposition system, which enabled direct decomposition of organic matter at lower temperatures. We also propose a method to quantitatively evaluate the accuracy of this system by analyzing simulated seawater consists of a soluble reference material of organic matter and sodium chloride. This method is expected to be applied not only to carbon isotope ratio analysis but also to analysis of trace elements and isotopes of various dissolved organic substances.
Nguyen, T. H.*; Le Ba, T.*; Tran, C. T.*; Nguyen, T. T.*; Doan, T. T. T.*; Do, V. K.; Watanabe, Masayuki; Pham, Q. M.*; Hoang, S. T.*; Nguyen, D. V.*; et al.
Hydrometallurgy, 213, p.105933_1 - 105933_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:83.6(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)A continuous counter-current extraction for the selective recovery of thorium (Th) and uranium (U) from the Yen Phu (Vietnam) rare earth concentrate leach solutions was systematically studied. The primary amine N1923 was used as an extractant which was prepared in the isoparaffin IP-2028 diluent. Thorium and uranium were selectively recovered in a hydrometallurgical circuit established by continuous mixer-settler extraction, scrubbing, and back-extraction at the laboratory scale. The desired purity of Th and U can be achieved by managing the volume ratio of organic to aqueous phase (O/A ratio) in the corresponding steps. Highly pure Th and U were recovered from the pregnant back-extraction liquor and the raffinate, respectively, which have satisfactory properties for further processing of the subsequent nuclear materials.
Kim, H.-S.*; Jeon, Y. M.*; Na, Y.-S.*; Ghim, Y.-C.*; Ahn, J.-W.*; Yoon, S. W.*; Bak, J. G.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Kim, J. S.*; Joung, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(8), p.083012_1 - 083012_11, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We evaluate the characteristics of global energy confinement in KSTAR (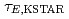 ) quantitatively by comparing it with multi-machine scalings, by deriving multiple regression equations for the L- and the H-mode plasmas, and evaluating confinement enhancement of the H-mode phase compared with the L-mode phase in each discharge. From the KSTAR database,
) quantitatively by comparing it with multi-machine scalings, by deriving multiple regression equations for the L- and the H-mode plasmas, and evaluating confinement enhancement of the H-mode phase compared with the L-mode phase in each discharge. From the KSTAR database, 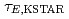 of L-mode plasmas exhibits
of L-mode plasmas exhibits 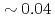 s to
s to 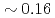 s and
s and 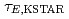 of H-mode plasmas
of H-mode plasmas 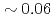 s to
s to 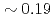 s. The multiple regression equations derived by statistical analysis present the similar dependency on PL and slightly higher dependency on IP compared with the multi-machine scalings, however the dependency on elongation
s. The multiple regression equations derived by statistical analysis present the similar dependency on PL and slightly higher dependency on IP compared with the multi-machine scalings, however the dependency on elongation  in both L- and H-mode plasmas draw the negative power dependency of
in both L- and H-mode plasmas draw the negative power dependency of 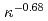 and
and 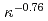 for H-mode and for L- mode database, respectively on the contrary to the positive dependency in all multi-machine empirical scalings. Although the reason is not clear yet, two possibilities are addressed. One is that the wall condition of KSTAR was not clean enough. The other is that striking points on the divertor plate were uncontrolled. For these reasons, as
for H-mode and for L- mode database, respectively on the contrary to the positive dependency in all multi-machine empirical scalings. Although the reason is not clear yet, two possibilities are addressed. One is that the wall condition of KSTAR was not clean enough. The other is that striking points on the divertor plate were uncontrolled. For these reasons, as  increases, the impurities from the wall can penetrate into plasmas easily. As a consequence, the confinement is degraded on the contrary to the expectation of multi-machine scalings.
increases, the impurities from the wall can penetrate into plasmas easily. As a consequence, the confinement is degraded on the contrary to the expectation of multi-machine scalings.
Yoon, S. W.*; Ahn, J.-W.*; Jeon, Y. M.*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hahn, S. H.*; Ko, W. H.*; Lee, K. D.*; Chung, J. I.*; Nam, Y. U.*; Kim, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(11), p.113009_1 - 113009_9, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:79.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Typical ELMy H-mode discharges have been achieved on the KSTAR tokamak with the combined auxiliary heating of NBI and ECRH. The minimum external heating power required is about 1.1 MW at a line-averaged density higher than 1.4 10
10 m
m and a toroidal field of 2 T. There is a clear indication of the increase of the L-H threshold power at densities lower than
and a toroidal field of 2 T. There is a clear indication of the increase of the L-H threshold power at densities lower than 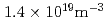 . The initial analysis of energy confinement time (
. The initial analysis of energy confinement time (
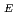 ) predicted that
) predicted that 
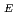 was higher than the prediction of multi-machine scaling laws by a factor 1.4-1.6. However, when the contribution of fast ion confinement to the total energy was taken into account,
was higher than the prediction of multi-machine scaling laws by a factor 1.4-1.6. However, when the contribution of fast ion confinement to the total energy was taken into account, 
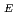 better agreed with the scaling results. A clear increase of electron and ion temperature in the pedestal was observed in the H-mode phase but the core ion temperature did not change significantly. On the other hand, the toroidal rotation also increased over all radii in the H-mode phase. The measured ELM frequency was from 30-50 Hz and the drop of total energy appeared to be less than 5%. Between large ELM spikes, small/grassy ELMs were also identified when mixed heating of NBI and ECRH was applied.
better agreed with the scaling results. A clear increase of electron and ion temperature in the pedestal was observed in the H-mode phase but the core ion temperature did not change significantly. On the other hand, the toroidal rotation also increased over all radii in the H-mode phase. The measured ELM frequency was from 30-50 Hz and the drop of total energy appeared to be less than 5%. Between large ELM spikes, small/grassy ELMs were also identified when mixed heating of NBI and ECRH was applied.
Na, Y. S.*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Ide, Shunsuke; Mueller, D.*; Kim, J. H.*; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Kim, S. H.*; Kim, H. S.*; Jeon, Y. M.*; Bae, Y. S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Development of advanced scenarios, an important experimental goal for the KSTAR project, has just begun. Target plasmas were successfully produced using large bore plasma and early divertor formation which exhibit low internal inductance with low magnetic shear at the centre and no sawtooth instability. Auxilliary heating during the current rampup phase was employed to slow the inductive current diffusion to the centre of the plasma. With respect to hybrid scenario development, so-called "Ip-overshoot" method being used in JET is applied for tailoring magnetic shear at reduced plasma current for higher poloidal beta and bootstrap current fraction. The confinement characteristics of these scenarios are investigated. Transport modeling is performed self-consistently with an integrated simulation package incorporating plasma equilibrium, transport, heating and current drive. Firstly, the current rampup phase is simulated and its impact on the target q-profile is addressed. Secondly, energy confinement of flattop phases is discussed. In addition, the non-inductive current drive fraction including the bootstrap current fraction is calculated. Lastly, these scenarios are compared with advanced scenarios developed in other tokamak devices and future directions in achieving advanced regimes are discussed.
Jeon, H.; Ogawa, Hiroshi*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi
no journal, ,
Radiocarbon content of marine dissolved organic carbon (DO C) can provide useful information on how organic carbon is produced, transported, and ultimately sequestered in the ocean interior. We conducted research to present the first set of full-depth profiles for DO
C) can provide useful information on how organic carbon is produced, transported, and ultimately sequestered in the ocean interior. We conducted research to present the first set of full-depth profiles for DO C along a transect from the central South Pacific Ocean to Chukchi Sea. In order to measure radiocarbon contents of seawater samples, they should be processed with a specific preparation system consists of the custom quartz reactor, dedicated vacuum line and UV lamp followed by radiocarbon counting with an accelerator mass spectrometer. As the first step of the study, we have developed the irradiation procedure using a low-pressure Hg lamp and an oxidation catalyst. We present here how the system is progressing as well as what radiocarbon study in the central Pacific Ocean means for better understanding of oceanic carbon cycle.
C along a transect from the central South Pacific Ocean to Chukchi Sea. In order to measure radiocarbon contents of seawater samples, they should be processed with a specific preparation system consists of the custom quartz reactor, dedicated vacuum line and UV lamp followed by radiocarbon counting with an accelerator mass spectrometer. As the first step of the study, we have developed the irradiation procedure using a low-pressure Hg lamp and an oxidation catalyst. We present here how the system is progressing as well as what radiocarbon study in the central Pacific Ocean means for better understanding of oceanic carbon cycle.
Jeon, H.; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Yamashita, Yohei*; Ogawa, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
The ocean is a huge reservoir of dissolved organic carbon that contains almost the same amount of carbon in the atmosphere. Radiocarbon signatures of dissolved organic carbon (DO C) in seawater can provide useful information on how organic carbon is produced, transported, and ultimately sequestered in the ocean's interior. In order to measure radiocarbon contents of seawater samples, they should be processed with a specific preparation system consists of the custom quartz reactor, dedicated vacuum line and UV lamp followed by radiocarbon counting with an accelerator mass spectrometer. As the first step of the study, we developed the irradiation procedure using a low-pressure Hg lamp and an oxidation catalyst. We present here not only how the system is progressing but also what radiocarbon study in the central Pacific Ocean means for better understanding of oceanic carbon cycle.
C) in seawater can provide useful information on how organic carbon is produced, transported, and ultimately sequestered in the ocean's interior. In order to measure radiocarbon contents of seawater samples, they should be processed with a specific preparation system consists of the custom quartz reactor, dedicated vacuum line and UV lamp followed by radiocarbon counting with an accelerator mass spectrometer. As the first step of the study, we developed the irradiation procedure using a low-pressure Hg lamp and an oxidation catalyst. We present here not only how the system is progressing but also what radiocarbon study in the central Pacific Ocean means for better understanding of oceanic carbon cycle.
Jeon, H.; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Yamashita, Yohei*; Ogawa, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
Measurements of the radiocarbon content of marine dissolved organic carbon (DO C) broadened our perspective on the role of DOC in the marine carbon cycle. However fewer measurements have been performed because of methodological difficulties associated with low concentration of DOC and an overwhelming proportion of salts. In order to collect enough DOC for radiocarbon analysis, UV oxidation is one of the most commonly used methods by irradiating seawater samples with ultraviolet light. Unlike other studies where medium pressure mercury arc UV lamp are used, this study attempts to improve the system with two grid lamps in order to reduce the demand for high electric power installation and to miniaturize the instrument for easier handling. We aim to verify the performance of improved equipment by processing
C) broadened our perspective on the role of DOC in the marine carbon cycle. However fewer measurements have been performed because of methodological difficulties associated with low concentration of DOC and an overwhelming proportion of salts. In order to collect enough DOC for radiocarbon analysis, UV oxidation is one of the most commonly used methods by irradiating seawater samples with ultraviolet light. Unlike other studies where medium pressure mercury arc UV lamp are used, this study attempts to improve the system with two grid lamps in order to reduce the demand for high electric power installation and to miniaturize the instrument for easier handling. We aim to verify the performance of improved equipment by processing  C reference materials as well as seawater samples.
C reference materials as well as seawater samples.
Jeon, H.; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Aze, Takahiro*; Miyairi, Yosuke*; Yokoyama, Yusuke*; Ogawa, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
Measurements of the dissolved organic radio carbon (DOC-14) are expected to broaden our perspective on the role of DOC in the marine carbon cycle. Although the authors had succeeded in the DOC-14 analysis in seawater, it was necessary to use a large preprocessing apparatus, and the analysis has not been applied widely. We here report on the improvements to make this system safer and easier to handle. Following the previous method, DOC-14 in seawater was extracted as carbon dioxide by irradiating ultraviolet (UV), purified in a vacuum line, and the C-14 isotopic ratio was analysed with an accelerator mass spectrometer. As a major improvement, low-pressure mercury lamp which can irradiate UV of short wavelength (172 nm and 185 nm) suitable for decomposition of organic matter was used as UV source. By this improvement, the temperature increase in sample during processing was greatly reduced, and the size of the irradiation reactor was reduced to about half.