Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Woo, W.*; Kim, Y. S.*; Chae, H. B.*; Lee, S. Y.*; Jeong, J. S.*; Lee, C. M.*; Won, J. W.*; Na, Y. S.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; et al.
Acta Materialia, 246, p.118699_1 - 118699_13, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:99.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) -decay spectroscopy of
-decay spectroscopy of  Ta
TaMukai, Momo*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Watanabe, Hiroshi*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Jeong, S. C.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Brunet, M.*; Ishizawa, Satoshi*; Kondev, F. G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 105(3), p.034331_1 - 034331_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:71.48(Physics, Nuclear)Woo, W.*; Naeem, M.*; Jeong, J.-S.*; Lee, C.-M.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; He, H.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 781, p.139224_1 - 139224_7, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:94.69(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Woo, W.*; Jeong, J.-S.*; Kim, D.-K.*; Lee, C. M.*; Choi, S.-H.*; Suh, J.-Y.*; Lee, S. Y.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10(1), p.1350_1 - 1350_15, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:100 Percentile:95.75(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Li(
Li( ,n)
,n) B reaction in a lower-energy region below the Coulomb barrier
B reaction in a lower-energy region below the Coulomb barrierDas, S. K.*; Fukuda, Tomokazu*; Mizoi, Yutaka*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Jeong, S. C.*; Ikezoe, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Makoto; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(5), p.055805_1 - 055805_4, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.67(Physics, Nuclear) Li
LiIshiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Jung, H. S.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Oyaizu, Mitsuhiro*; Osa, Akihiko; Otokawa, Yoshinori; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 376, p.379 - 381, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.65(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Choi, I. W.*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Tatsufumi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Daito, Izuru*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 57(2), p.025001_1 - 025001_9, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.55(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Projection images of a metal mesh produced by directional MeV electron beam together with directional proton beam, emitted simultaneously from a thin foil target irradiated by an ultrashort intense laser. The mesh patterns are projected to each detector by the electron beam and the proton beam originated from tiny virtual sources of  20 micron meter and
20 micron meter and  10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
 Li tracer
Li tracerIshiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Oyaizu, Mitsuhiro*; Katayama, Ichiro*; Osa, Akihiko; Otokawa, Yoshinori; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 53(11), p.110303_1 - 110303_4, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.06(Physics, Applied)Kim, H.-S.*; Jeon, Y. M.*; Na, Y.-S.*; Ghim, Y.-C.*; Ahn, J.-W.*; Yoon, S. W.*; Bak, J. G.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Kim, J. S.*; Joung, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(8), p.083012_1 - 083012_11, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:38.69(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We evaluate the characteristics of global energy confinement in KSTAR (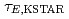 ) quantitatively by comparing it with multi-machine scalings, by deriving multiple regression equations for the L- and the H-mode plasmas, and evaluating confinement enhancement of the H-mode phase compared with the L-mode phase in each discharge. From the KSTAR database,
) quantitatively by comparing it with multi-machine scalings, by deriving multiple regression equations for the L- and the H-mode plasmas, and evaluating confinement enhancement of the H-mode phase compared with the L-mode phase in each discharge. From the KSTAR database, 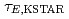 of L-mode plasmas exhibits
of L-mode plasmas exhibits 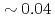 s to
s to 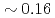 s and
s and 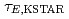 of H-mode plasmas
of H-mode plasmas 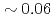 s to
s to 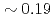 s. The multiple regression equations derived by statistical analysis present the similar dependency on PL and slightly higher dependency on IP compared with the multi-machine scalings, however the dependency on elongation
s. The multiple regression equations derived by statistical analysis present the similar dependency on PL and slightly higher dependency on IP compared with the multi-machine scalings, however the dependency on elongation  in both L- and H-mode plasmas draw the negative power dependency of
in both L- and H-mode plasmas draw the negative power dependency of 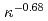 and
and 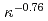 for H-mode and for L- mode database, respectively on the contrary to the positive dependency in all multi-machine empirical scalings. Although the reason is not clear yet, two possibilities are addressed. One is that the wall condition of KSTAR was not clean enough. The other is that striking points on the divertor plate were uncontrolled. For these reasons, as
for H-mode and for L- mode database, respectively on the contrary to the positive dependency in all multi-machine empirical scalings. Although the reason is not clear yet, two possibilities are addressed. One is that the wall condition of KSTAR was not clean enough. The other is that striking points on the divertor plate were uncontrolled. For these reasons, as  increases, the impurities from the wall can penetrate into plasmas easily. As a consequence, the confinement is degraded on the contrary to the expectation of multi-machine scalings.
increases, the impurities from the wall can penetrate into plasmas easily. As a consequence, the confinement is degraded on the contrary to the expectation of multi-machine scalings.
Sonoda, Tetsu*; Wada, Michiharu*; Tomita, Hideki*; Sakamoto, Chika*; Takatsuka, Takaaki*; Furukawa, Takeshi*; Iimura, Hideki; Ito, Yuta*; Kubo, Toshiyuki*; Matsuo, Yukari*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 295, p.1 - 10, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:81.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Mihara, Mototsugu*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Jeong, S. C.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Momota, Sadao*; Hashimoto, Takashi*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Matsuta, Kensaku*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 48(5), p.54_1 - 54_10, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.19(Physics, Nuclear) mixed gas
mixed gasIshiyama, Hironobu*; Yamaguchi, Kanako*; Mizoi, Yutaka*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Das, S. K.*; Hashimoto, Takashi*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Oyaizu, Mitsuhiro*; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 7(3), p.C03036_1 - C03036_14, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:35.97(Instruments & Instrumentation)We developed an active-target type gas counter operating with low He/CO (10%) detector gas for application in studying low-energy nuclear reactions using radioactive beams. A 400-
(10%) detector gas for application in studying low-energy nuclear reactions using radioactive beams. A 400- m-thick gas electron multiplier (THGEM) was used as the proportional counter for high injection rate capability. We examined the gas gain stability and the influence of ion feedback on particle tracks at high beam injection rates of up to 10
m-thick gas electron multiplier (THGEM) was used as the proportional counter for high injection rate capability. We examined the gas gain stability and the influence of ion feedback on particle tracks at high beam injection rates of up to 10 particles per second (pps) using a low-energy
particles per second (pps) using a low-energy  C beam. From the result of this examination, we found that the THGEM was found to be applicable for our active target at high injection rates of up to 10
C beam. From the result of this examination, we found that the THGEM was found to be applicable for our active target at high injection rates of up to 10 pps.
pps.
Okada, Masashi*; Niki, Kazuaki*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S. C.*; Katayama, Ichiro*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Oyaizu, Mitsuhiro*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; et al.
Physical Review Special Topics; Accelerators and Beams, 15(3), p.030101_1 - 030101_10, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:31.92(Physics, Nuclear)Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Dairaku, Masayuki; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Inoue, Takashi; Hanada, Masaya; Jeong, S. H.*; Chang, D. H.*; Kim, T. S.*; Kim, B. R.*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 82(6), p.063507_1 - 063507_6, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:57.19(Instruments & Instrumentation)A long pulse plasma generator for neutral beam injectors has been developed. The plasma generator was designed to produce 65 A at 120 keV from a beam extraction area of 12 cm  46 cm. A type of the plasma generator is a multi-cusp plasma generator with SmCo permanent magnets. A long pulse test of the plasma generator was performed at the KSTAR NBI test stand in Korea under the Japan - Korea Fusion collaboration. It was successfully demonstrated of the long pulse operation of the plasma generator for 200 s at an arc discharge power of 70 kW which can produce 65 A beams. Plasma spatial uniformity at the beam extraction area was confirmed to be smaller than
46 cm. A type of the plasma generator is a multi-cusp plasma generator with SmCo permanent magnets. A long pulse test of the plasma generator was performed at the KSTAR NBI test stand in Korea under the Japan - Korea Fusion collaboration. It was successfully demonstrated of the long pulse operation of the plasma generator for 200 s at an arc discharge power of 70 kW which can produce 65 A beams. Plasma spatial uniformity at the beam extraction area was confirmed to be smaller than  8% of the deviation from an averaged ion saturation current density. A high arc efficiency of 0.9-1.1 A/kW was obtained at the beam extraction with 73 keV, 41 A for 5 sec. From these experimental studies, a performance of this plasma generator for long pulse ion sources was confirmed.
8% of the deviation from an averaged ion saturation current density. A high arc efficiency of 0.9-1.1 A/kW was obtained at the beam extraction with 73 keV, 41 A for 5 sec. From these experimental studies, a performance of this plasma generator for long pulse ion sources was confirmed.
Yang, H. L.*; Kim, Y. S.*; Park, Y. M.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Kim, H. K.*; Kim, K. M.*; Lee, K. S.*; Kim, H. T.*; Bang, E. N.*; Joung, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Because the 2010 operation of Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR) mainly aims to achieve strongly elongated and diverted plasma, all the necessary hardware systems to provide an essential circumstance for the plasma shaping were newly installed and upgraded in 2010. In this paper, general configuration of the upgraded systems described earlier will be outlined. Moreover, several key performances and test results of the systems will be also reported in summary.
 Zn
ZnImai, Nobuaki*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Nagae, Daisuke*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 46(2), p.157 - 160, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.02(Physics, Nuclear)Stober, J.*; Jackson, G. L.*; Ascasibar, E.*; Bae, Y.-S.*; Bucalossi, J.*; Cappa, A.*; Casper, T.*; Cho, M. H.*; Gribov, Y.*; Granucci, G.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Jeong, S. C.*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Miyatake, Hiroari
International Journal of Modern Physics E, 19(5&6), p.989 - 996, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)We have measured quasi-elastic scattering cross sections in reactions of  Ti,
Ti,  Cr,
Cr,  Fe,
Fe,  Ni and
Ni and  Zn +
Zn +  Pb, relating to Pb-based cold fusion reactions for super-heavy elements 104, 106, 108, 110 and 112, respectively. A thin target of
Pb, relating to Pb-based cold fusion reactions for super-heavy elements 104, 106, 108, 110 and 112, respectively. A thin target of  Pb was bombarded by heavy-ion beams supplied from the JAEA tandem-booster accelerator with changing the beam energy in steps of 1.5 MeV. The barrier distributions were derived from the first derivative of the excitation functions measured at backward angles of 172
Pb was bombarded by heavy-ion beams supplied from the JAEA tandem-booster accelerator with changing the beam energy in steps of 1.5 MeV. The barrier distributions were derived from the first derivative of the excitation functions measured at backward angles of 172 , 168
, 168 and 162
and 162 . The centroid of the barrier distributions showed a deviation from several predicted barrier heights toward the low energy side. The shape of the barrier distributions was well reproduced by the results of a coupled-channel calculation taking account of the coupling effects of the collective vibrational excitations in the projectile and target nuclei. We have recently obtained similar results in heavier reactions of
. The centroid of the barrier distributions showed a deviation from several predicted barrier heights toward the low energy side. The shape of the barrier distributions was well reproduced by the results of a coupled-channel calculation taking account of the coupling effects of the collective vibrational excitations in the projectile and target nuclei. We have recently obtained similar results in heavier reactions of  Ge and
Ge and 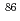 Kr +
Kr +  Pb.
Pb.
Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Jeong, S. C.*; Otsuki, Tsutomu*; Hirose, Kentaro*
Nuclear Physics A, 834(1-4), p.172c - 175c, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:13.43(Physics, Nuclear)The Coulomb barrier distribution between heavy nuclei is important quantity to investigate the effect of quantum couplings of nuclear vibration and nucleon transfer to nucleus-nucleus interaction. We obtained the barrier distributions of lead-based fusion reactions of  Ti,
Ti,  Cr,
Cr,  Fe,
Fe,  Ni,
Ni,  Zn,
Zn,  Ge, and
Ge, and 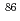 Kr projectiles on
Kr projectiles on  Pb by means of the measurements of the quasi-elastic cross sections at backward scattering angles. The obtained positions and widths of the barrier distributions are compared with a calculation taking account of the channel couplings. The effect of the nuclear deformation on reaction process was also investigated by means of the measurements of product mass distributions for the systems of
Pb by means of the measurements of the quasi-elastic cross sections at backward scattering angles. The obtained positions and widths of the barrier distributions are compared with a calculation taking account of the channel couplings. The effect of the nuclear deformation on reaction process was also investigated by means of the measurements of product mass distributions for the systems of  Si,
Si,  S,
S,  Ar projectiles on
Ar projectiles on  U. We found that the collision at polar side gives rise to quasi-fission, where an asymmetric fission is dominant.
U. We found that the collision at polar side gives rise to quasi-fission, where an asymmetric fission is dominant.
 Li
LiJeong, S.-C.*; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Yahagi, Masahito*
Nihon Butsuri Gakkai-Shi, 64(9), p.687 - 691, 2009/09
We have demonstrated a non-destructive and on-line radiotracer method for diffusion studies in lithium ionic conductors, by using, as a tracer, the short-lived alpha-emitting radioisotope of  Li from TRIAC (Tokai Radioactive Ion Accelerator Complex). The method has been successfully applied to measure the lithium diffusion coefficients in a typical defect-mediated lithium ionic conductor of LiGa, well demonstrating that the method is very effective to measure the diffusion in the micrometer regime per second. Anomalous composition-dependence of Li diffusion coefficients in LiGa was observed. The anomaly was discussed qualitatively in terms of the formation of defect complex and the interaction between the constituent defects. The ordering of the Li vacancies in the Li-deficient LiGa was observed for the first time in terms of the Li diffusion by the present method, and its thermodynamic aspect was discussed.
Li from TRIAC (Tokai Radioactive Ion Accelerator Complex). The method has been successfully applied to measure the lithium diffusion coefficients in a typical defect-mediated lithium ionic conductor of LiGa, well demonstrating that the method is very effective to measure the diffusion in the micrometer regime per second. Anomalous composition-dependence of Li diffusion coefficients in LiGa was observed. The anomaly was discussed qualitatively in terms of the formation of defect complex and the interaction between the constituent defects. The ordering of the Li vacancies in the Li-deficient LiGa was observed for the first time in terms of the Li diffusion by the present method, and its thermodynamic aspect was discussed.